Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Bloodpressure-5204833-final-7927123aab224096bc5494908bbdc873.jpg) |  |
 | |
 | 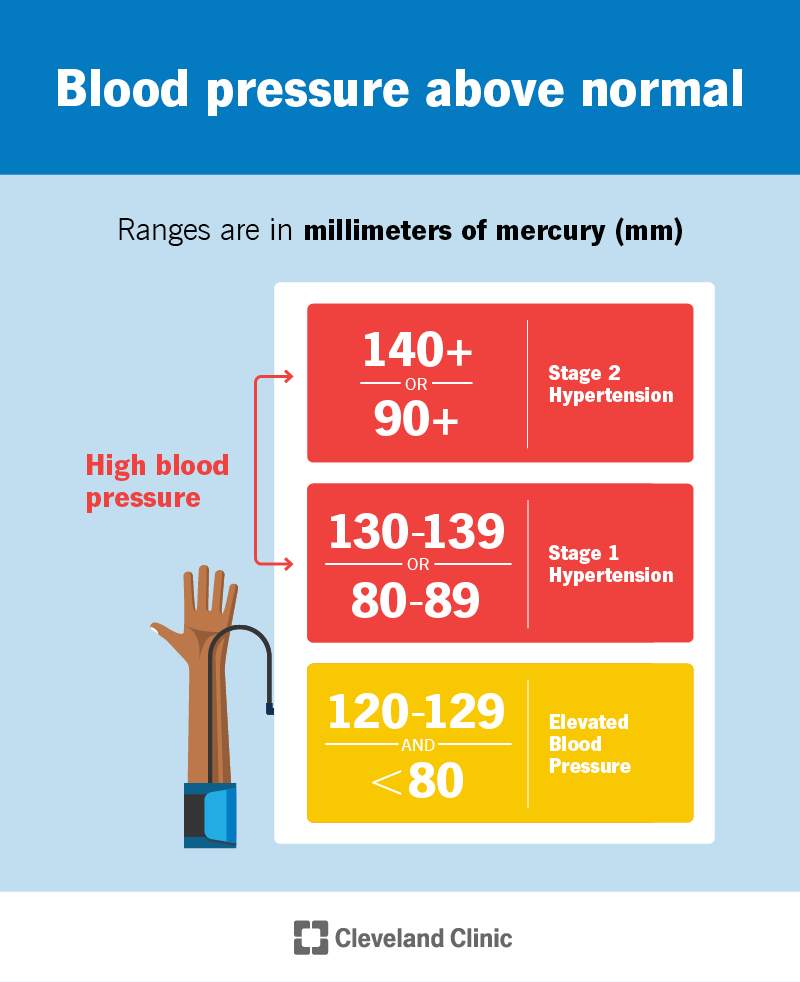 |
 | |
 |  |
Low blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. Along with causing dizziness, gabapentin can worsen your coordination. This can increase your risk of falls, which is especially dangerous for older adults. If you’re just starting to take gabapentin or your dose has increased, avoid driving or doing any activity that requires alertness. After childbirth, gabapentin passes into breast milk. At low levels, Gabapentin reduces blood pressure and heart rate through the nucleus tractus solitarii. https: Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: I suggest you contact your Dr. asap. Summary: Hypotension is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. Hypotension is when your blood pressure drops too low. It can have many causes, including dehydration, heart problems, and neurologic conditions like Parkinson’s disease. Some medications can also cause low blood pressure. Examples include blood pressure medications, nitrates, and opioids. Ligands of auxiliary α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) decrease elevated L-type VDCCs surface expression in arterial myocytes and arterial constriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of 3. Blood Pressure Medications . Blood pressure medications like Norvasc (amlodipine), Calan or Verelan (verapamil), and Cardizem (diltiazem) belong to a group of drugs called calcium channel blockers. These medications are prescribed to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart conditions. They work by relaxing your blood vessels. Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. Pain and blood pressure appear to be strictly related. According to available evidence, both pain and analgesic therapies may induce a clinically significant destabilization of blood pressure values. The subsequent implications on hypertension incidence and blood pressure control remain unclear and should be explored in future studies. Funding Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. Results: Unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS produced prominent dose-related depressor and bradycardic effects in SHR rats. The cardiovascular Gabapentin can affect your heart rate in a few different ways. In a double-blind, observational study, patients undergoing elective surgery were administered different doses of gabapentin. The study found that 400mg of gabapentin resulted in a higher heart rate and blood pressure, whereas 800mg of gabapentin resulted in a lowered heart rate. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. No.: Exceedingly rare individual side-effects or drug reactions/allergies aside, no it does not effect BP. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Initially, gabapentin has been shown to lower blood pressure. This effect is believed to be mediated through the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) in the brain, a region involved in cardiovascular regulation. Many people only need to take an oral steroid for a short period of time. In this case, the swelling should go away after you stop taking it. But others may need to take steroids long term, and fluid retention may start affecting your blood pressure. Eating salty foods can make swelling from steroids worse. Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic used to reduce intracranial pressure and intraocular pressure. Drugs that can cause low potassium levels (Hypokalemia) Some medications may cause your blood level of potassium to decrease, which is known as hypokalemia. The following drugs may cause low potassium: Diuretics, such as: Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) Yes, gabapentin can lower blood pressure. However, in the vast majority of people taking gabapentin, it does not lower blood pressure to a worrisome extent. A blood pressure of 113/64 is below average, but it is not at a worrisome level unless it is associated with any lightheadedness or dizziness.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Bloodpressure-5204833-final-7927123aab224096bc5494908bbdc873.jpg) |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |