Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
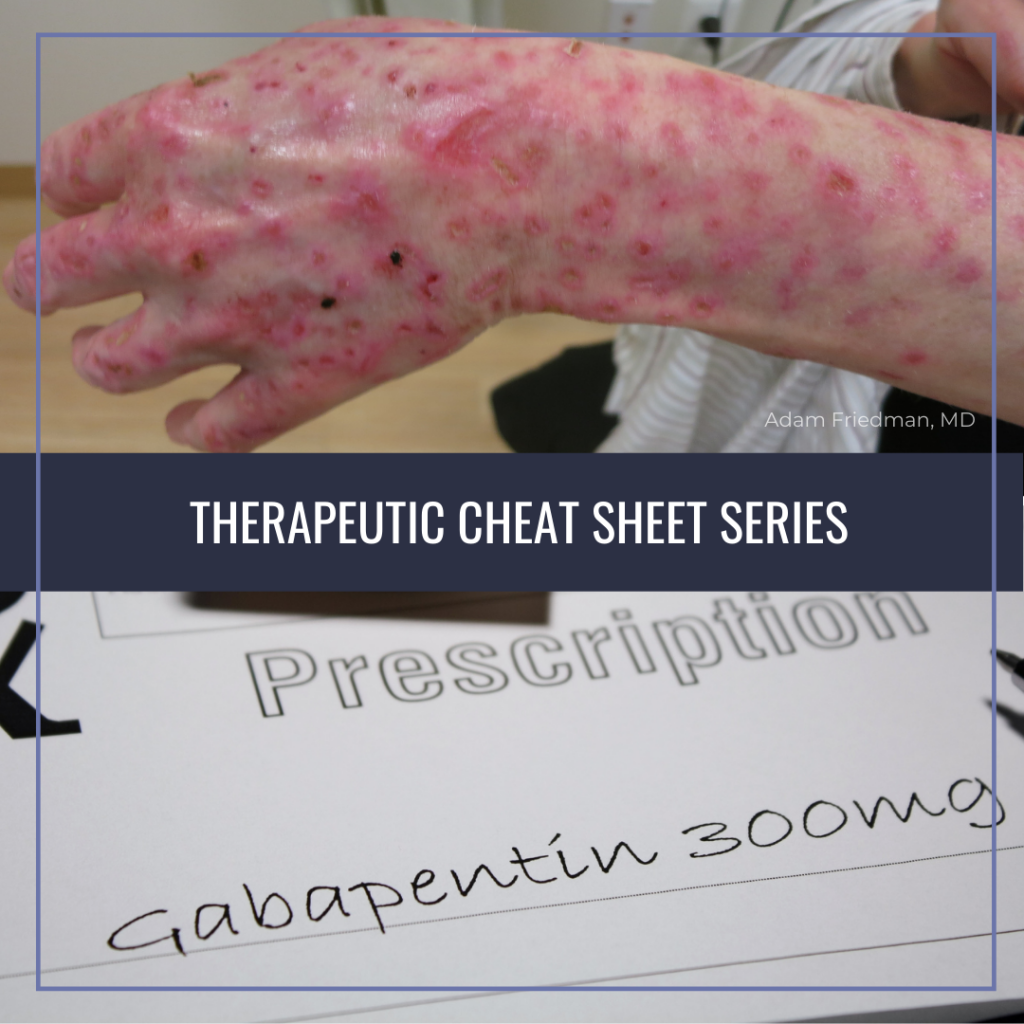
Ligands of auxiliary α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) decrease elevated L-type VDCCs surface expression in arterial myocytes and arterial constriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of Gabapentin can be used in elderly patients, but caution should be exercised due to age-related changes in renal function. A lower starting dose may be necessary to prevent overdose and accumulation of the drug in the body. Monitoring of kidney function is recommended. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients Researchers studying the effects of gabepentin found it has an effect on arterial BP in cats with and without chronic kidney disease. This effect appears to be more than just the result of stress reduction. These findings should be taken into account when gabapentin is administered to patients for which measurement of BP is needed. In cats, gabapentin is most often used as a pain medication for chronic pain, such as from arthritis. Gabapentin is also recognized as beneficial in reducing the fear responses that a kitty may have to the stress of handling and being examined at the vet. While there are currently no known side effects in cats, this medication does tend to lower their heart rates, which can be detrimental to cats with heart conditions. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of gabapentin on feline heart function. Gabapentin and melatonin significantly increased the cats' compliance without interfering with cardiac assessment. Eight cats presented with mild sedation, seven after gabapentin and one after melatonin. No major side effects were observed. The authors concluded that gabapentin affects BP in cats with and without CKD, which should be considered when gabapentin is administered to cats that require BP measurement. Conclusions and relevance: Gabapentin may decrease arterial BP in cats with and without CKD and these findings should be taken into account when gabapentin is administered to patients in which measurement of BP is needed. Gabapentin is eliminated almost entirely through renal excretion, and decreased renal function significantly influences the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in humans. 14 While doses of gabapentin in the range of 50–150 mg/cat have been used in normal cats, 4,5,11 it should be noted that higher doses may be unsuitable for cats with CKD. 15 In a In the healthy cat subgroup, BP was significantly lower after administration of gabapentin (median 121 mmHg, range 82–139) than after administration of the placebo (median 137 mmHg, range 102–177; P = 0.002). This article synthesizes findings from various research studies to determine whether gabapentin can lower blood pressure. Acute Effects of Gabapentin on Blood Pressure Hemodynamic Response in Hypertensive Rats. Research on spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) has shown that acute administration of gabapentin significantly lowers blood pressure In the CKD subgroup, BP was significantly lower after administration of gabapentin (median 129mmHg, range 96–170) than after administration of the placebo (median 155 mmHg, range 102–191; P = 0.008). In the healthy cat subgroup, BP was significantly lower after administration of gabapentin (median 121mmHg, range 82–139) than Gabapentin is eliminated almost entirely through renal excretion, and decreased renal function significantly influences the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in humans. 14 While doses of gabapentin in the range of 50–150 mg/cat have been used in normal cats, 4,5,11 it should be noted that higher doses may be unsuitable for cats with CKD. 15 In a Conclusions and relevance: Significant effects of gabapentin on direct SBP were not identified, though a type II error is possible. Situational increases cannot be excluded in gabapentin-treated cats with high SBP. Keywords: Blood pressure; Doppler sphygmomanometry; radiotelemetric catheter; simulated veterinary visit. Gabapentin is eliminated almost entirely through renal excretion, and decreased renal function significantly influences the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in humans. 14 While doses of gabapentin in the range of 50–150 mg/cat have been used in normal cats, 4,5,11 it should be noted that higher doses may be unsuitable for cats with CKD. 15 In a Situational increases in blood pressure (BP) frequently confound the accurate diagnosis of pathological systemic hypertension in cats. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of gabapentin on direct, ambulatory systolic arterial BP (SBP) in cats in at-home and in-clinic environments. While 0.625mg is the low end of the dosage range, this medication should only be used in cats with documented hypertension (high blood pressure) where an attending veterinarian has prescribed it and where a treatment plan exists to recheck blood pressure measurements, ensuring the medication is dosed appropriately. RESULTS Stress scores were similar in cats treated with gabapentin and alprazolam and gabapentin-treated cats had significantly lower stress score than those of the placebo group. Enclosure Gabapentin is eliminated almost entirely through renal excretion, and decreased renal function significantly influences the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in humans. 14 While doses of gabapentin in the range of 50–150 mg/cat have been used in normal cats, 4,5,11 it should be noted that higher doses may be unsuitable for cats with CKD. 15 In a
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |