Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
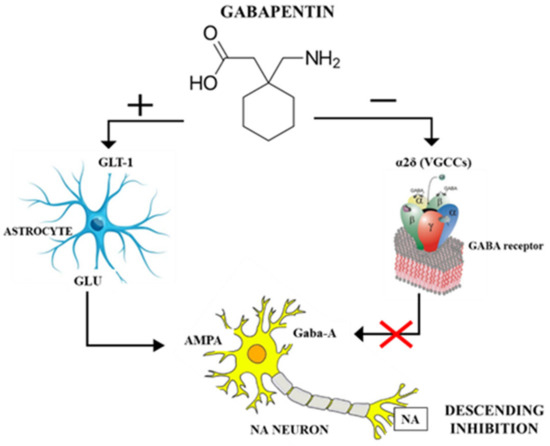
In the present study, systemic administration of gabapentin significantly attenuated the increase of BDNF and the enhancement of glutamatergic transmission in dorsal horn and ameliorated the hypersensitivity to the mechanical stimuli in rats receiving oxaliplatin. The number of doublecortin (DCX) positive neurons and the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in hippocampal dentate gyrus were observed by immunohistochemical staining, and the morphological changes of the hippocampal neurons were observed by Golgi staining. Results: Gabapentin treatment at the therapeutic level interfered with the neurogenesis and morphogenesis of vmDA neurons in the fetal brain by causing changes in morphology and alterations in the expression of key developmental genes, such as Nurr1, Chl1, En1, Bdnf, Drd2, and Pitx3. Bdnf is known to be a trophic factor for vmDA neurons and is therefore critical for their viability (Hyman et al., 1991).Drd2 and Dat are crucial genes for the development, maturation and We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Since BDNF signals via tropomyosine receptor kinases (trks), we tested whether trk blockade by repeated spinal injection of the trk inhibitor K252a would reduce anatomical (spinal noradrenergic and cholinergic fiber density), functional (α2-adrenoceptor-mediated direct stimulation of spinal cholinergic terminals), and behavioral (anti These results illustrated an increased expression of BDNF and enhanced glutamatergic transmission in rats with oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain, which was markedly attenuated by gabapentin. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission co-occur in brain conditions (depression, schizophrenia and age-related disorders) and are Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Results: Gabapentin treatment at the therapeutic level interfered with the neurogenesis and morphogenesis of vmDA neurons in the fetal brain by causing changes in morphology and alterations in the expression of key developmental genes, such as Nurr1, Chl1, En1, Bdnf, Drd2, and Pitx3. Background: In animal models of neuropathic pain (NP), promising results have been reported with the administration of minocycline, possibly through inhibition of spinal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression. No data are available on the effect of amitriptyline and gabapentin on spinal BDNF expression. Pharmacological inhibition of thrombospondin-1 using the FDA-approved drug gabapentin decreases glioblastoma proliferation. 10 ng ml −1 BDNF and 10 ng ml −1 NT-3 for 10 days to induce Gabapentin (GABAP) is used in this condition for pain relief, while atorvastatin (ATORV) has demonstrated neuroprotective effects in preclinical studies. We have investigated the influence of GABAP and ATORV on nerve injury. Brain derived neurotropic factors (BDNF) can be secreted either as a pro-BDNF or a mature form (mBDNF) through γ-amino-butyric acid (GABAA) receptors activation. Depolarization of GABA neurons in spinal cord can be mediated through N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor due to the exo bdnf表达水平的下降直接参与抑郁症发生的病理生理过程 [18-19] 。慢性疼痛时海马dg的bdnf的表达水平下调,导致神经发生受阻,神经突起长度缩短且密度下降,海马神经元在应激反应中的坏死过程加速 。抗抑郁药物可通过上调脑区bdnf的表达逆转神经元的坏死 。 We investigated the modulation of BDNF by GABA A agonist i.e., gabapentin, indomethacin (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory) and their low-dose combination on adjuvant-induced inflammatory Researchers have identified a mechanism by which brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) can suppress GABAergic transmission in hippocampus. In this article, Dr. Rajamani Selvam explains how he and his team achieved these results, and their potential impact on the treatment of neurological disease. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) can be used for treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. A: 42: Amitriptyline, nortriptyline (Pamelor), and desipramine can be used for pain relief in Background In animal models of neuropathic pain (NP), promising results have been reported with the administration of minocycline, possibly through inhibition of spinal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression. No data are available on the effect of amitriptyline and gabapentin on spinal BDNF expression. If the mechanism of action of the latter drugs does not involve brain-derived
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |