Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
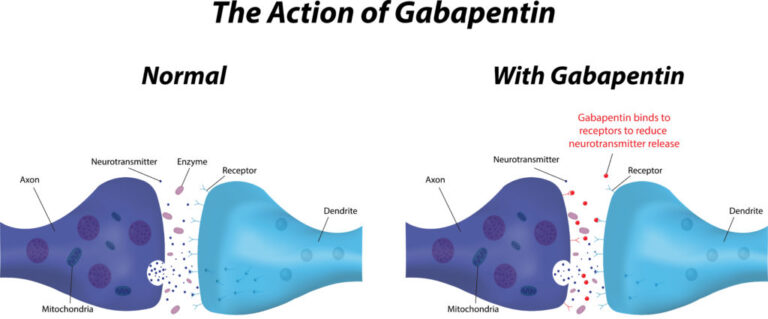
Studies in humans and laboratory animals indicate that perioperative administration of gabapentin to animals with nerve injury may reduce the potential establishment of, or ongoing, neuropathic pain. Based on blood concentrations in dogs, dose at 10 mg/kg PO q8h (5 mg/kg PO q12h in cats), increasing as needed Gabapentin (also marketed under brand name Neurontin (®)) is an anticonvulsant and pain relief medicine intended for the relief of neuropathy (nerve pain). It is also sometimes used for the treatment for seizures, but not usually as a primary means of treatment. Instead it is used for support. Disorders of the somatosensory system such as neuropathic pain are common in people with chronic neurologic and musculoskeletal diseases, yet these conditions remain an underappreciated morbidity in veterinary patients. This is likely because assessment of neuropathic pain in people relies heavily o Gabapentin is highly effective for managing neuropathic pain in dogs, which is pain caused by damage to nerves or the nervous system. This type of pain can result from conditions like intervertebral disc disease , cancer-related pain , diabetic neuropathy , or post-surgical nerve damage . Gabapentin is primarily an anticonvulsant medication used in people for treating neuropathic and chronic pain, and it has been introduced to veterinary medicine, but as an off-label drug in most countries and states. Gabapentin should be administered to patients with a known neuropathic lesion (e.g., extruded disc, nerve injury), suspected neuropathic lesion (e.g., painful back, neck), or chronic pain that is not controlled by anti-inflammatory drugs or for which these drugs are contraindicated. Gabapentin is usually used to manage chronic pain, especially nerve-related pain. It is also used (primarily in cats) to relieve anxiety associated with veterinary procedures, travel, and other fear-generating situations. Gabapentin can also be used as an additional medication in seizure management. Gabapentin works best for managing neuropathic pain – pain that stems from issues like extruded discs and nerve injuries. It is also very efficient in managing joint pain and postoperative pain. When used together with NSAIDs and opioids, it boosts their efficacy and allows lowering their doses. How Does Gabapentin Work for Nerve Pain? Gabapentin vs. Other Pain Medications. Is Gabapentin Safe for Dogs? 1. How quickly does gabapentin work for nerve pain in dogs? 2. Is human gabapentin the same as dog gabapentin? 3. Is 100 mg of gabapentin a lot for a dog? 4. Does gabapentin heal nerves or just mask pain? 5. Neuropathic pain is pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory system and should be suspected in the presence of central sensitization resulting in allodynia and hyperalgesia. 2 Clinical signs of neuropathic pain are nonspecific and often require multidisciplinary collaboration to reach diagnosis. Surgery, primary neurologic Neuropathic pain is likely an under-recognized condition in veterinary patients with an assortment of neuromusculoskeletal diseases. Specific literature related to diagnosis and treatment of neuropathic pain in dogs is limited, although information related to mechanisms and treatment options can be extrapolated from the human literature. Neuropathic pain is likely an under-recognized condition in veterinary patients with an assortment of neuromusculoskeletal diseases. Specific literature related to diagnosis and treatment of neuropathic pain in dogs is limited, although information related to mechanisms and treatment options can be extrapolated from the human literature. This article will give you a vet’s guide for administering a specific medication, called Gabapentin*, that is used to treat chronic or neuropathic (peripheral or central nerve) pain in dogs, as well as seizures. The short answer is yes, you can give your dog gabapentin for pain, but it’s crucial to do so under the guidance of a veterinarian. Gabapentin is a medication frequently used in veterinary medicine, primarily for managing chronic pain in dogs, such as that associated with arthritis or back problems. evidence many chronic pain conditions such as low back pain in man have a central neuropathic component. For a discussion of the mechanisms of NeP, the reader is referred to my previous article “So what is neuropathic pain?” (VT 43.17). Drug therapy in chronic pain. NSAIDs are the mainstay of analgesic management in chronic pain. One medication that has been used with success for long-term pain is gabapentin. This anti-seizure drug has analgesic properties that are particularly effective for reducing neuropathic pain in dogs. Gabapentin is given once daily for pain control and can be given with or without food.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |