Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
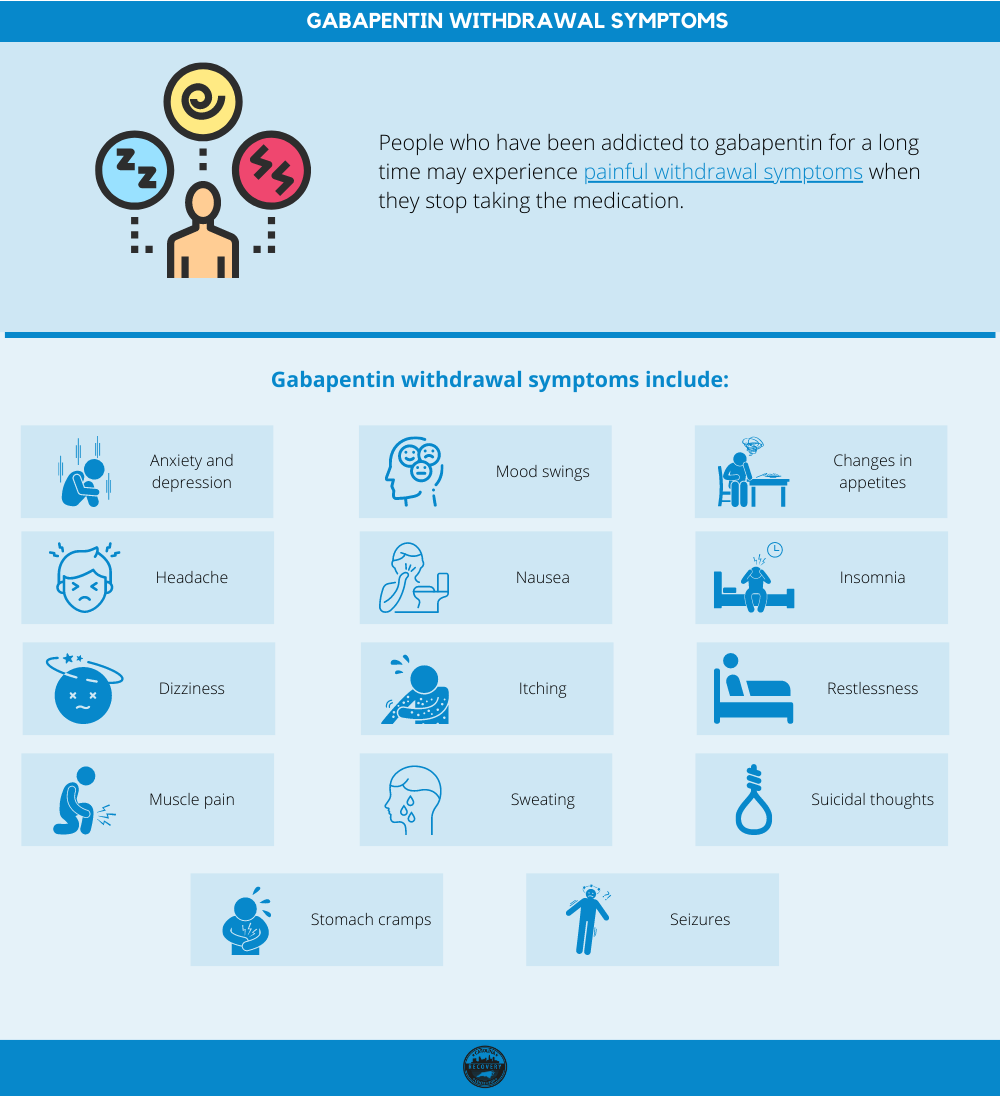
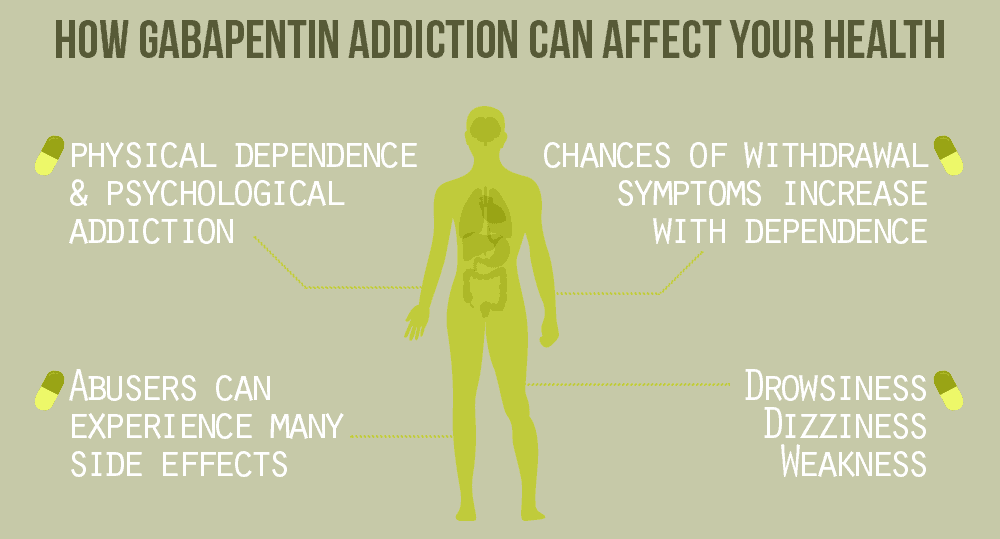
Gabapentin slightly increased spontaneous absence-like seizures in a genetically susceptible strain recorded with electroencephalography. All of these effects of gabapentin were seen at dosages at or below the threshold for producing ataxia. Gabapentin also has been tested in a wide variety of animal models that are relevant for analgesic When Your Brain Goes Rogue: Neurological Side Effects. Now, let’s venture into the realm of neurological side effects – because apparently, messing with our emotions wasn’t enough for gabapentin. These effects can have a significant impact on our mental well-being, even if they’re not directly classified as “mental” side effects. Gabapentin has been successfully used to treat some of the effects of brain damage. However, prolonged use can cause serious side effects. This article will summarize the use of gabapentin for brain damage and discuss which symptoms it can help relieve. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. We would not get overly concerned with this off-label prescribing if this drug were perfectly safe. But gabapentin side effects are not trivial, as you will read. And a brand new gabapentin side effect has just emerged. Canadian researchers have just dropped a bombshell on gabapentin (Annals of Internal Medicine, Jan. 15, 2024). They compared Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Overall, the risk of being hospitalized with altered mental status after initiating gabapentin remains low, but may be reduced through the judicious use of gabapentin, use of the lowest dose to control pain, and vigilance for early signs of altered mental status. But the new findings raise questions about gabapentin's effect in situations where synapse formation is widespread and crucial, most notably in pregnancies. The vast bulk of the brain's synapses are formed during gestation and the very early months and years after birth. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. The Impact of Gabapentin Administration on Brain GABA and Glutamate Concentrations: A 7T 1 H-MRS Study Kejia Cai 1,5 , Ravi PR Nanga 1,5 , Lisa Lamprou 2,3 , Claudia Schinstine 2,3 , Mark Elliott Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin new users with normal cognition at the visit of gabapentin initiation (i.e., index visit) were included. New-users were matched on year of first enrollment and time of gabapentin initiation since enrollment to randomly select nonusers with replacement. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. We conducted a gabapentin (900 mg) challenge in healthy human subjects to confirm and explore its effects on GABA and glutamate concentrations, respectively, and to test the ability of single voxel localized proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (¹H-MRS) to reliably measure GABA and glutamate in Studies suggest that chronic gabapentin use may contribute to neurodegenerative changes in the adult brain, impacting key areas like the hippocampus and striatum. Can gabapentin cause brain fog? Gabapentin is a medication that can cause side effects. Brain fog is not a common side effect of gabapentin, but it has been reported in some people taking the drug. The possible cause of gabapentin fog may be related to how the drug works. Gabapentin decreases electrical signals in the brain. Explore gabapentin's effects on mental function, memory, and cognition. Learn about managing side effects and balancing therapeutic benefits with potential risks. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Gabapentin is widely used to treat seizures and shingles, but its effect on memory has been a topic of ongoing debate. While some patients may experience brain fog or slight confusion, studies have shown that gabapentin alone does not cause long-term memory loss. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |