Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
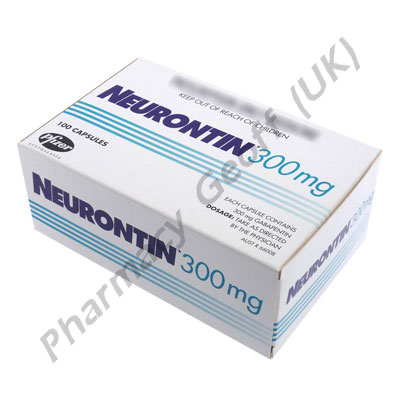
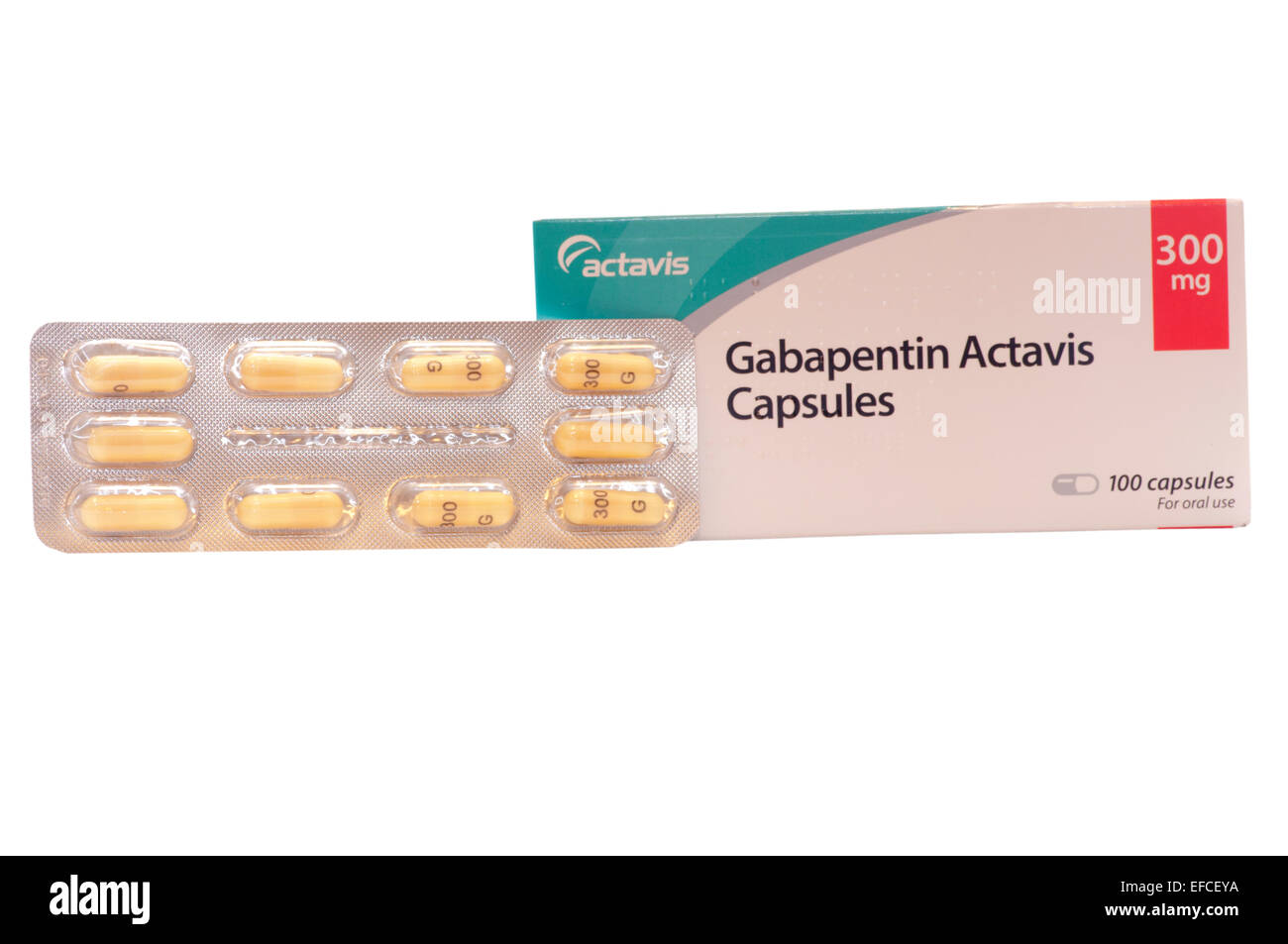
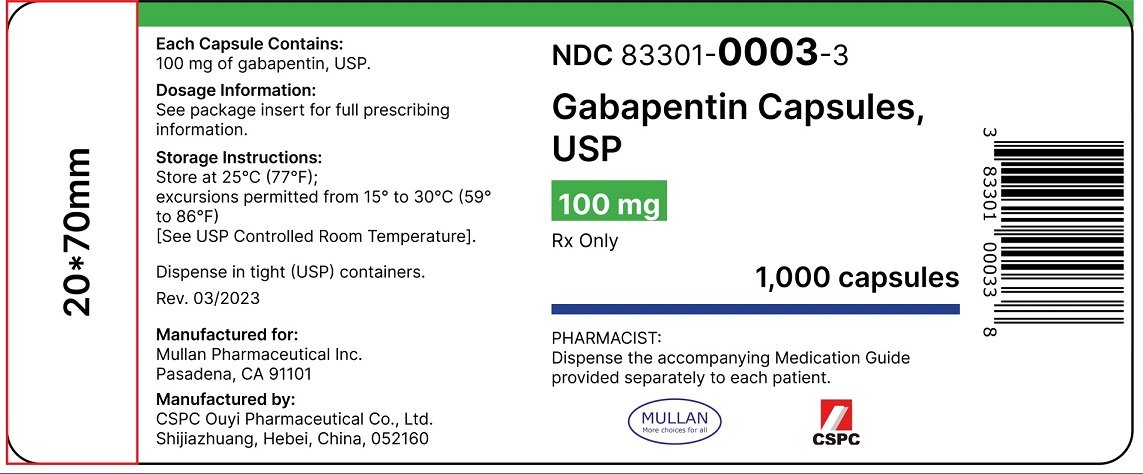
Percutaneous endoscopic gastro-jejunostomy (PEGJ), inserted into the jejunum via the abdominal wall and through the stomach. Drug charts should state the route of administration, e.g. NJ, and specify the lumen to be used. Ensure the siting of the tube has been medically confirmed. Stop the infusion of the feed when administering drugs. Feeding Tube: In Vitro Testing 22 powders, suspensions, capsules, and tablets. Gastrostomy 12-30 Gastrojejunal 12-22 Jejunostomy 12-18 105 * Fr = French 106 Stop feed and/or flush enteral tube with 15-30mL of water prior to drug administration. Ensure the patient is sitting up at an angle of at least 30 degrees to avoid reflux of medication or water. Give medication via enteral tube as directed by the guidance within the table. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2008;65(24):2347-2357. Administer medications via the oral route when possible. Determine the enteral feeding tube size (e.g., small bore or large bore), insertion site (e Hard gelatin capsules - enteral tubes Prepare the capsule as follows: 1. Gently ease open the capsule to release the powder. 2. Tip the powder into a beaker - be sure to obtain all the powder. 3. Mix the powder with 15-30mL of water. 214,225 4. Draw up the solution in an enteral syringe. 5. Administer the solution through the enteral feeding Many medications may be put into your PEG. Here are some important things you need to know: If any medications cannot be put in your PEG, your pharmacist may help you by reaching out to the healthcare provider that prescribed a medication to suggest another option. Of the 432 capsules, 359 capsules (83.1%) disintegrated within 10 min and passed the tube passage test. Seventy-three (16.9%) capsules did not pass the tube. On the other hand, with the decapsulated method, 272 capsules (63.0%) of the 432 capsules could be decapsulated, according to the interview forms of each capsule. Flush tube three times with 5ml of water after liquid administration †Contact neurology for advice if no enteral tube † Advice from neurology is sought via Queen Elizabeth University Hospital (QEUH) switchboard. Gabapentin Rosemont Oral Solution 50mg/mL Instructions for administration via nasogastric (NG) or percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. Gabapentin Rosemont Oral Solution is suitable for use with the following type of NG and PEG tubes: Ensure that the enteral feeding tube is free from obstruction before administration. 1. Embeda morphine sulfate Capsule Extended‐release (a); do not give via N/G tube E‐Mycin erythromycin Tablet Enteric‐coated Enablex darifenacin Tablet Slow‐release Entocort EC budesonide Capsule Extended‐release; Enteric‐coated (a) Equetro carBAMazepine Capsule Extended‐release (a) tube 4 3. Flushing enteral feeding tubes 9 4. Restoring and maintaining patency of enteral feeding tubes 15 5. Drug therapy review 23 6. Choice of medication formulation Alimemazine (Trimeprazine) tartrate25 7. The legal and professional consequences of administering drugs via enteral feeding tubes 38 8. Health and safety and clinical If necessary, Gabapentin Colonis 50 mg/ml Oral Solution can be administered via intragastric feeding tubes (nasogastric (NG) or percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes). Tubes should be rinsed twice with 10 ml of water immediately after administration. The recommendation for Gabapentin is not to compound a liquid using the tablet or capsule, but to use the suspension. Reports have suggested increased adverse effects when switching generic formulations of antiepileptic drugs, particularly with gabapentin. 45 medication administration can be improved or maintained through the appropriate use of enteral alternatives such as gastrostomy tubes (GT), nasogastric tubes (NG), gastrostomy buttons (G-Buttons; GB), jejunostomy tubes (JT), and nasojejunal tubes (NJ). Introduction: Drug therapy can be com-plicated in hospitalized patients requir-ing an enteral feeding tube (EFT). Some medications may be given via an EFT while others are unsuitable for this form of administration. Inappropriate drug selection for EFT administration can cause potential toxicity, reduced efficacy, and tube obstruction. The following liquid medicines manufactured by Rosemont Pharmaceuticals have recently received UK licenses for administration via nasogastric (NG) or percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy (PEG) tube: Furosemide Oral Solution 20mg/5mL, 40mg/5mL and 50mg/5mL Ramipril Oral Solution 2.5mg/5mL Metoclopramide Hydrochloride Oral Solution 5mg/5mL Clonazepam Oral Solution 0.5mg/mL, 2mg/mL Gabapentin Oral Some oral solutions are licensed for administration via NG/PEG feeding tubes, check product information for specific advice. Notes NICE guidelines advise that patients prescribed Gabapentin for epilepsy should receive the same formulation consistently. Tube Placement There are more likely to be problems with drug absorption where the tube is placed beyond the stomach e.g. percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy (PEJ) tubes. Staff should be aware of situations in which the drug may be administered beyond the drugs main site of absorption eg digoxin, cephalexin, ketoconazole, phenytoin and other Gastrostomy tubes may be inserted endoscopically (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy or PEG), radiologically (radiologically inserted gastrostomy tube, or RIG) or surgically inserted.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |