Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 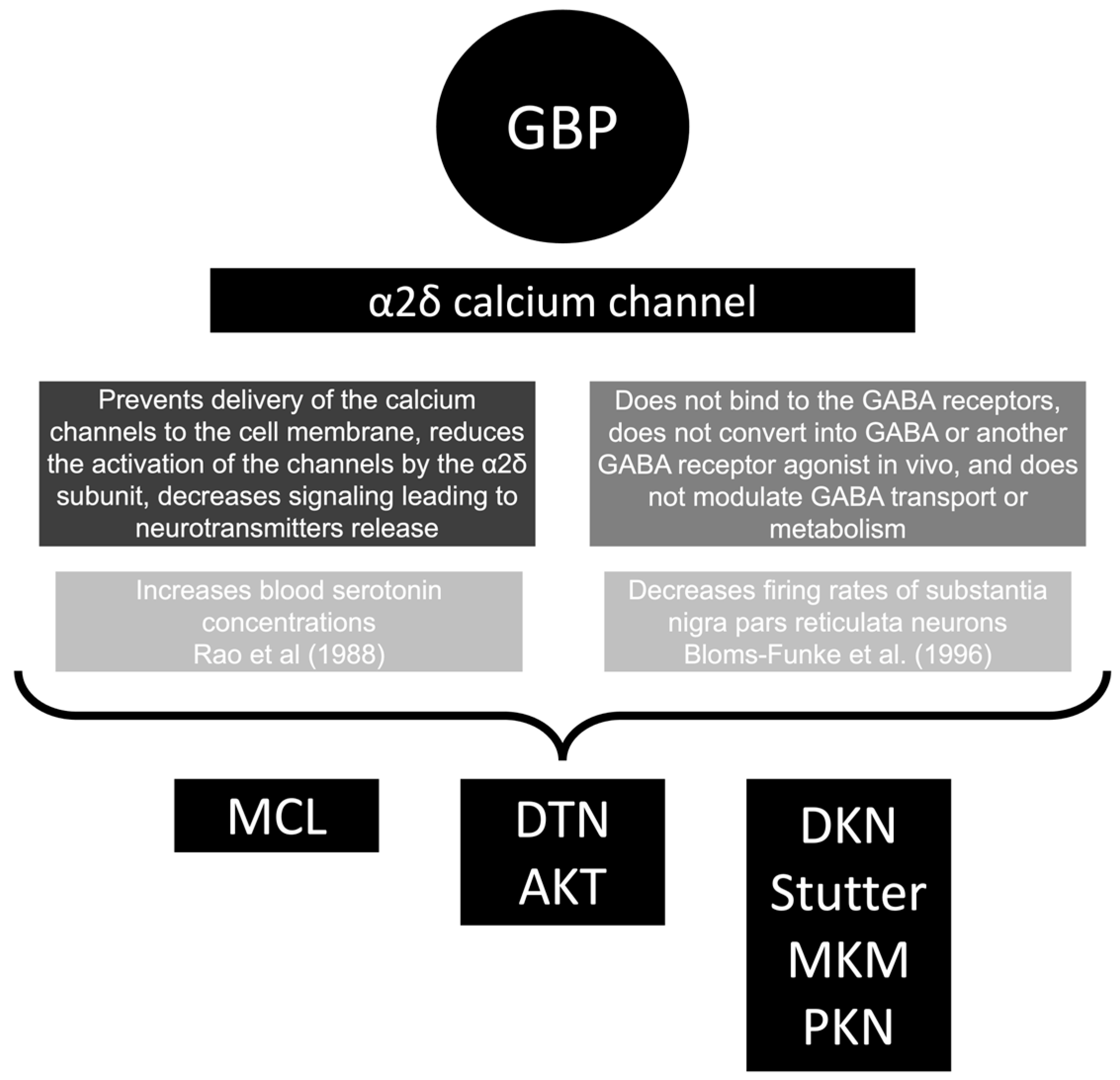 |
Lab work revealed abnormal liver function tests, with ALP 1,232 IU/L, AST 291 IU/L, and ALT 188 IU/L, and normal total bilirubin of .8 mg/dL. Prior records revealed completely normal liver function tests 6 months prior to presentation. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. Gabapentin (GPN) is a new antiepileptic agent currently in used as add-on therapy in adult patients suffering from partial seizures. The extent of liver damage at different dosage and long term treatment with GPN is not yet clear. Therefore this study was undertaken to find out the possibility of li LFTs measure liver enzymes (proteins), and increased numbers point to possible liver injury. These numbers are collected by your healthcare team through blood tests. Serious liver damage is rare. The levels of total bilirubin and conjugated bilirubin in serum (A) and the brain-to-plasma concentration ratio of gabapentin in the cortex, hippocampus, and striatum (B). Levels of total LAT1 protein ( C , D ) in the cortex, hippocampus, and striatum. LDL and bilirubin showed significantly lower range than the global values and the reference range values reported by the ministry of health Saudi Arabia. The LAT1 function was assessed using the brain distribution of gabapentin. It was found that BDL significantly increased levels of gabapentin, phenylalanine, and tryptophan in the cortex, hippocampus, and striatum of rats, and upregulated the expression of total LAT1 protein in hippocampus and striatum as well as cortex membrane LAT1 protein. (Patient developed jaundice, fever and pain 2 months after starting gabapentin, had inflamed gallbladder and underwent cholecystectomy, but bilirubin continued to rise [bilirubin either 2.7 or 27 mg/dL, ALT 8 times ULN, Alk P 12 times ULN]; gabapentin was stopped, ultimate complete recovery in ~1 month; unclear whether gabapentin or gallstones The man's treatment with gabapentin was discontinued and his liver enzymes started to downtrend with discharge values of AST 16, ALT 35, ALP 413, total bilirubin 9.3 and INR 1.1. Reference Fayad MA, et al. Drug-Induced Liver Injury Secondary to Gabapentin. DRESS was common with liver injury caused by lamotrigine, phenytoin, and carbamazepine, but not valproate or gabapentin. Liver injury severity was moderate to severe in the majority: five died, and three underwent liver transplantation (OLT). Acetaminophen is only effective at relieving pain and fever, while ibuprofen relieves inflammation in addition to pain and fever. Official answer: Many medications can cause liver enzymes to be elevated. A familiar over-the-counter medication that can cause liver Histologically, acute hepatitis was seen in five cases, and chronic hepatitis was seen in one case. Gabapentin was reported to cause cholestasis in two case reports. Despite the small number of reported cases of hepatotoxicity, trazodone and gabapentin are known causes of liver injury, and clinicians should be aware of this possibility. The x-axis show chronology of gabapentin administration. The left y-axis shows alkaline phosphatase levels in IU/L. The right y-axis shows total bilirubin levels in mg/dL. There have been four reports of jaundice (one cholestatic) associated with the use of gabapentin and, as far as we know, none of these have been published. To the best of our knowledge this is the first reported case of gabapentin induced cholestatic jaundice. Gabapentin should be added to the list of drugs capable of producing this adverse Gabapentin caused elevated liver function enzymes AST, ALT, and ALP beside bilirubin. Gabapentin effects on Lipid profile, Blood electrolytes, and functions of Kidney and Liver of Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. Along with its needed effects, gabapentin (the active ingredient contained in Neurontin) may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. The activity of liver enzymes, with 20 mg/kg of GPN were not significantly different from the control group but, the serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, direct bilirubin and total bilirubin were enhanced significantly with 100 mg/kg of GPN.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |