Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
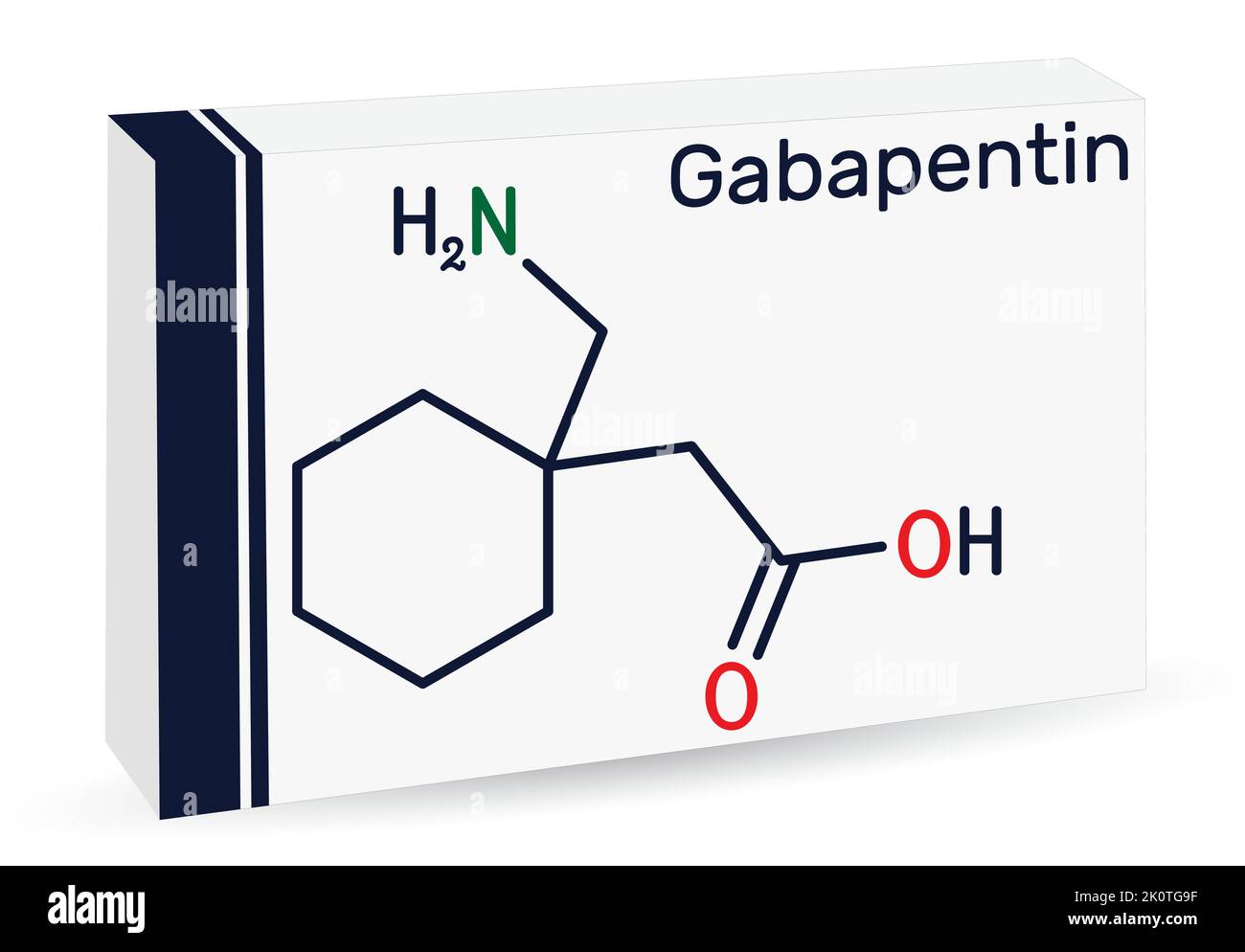
Discussion: Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. In this case report, we present a patient with chronic renal impairment who experienced devastating myoclonic jerky movements shortly after increasing his gabapentin dose. Gabapentin and pregabalin are fully excreted unchanged by the kidney Drugs and effects on kidney function Nephrotoxicity is defined as a rapid deterioration in kidney function caused by the toxic effect of drugs or chemicals. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin Accumulation leading to increase in CNS side effects Reduce dose Levetiracetam Accumulation leading to increase in CNS side effects Reduce dose Antihypertensives Antihypertensives (including Ca-channel blockers, -blockers, -blockers, etc) Hypotension. May exacerbate renal hypoperfusion Consider withholding / reduce dose Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Serum gabapentin concentrations progressively escalated with the decline of estimated glomerular filtration rate. The numbers above individual dots are serum gabapentin concentration values, the numbers below individual dots are the corresponding estimated glomerular filtration rates, and the numbers in parentheses are the number of patients. We report a case of gabapentin toxicity in a patient on long-term PD who was treated with continuous automated cycling PD. We find that continuous PD provides significant clearance of gabapentin. Gabapentin toxicity should be considered one of the differential diagnoses of altered consciousness in patients with compromised renal function, even after a single dose. We report a 57-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus and uraemia on regular Gabapentin toxicity should be considered one of the differential diagnoses of altered consciousness in patients with compromised renal function even after a single dose. We report a 57-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus and uraemia on regular haemodialysis who developed severe dizziness and lethargy after a single recommended dose of gabapentin for bilateral leg dysthesia. Because of We examined the Mayo Clinic Rochester database from 1998 to 2007 in patients with serum gabapentin measurements and known medical outcomes. A total of 729 patients were stratified according to their estimated glomerular filtration rate: group I, 126 individuals with estimated glomerular filtration greater than 90 mL/min/1.72 mm 3; group II, 594 individuals with estimated glomerular filtration Numerous drugs used to manage and treat multiple diseases, including hypertension, diabetes, and other pathologies, are nephrotoxic. These agents are in various classes and categories of medication. This activity reviews the indications, action, and contraindications for nephrotoxic drugs as a valuable agent in choosing key treatment strategies. This activity will highlight the mechanism of The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 We found that patients with chronic kidney disease had elevated serum gabapentin concentrations, in some cases leading to gabapentin toxicity; those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities were more prone to the toxicity, and the toxicity tended to be underrecognized. [3–9]. Other case reports describe nephrotoxicity secondary to non-hypersensitivity reactions in patients using carbamazepine, valproic acid, phenobarbital, ethosuximide, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetir-acetam and injectable lorazepam [10–34]. Available literature demonstrates that valproic acid can cause renal Gabapentin toxicity and side effects are well-known among nephrologists and fully described in the literature as myoclonic twitches, myopathy, neurotoxicity, etc., particularly in dialysis patients. 2,4 Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Population-based cohort study. Nephrotoxicity is defined as a rapid deterioration in kidney function caused by the toxic effect of drugs or chemicals. Cohort studies suggest that drug-induced nephrotoxicity could occur in as many as 14–26% of AKI episodes. Drug-induced AKI can be either dose related or idiosyncratic. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |