Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
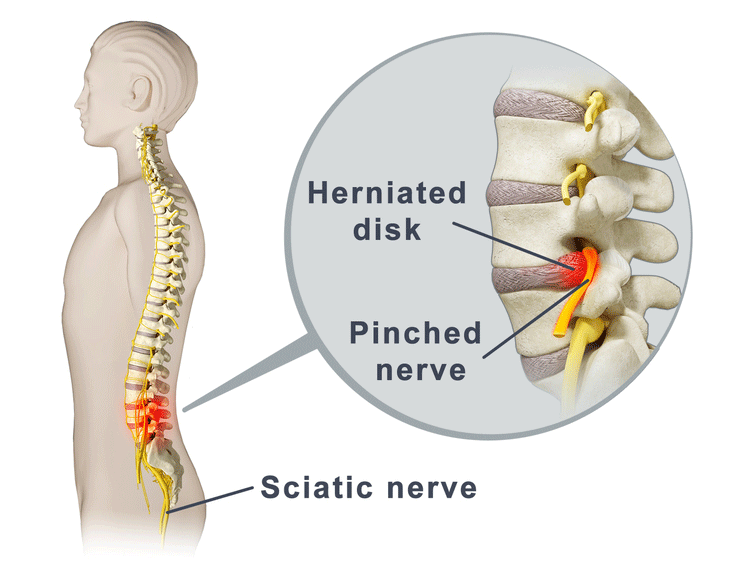 |  |
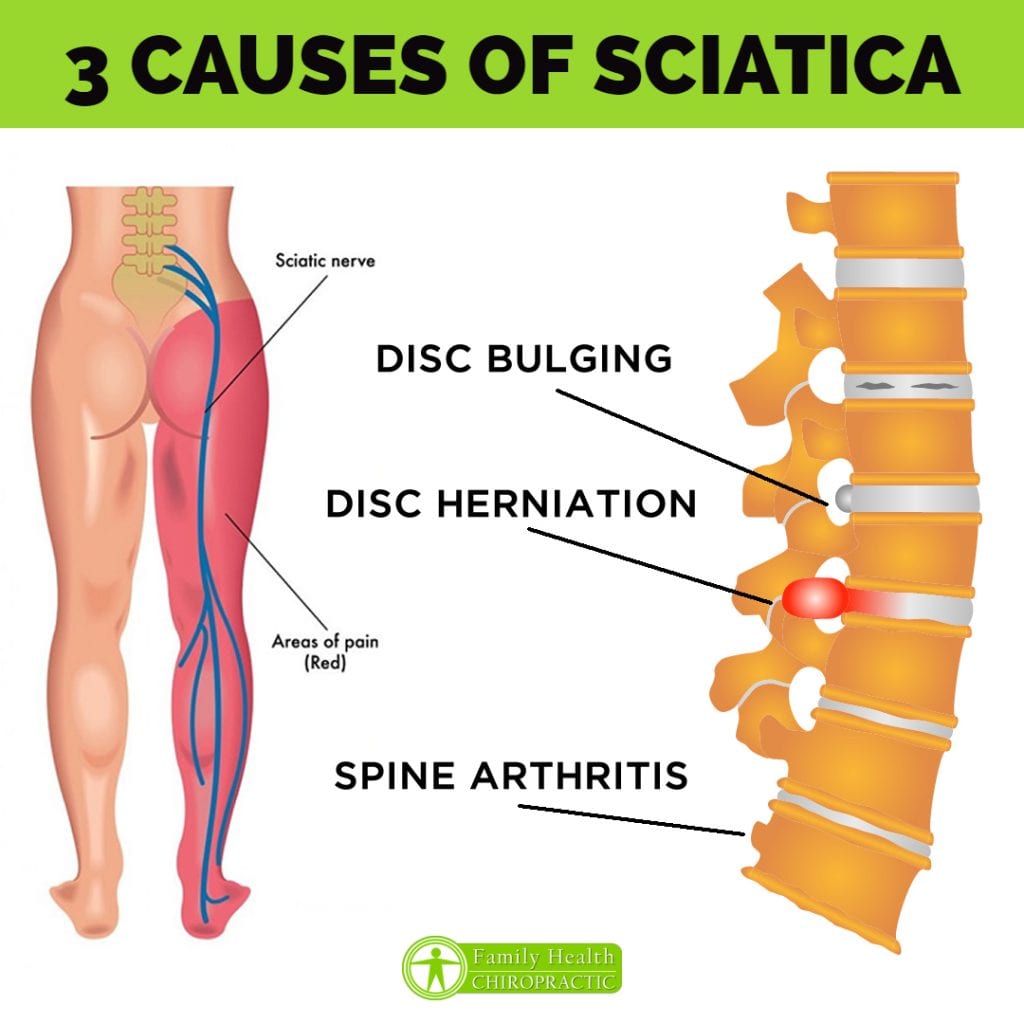
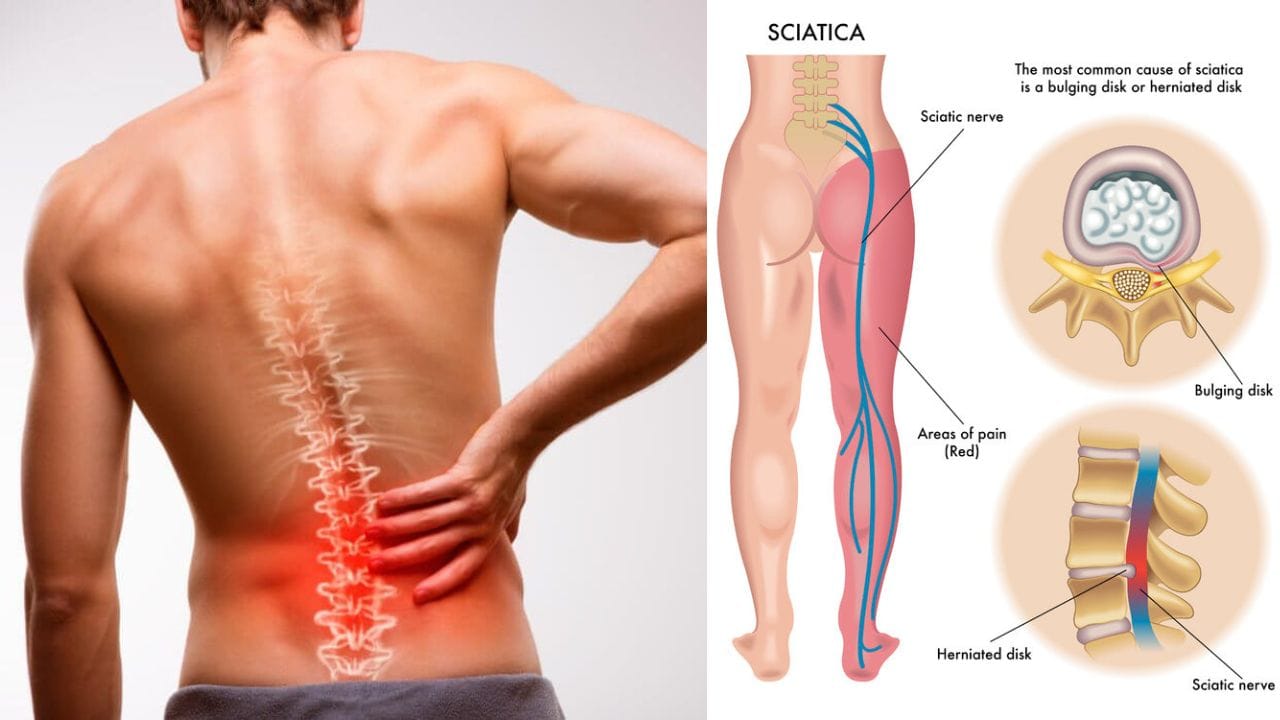
Medication is among the courses of action that you can try for sciatica. Options include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), gabapentinoids, corticosteroids, and benzodiazepines. How long does it take for Gabapentin to work for sciatica? Gabapentin for sciatica pain can take 1-2 weeks to start showing any noticeable effects. Although, depending on the patient’s condition, dosage and response to the treatment, it may take longer to register relief. Finding the right dosage of gabapentin can be tricky. If your dosage is too low, it may not provide adequate relief, leaving your nerve pain unchanged—or in some cases, making it feel worse because of heightened awareness of the discomfort. Because gabapentin can enhance the psychological effect of opioids, it has the potential to be abused and has contributed to drug overdose deaths. Drugs such as gabapentin have been linked in rare cases to an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. However, for management of sciatica NICE refer to their Neuropathic pain guidelines, which do recommend gabapentin or pregabalin as initial treatment options for neuropathic pain. While gabapentin is not a cure for sciatica, it can provide a 1-2 point average reduction in pain scores, allowing better mobility and function. Its favorable side effect profile, lack of drug interactions, and reduced risks of dependency make gabapentin a potentially useful part of a comprehensive sciatica treatment plan. Here is what you shouldn’t you be doing if you are experiencing the pain that sciatica causes.. 1. Avoid Exercises That Stretch Your Hamstrings. Stretching your hamstrings can worsen sciatica The evidence showed that gabapentinoids did not improve sciatica symptoms, and oral corticosteroids did not improve pain or function, but may have an impact on quality of life. Both increased the risk of adverse events in the long-term. Back pain can be a potential side effect of Gabapentin. If your back pain is related, it may decrease in severity or go away entirely within 1-3 months, on average. Gabapentin is usually well tolerated. Taking gabapentin with opioids (e.g., morphine, hydrocodone) can cause respiratory depression and sedation, and lead to fatal outcomes. Tell your healthcare provider if you are also taking opioids. Do not stop taking gabapentin without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping suddenly can cause serious problems. No evidence supports the use of pregabalin or gabapentin for sciatica pain or low back pain, as their effectiveness is not superior to placebo. Additionally, reported adverse effects raise concerns, making their routine clinical use unsupported. Sciatica symptoms are often worse with sitting or coughing and may be accompanied by numbness or tingling in the leg. A physical exam can confirm that the sciatic nerve is involved. If there is muscle weakness or diminished reflexes in the involved leg, an imaging test such as a back MRI can be useful and help guide a decision for early surgery. Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back to the buttock and down the back of each leg. The lower lumbosacral nerve roots make up the sciatic nerve which is the longest nerve in the body. Although many people think of sciatica as a condition, it is actually a collection of symptoms. I was just wondering if it is possible that gabapentin can sometimes make neuropathy pain worse. My EMG and biopsy results are negative for short fiber neuropathy so far. Interested in more discussions like this? Go to the Neuropathy Support Group. Previous trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with chronic low back pain or sciatica did not show a beneficial effect over placebo. 10,11 Our trial extends this finding by the inclusion Drugs like gabapentin, duloxetine, nortriptyline and pregabalin can be useful for managing severe pain or pain that makes it hard to sleep. Corticosteroids are another treatment option. These potent anti-inflammatory drugs are delivered via an injection that places the medication just where it is needed. Currently, using gabapentin for sciatica is not recommended because its risk of side effects outweigh potential benefits. How does gabapentin work to relieve sciatic nerve pain? In general, gabapentin calms down neurons (nerve cells) to relieve nerve pain. Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and This is true for all gabapentin products, which can cause withdrawal symptoms like anxiety, agitation, and nausea or vomiting. More seriously, stopping treatment with gabapentin abruptly can lead to seizures. If you want to stop taking gabapentin, don’t make any changes without talking to your prescriber. Gabapentin enacarbil available under the trade name Horizant is the only gabapentin product approved for treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS). A daily dose of 1200 mg provided no additional benefit compared with the 600 mg dose, but caused an increase in adverse reactions.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |