Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
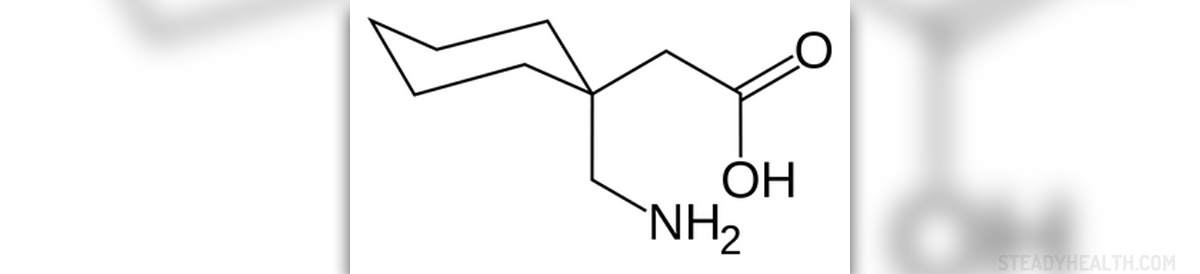
Interactions may include dizziness or lightheadedness. Some interactions may be more serious. Animal studies have found that there may be damage to a fetus (teratogenicity). Summary: Headaches is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Vitamin D3, and have Multiple sclerosis. We offer a panoramic view of nociception, from a central perspective, and discuss various pharmacological options available to treat headache and neck pain. We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. It is now considered to be an emergent treatment for pain syndrome. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Problem I'm having is blurred vision, and a constant pounding headache. Will these side effects go away after a certain amount of time? These headaches will not go away, no matter what I take for them. It's affecting my life in a negative way. I started gabapentin a few days ago. 100mg twice a day. I took 100mg once a day and I'm on the 4th day. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. More rarely, gabapentin can cause fluid buildup (edema), weight gain, and vision problems. It can also cause diarrhea. More serious (but rare) side effects include suicidal thoughts or behavior, and mood changes in children. Ask your pharmacist to recommend a painkiller. Headaches should usually go away after the first week of taking gabapentin. Talk to your doctor if they last longer than a week or are severe. Note: This document provides detailed information about Neurontin Side Effects associated with gabapentin. Some dosage forms listed on this page may not apply specifically to the brand name Neurontin. Applies to gabapentin: oral capsule, oral solution, oral suspension, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release 24 hr. Serious side effects of Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention . Headaches can be a side effect with gabapentin either when first starting the medication or sometimes after a dosage increase especially if the dosage increase is significant. They usually resolve within a few days to several weeks but everybody's response to the medication is different. What dosage were you taking and what was it increased to? Memory Issues: Gabapentin is associated with memory decline and can cause confusion in some older patients. Headaches: Headaches are another common side effect of gabapentin, which can be attributed to other symptoms, including mood changes, dizziness, and thinking issues. I actually am taking 900 mg of Gabapentin 3Xs a day for seizures and migraine prevention. My seizures have decreased, but I do still have migraines and tension headaches, but not nearly as often. I was also told headaches were a side effect until the right dose is found. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1, 2. However, gabapentin is not helpful for migraine aura, vertigo, or other accompaing symptoms. Gabapentin is a good preventive therapy for migraines refractory to standard medications 3. In some cases, patients have reported experiencing headaches while on gabapentin therapy. This raises an important question: Could gabapentin be a trigger for migraines or headaches in certain individuals? The relationship between gabapentin and migraines isn’t straightforward. Summary: Headache is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Vitamin D3, and have Multiple sclerosis. The American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and the American Headache Society (AHS) do not list gabapentin as "effective" or "probably effective" for preventing migraines in their 2012 guidelines. Instead, gabapentin is given a level U rating, which means the evidence is conflicting or inadequate to support or refute its use for migraine prevention. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Due to this ambiguity, a clinical evidence literature review was performed investigating GBP's efficacy in headache disorders. Common side effects of gabapentin include: flulike symptoms such as fever or body aches. Rare but serious side effects of gabapentin include: changes in memory, ability to concentrate, or personality. Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |