Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
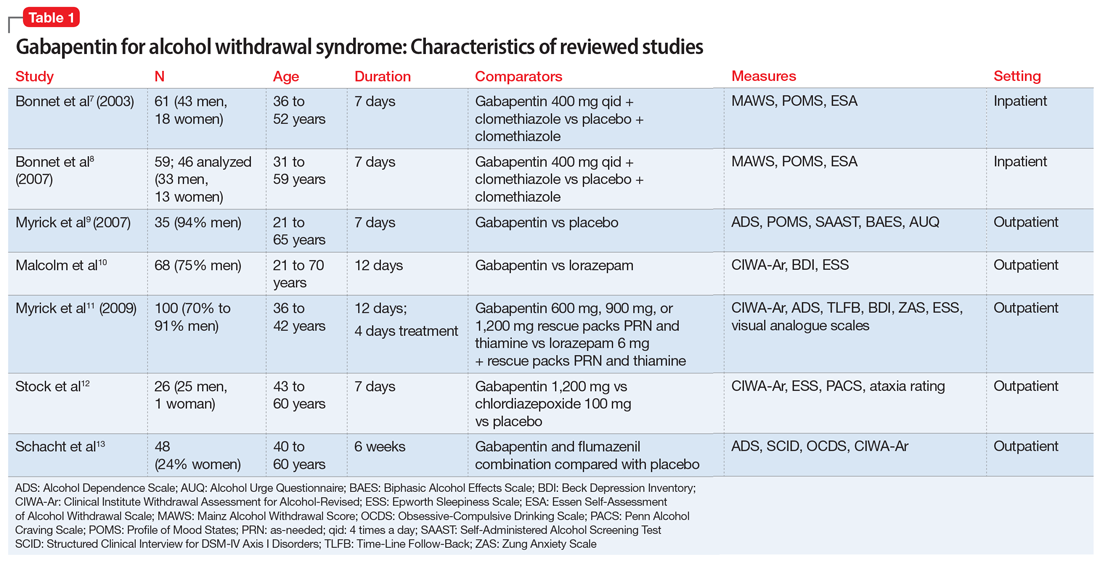
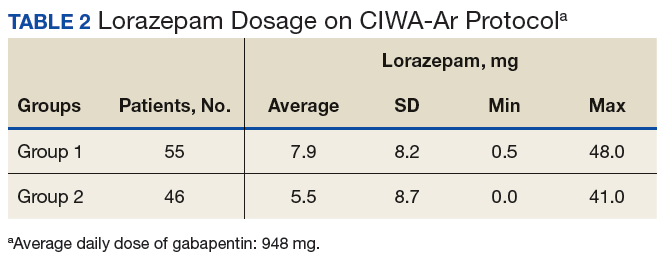
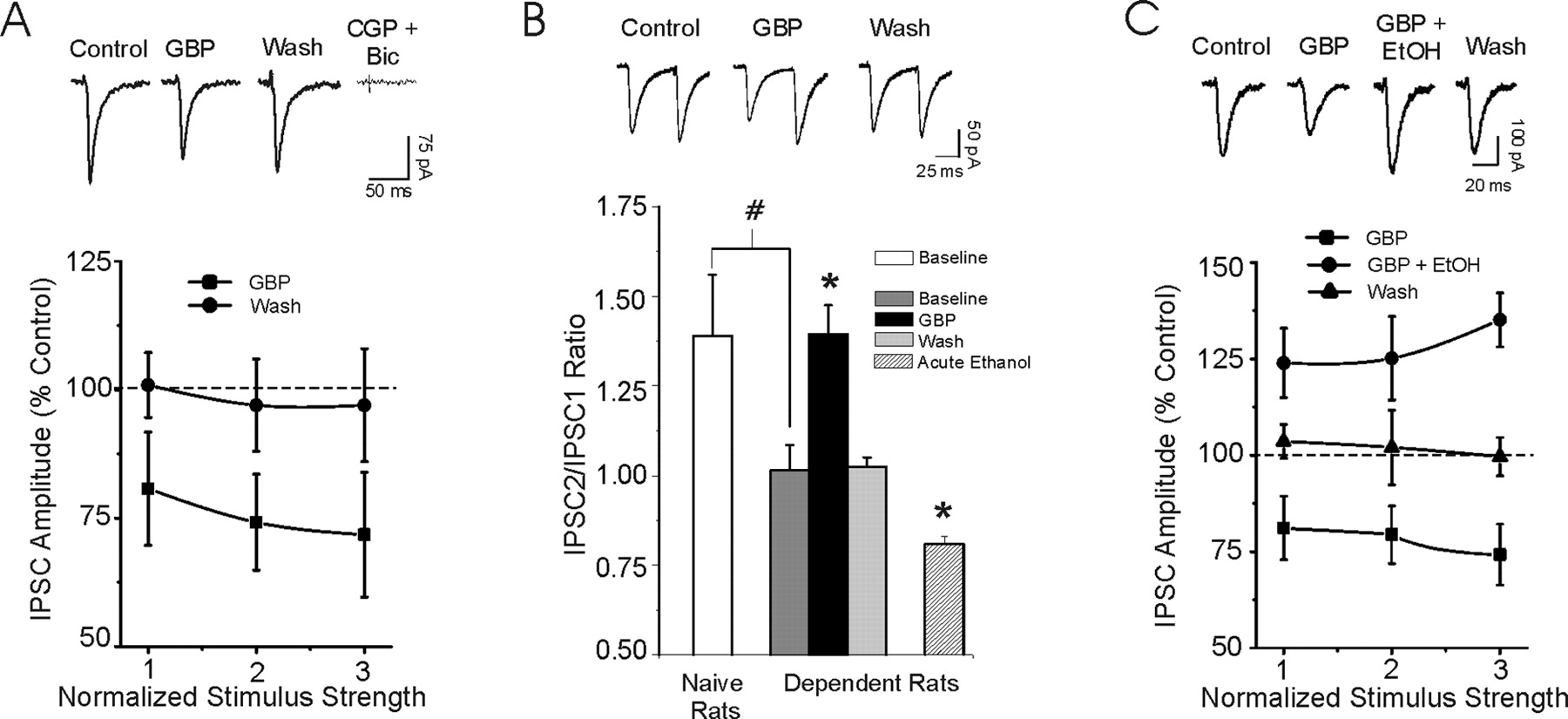
There have been numerous documented cases of gabapentin abuse, dependence, and withdrawal. Even though gabapentin is sometimes considered as a treatment option for alcohol and substance abuse, it is important to monitor for drug-seeking behaviors. A history of alcohol or substance abuse appears to b Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Long-term gabapentin and alcohol interaction may result in tolerance, dependence, and increased risk of accidents. Patients on gabapentin should avoid alcohol to prevent adverse effects and ensure treatment safety. Gabapentin and Alcohol Interaction: Risks, Side Effects, and Safety Tips Because its mechanism of action is unclear and it is assumed to have no abuse potential, gabapentin is widely used off-label to treat an array of disorders, including insomnia, various neuropathic pain conditions, drug and alcohol addiction, anxiety, bipolar disorder, borderline personality disorder, menopausal conditions, vertigo, pruritic Objective: Naltrexone, an efficacious medication for alcohol dependence, does not work for everyone. Symptoms such as insomnia and mood instability that are most evident during early abstinence might respond better to a different pharmacotherapy. Gabapentin may reduce these symptoms and help prevent early relapse. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or In animal models of alcohol dependence, gabapentin decreased the amplitudes of GABA receptor mediated inhibitory post synaptic currents (IPSCs) in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA), and decreased dependence-induced alcohol drinking. Importance Approved medications for alcohol dependence are prescribed for less than 9% of US alcoholics.. Objective To determine if gabapentin, a widely prescribed generic calcium channel/γ-aminobutyric acid–modulating medication, increases rates of sustained abstinence and no heavy drinking and decreases alcohol-related insomnia, dysphoria, and craving, in a dose-dependent manner. The role of gabapentin in the management of alcohol withdrawal and dependence. Leung JG. Jonathan G; Hall-Flavin D. Daniel; Nelson S. Sarah; Schmidt KA. Kristen A; Schak KM. Kathryn M. The Annals of pharmacotherapy. 2015. Aug; 49(8):897-906 A rising number of reports 10,11 support its use for alcohol dependence as well as alcohol withdrawal symptomatology. Possible mechanisms include normalization of stress-induced GABA activation in the amygdala, which is associated with alcohol dependence. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Conclusions and relevance: Gabapentin (particularly the 1800-mg dosage) was effective in treating alcohol dependence and relapse-related symptoms of insomnia, dysphoria, and craving, with a favorable safety profile. The generic anticonvulsant medication gabapentin shows promise as an effective treatment for alcohol dependence, based on the results of a 150-patient clinical trial of the medication. Though an off-label use, gabapentin has also been found useful in treating certain mental health disorders. 3 So, during addiction treatment, a person could be prescribed gabapentin to help with symptoms of cannabis, opioid, or alcohol use disorders or to help with co-occurring mental disorders such as anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder Gabapentin may have a role in the treatment of mild alcohol withdrawal, but future studies should focus on adequate dosing strategies. Gabapentin should be considered for the treatment of alcohol dependence when barriers prevent the use of traditional agents. Additional studies should be conducted t Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate gabapentin’s effects on six alcohol-related outcomes, test potential moderators, examine publication bias, and evaluate the quality of the studies. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or 5 GABAPENTIN FOR ALCOHOL USE DISORDER. Introduction. Based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is defined as a problematic problem of alcohol use leading to clinically There is a general debate in clinical settings about the appropriate or recommended dose of gabapentin for alcohol dependence and withdrawal symptoms. Numerous clinical trials 10, 11, 17-20, 24-27 have suggested several dosing regimens of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal, which range from 300 mg twice daily to 600 mg 3 times a The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |