Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 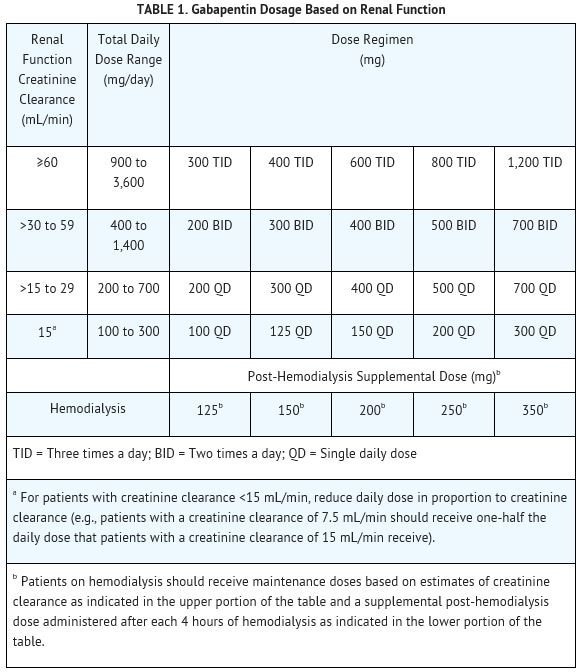 |
For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight. Gabapentin is available as a lower-cost generic. But certain products are brand-only. Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a].However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. In elderly individuals, it’s often prescribed to alleviate pain associated with conditions such as diabetic neuropathy and shingles. Common Side Effects. Despite its effectiveness, Gabapentin can cause several side effects, especially in older adults. Common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and coordination problems. What are the common side effects of gabapentin in the elderly? Common side effects of gabapentin in the elderly may include dizziness, drowsiness, unsteadiness, fatigue, and peripheral oedema. Some seniors may also experience gastrointestinal issues like nausea and constipation. These side effects can impact their daily activities and quality For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. It may be reasonable to start older adults on a low dose of gabapentin, which can be effective to treat pain while exposing patients to a lower risk of adverse mental status side effects of gabapentin (dizziness, drowsiness and confusion) [7]. Generic brands of gabapentin capsules, USP are used for postherpetic nerve pain and for add on therapy for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Gabapentin can cause life-threatening breathing problems, especially if you already have a breathing disorder or if you use other medicines that can make you drowsy or slow your breathing. During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for People who are 65 years of age or older can be at a greater risk for some side effects of gabapentin. Talk to your healthcare provider about your risks if you are in this age group. o Patients 12 years of age and older: starting dose is 300 mg three times daily; may be titrated up to 600 mg three times daily o Patients 3 to 11 years of age: starting dose range is 10 to Gabapentin should be titrated until two months, every seven days, to achieve a maximum tolerated dose. The starting dosage is 100 mg three times a day. At the beginning of titration, a single increased bedtime dose should be considered to avoid daytime sedation. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed and tolerated. However, the dose is usually not more than 1800 mg per day (600 mg 3 times per day). Children 3 to 11 years of age—Dose is based on body weight and must be determined by your doctor. The starting dose is 10 to 15 milligrams (mg) per kilogram (kg) of body weight per day and divided in 3 What dosage strengths and forms does gabapentin come in? Gabapentin is available as: Gabapentin tablets. It’s available as 300- and 600-milligram tablets (Gralise) and 600- and 800-milligram tablets (Neurontin or generic gabapentin). Gabapentin oral solution. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Many older adults, their families, and caregivers usually have many questions about this drug. Here’s the answer to some frequently answered questions about gabapentin side effects in the elderly: Does gabapentin affect urination or cause incontinence? Incontinence is a rare side effect of gabapentin, and it has been described in some older During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1,800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Learn about the common side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including dizziness, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and more. Explore the connection between gabapentin and depression, mechanisms behind gabapentin-related depression, and strategies to manage and mitigate side effects. Gabapentin side effects in elderly patients can vary in duration. Some effects, like dizziness or drowsiness, may improve within days to weeks as the body adjusts. However, elderly patients often take longer to adapt due to slower metabolism and age-related factors. If side effects persist or worsen, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |