Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
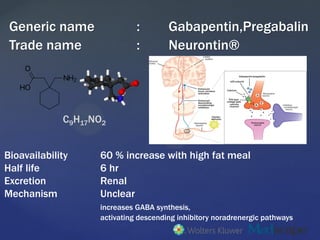
The elimination half-life of gabapentin in dogs is 3-4 hours in dogs, meaning that it may be difficult to attain steady state levels in dogs even with tid dosing. The dose at present estimated to be necessary to achieve some effect in dogs is 30 to 60 mg/kg divided tid to qid. Typically, Gabapentin has a half-life of around 3 to 4 hours in dogs, meaning it takes roughly that amount of time for half the drug to be eliminated. Nevertheless, it can take approximately 5 to 6 half-lives for a drug to be fully removed from the system. Gabapentin has a half-life of around 5-7 hours in dogs, meaning it will be eliminated from their system within a day or two. However, the effects of the medication may last longer due to its cumulative nature in the body. It has a short half-life (3.3 to 3.4 hours in a study of the pharmacokinetics of oral gabapentin in Greyhound dogs). This means the body has broken down and eliminated half of the dose in about 3.5 hours. Maximum blood levels are achieved in one to three hours and it has an elimination half-life of three to four hours.6 Gabapentin is excreted almost completely by the kidneys and it does not rely on hepatic biotransformation,7 making it a good choice for patients with hepatic disease. Elimination half-lives range between 2-3 h in rats, 3-4 h in dogs, and 5-6 h in man. Gabapentin is nearly exclusively eliminated via the kidneys. Renal elimination was up to 99.8% in rats and approx. 80% in man following oral administration. The half-life of gabapentin in most species is between 5-7 hours. This means that the effects of a 300 mg dose will gradually decrease over that time, typically requiring dosing every 8-12 hours for consistent results. Median plasma terminal half-life reported in horses (3.4 h) by Dirikolu et al. (2008) resulted very similar to that reported by KuKanich and Cohen (2011) in dogs (3–4 h) at the oral dose of 5 mg/kg, whereas Terry et al. (2010) indicated a mean value of 7.7 h following an oral administration at 20 mg/kg [92,96,105]. Results obtained after In dogs, the half life of gabapentin can vary, typically ranging between 2-4 hours. This means that after a single dose, gabapentin’s effectiveness gradually decreases over time. Why is knowing the half life of gabapentin important? ⏳ How Often Should Gabapentin Be Given?. Gabapentin is typically administered every 8 to 12 hours, but the exact schedule depends on what it’s being used for:. For Pain Relief: Gabapentin has a relatively short half-life in dogs, which means it leaves their system quickly. Pharmacokinetic studies have reported that the half-life of gabapentin in dogs ranges from 2.2 to 3 hours for oral doses of 50 to 60 mg/kg 52,53 and from 1.3 to 1.5 hours for oral doses of 10 to 20 mg/kg, respectively. 54 Another recent study 55 that used an orally administered 50-mg/kg dose of gabapentin 2 hours before the induction of The elimination half-life for this drug is 3-4 h. in dogs and 2.5-3.5 h. in cats, which unfortunately necessitates a three times a day treatment. Due to the short half-life and its lack of anti-inflammatory properties, gabapentin can safely be given before a potential referral as it will not interfere with our examinations. The half-life of gabapentin in dogs is 2 to 3 hours, the same as it is in humans and rats. This means that although gabapentin doesn’t linger around for very long, regular dosing enables it to have a cumulative effect. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. It is used to treat partial seizures‚ postherpetic neuralgia following shingles and restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin works by calming overactive nerves in your body. It should be mentioned that gabapentin has extremely short half-life and consequently stays within the dog’s system for no more than 2 to 3 hours. Last but not least, although gabapentin for humans is same as gabapentin for dogs, the human dosage is totally different from the canine dosage. Diazepam is not suitable for oral maintenance therapy in dogs, because it is absorbed poorly, has a short half-life of 2.5–3.2 hr, and tolerance to its anticonvulsant effects develops rapidly. However, cats not only have a longer half-life (15–20 hr) than dogs but also do not develop a tolerance to the anticonvulsant effects. When it comes to Gabapentin, there are a few key factors that can affect how long it takes for the medication to start working in dogs. These factors include the dosage of Gabapentin prescribed, the individual dog 's metabolism, and the severity of the condition being treated. The duration of gabapentin in a dog’s system depends on several factors, including the dog’s age, weight, and liver function. Gabapentin has a half-life of approximately three to four hours in dogs, meaning that half of the medication is eliminated from the body within that time frame. It is noteworthy that the plasma elimination half-life of gabapentin in the present study (11.02 ± 3.68 h) in calves was considerably longer than previously reported in children (4.44 ± 1.32 h), horses (3.40 ± 0.48 h) and dogs (3.25 h) (Haig et al., 2001; Dirikolu et al., 2008; KuKanich and Cohen, 2011). Gabapentin has a half-life of approximately 5 to 7 hours in dogs, meaning that it takes this amount of time for half of the medication to be eliminated from the body. The duration of action may vary depending on the individual dog 's metabolism and medical condition.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |