Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
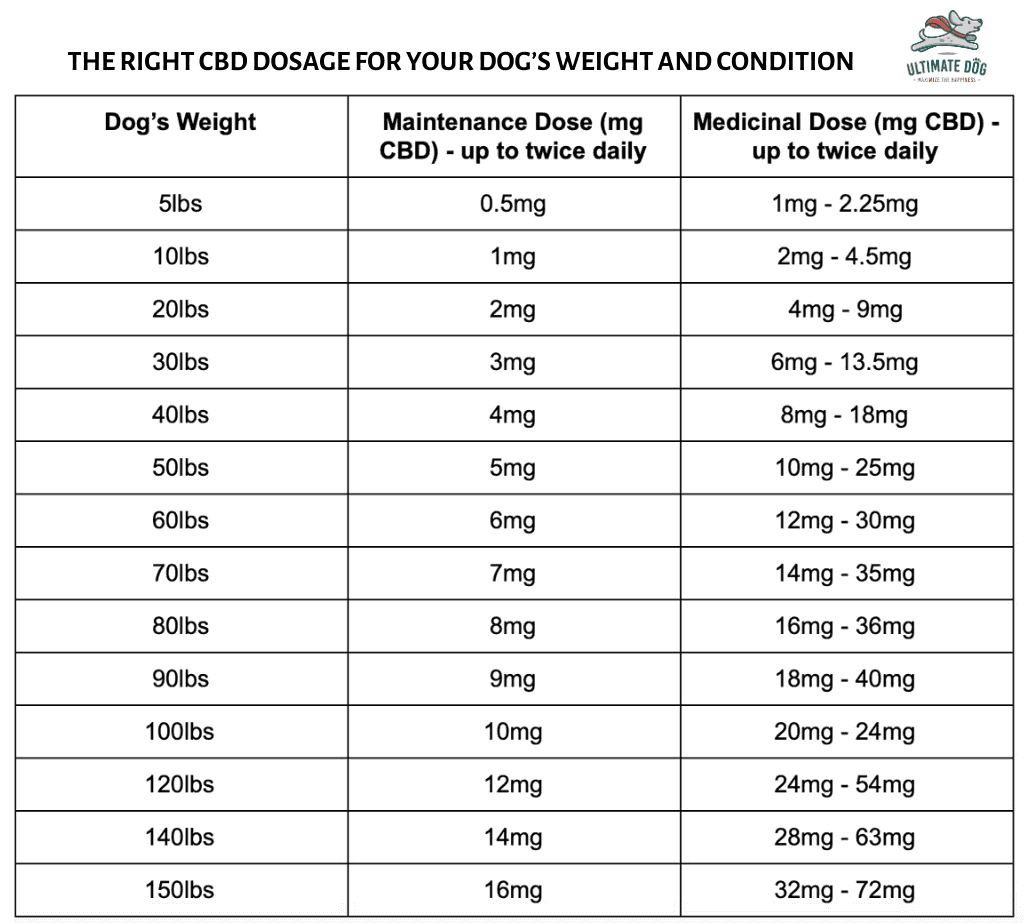
For those who have difficulty staying asleep, low-dose doxepin and the z-drugs should be considered. Benzodiazepines are not recommended because of their high abuse potential and the availability The dosage ranges for gabapentin when used for sleep typically span from 100 mg to over 600 mg. Low doses (100 mg – 200 mg) may suffice for mild insomnia, while higher doses (300 mg – 600 mg) may be required for more severe sleep issues. For treating insomnia or sleep disturbances, Gabapentin doses typically range from 100 mg to 600 mg per day, with 300 mg being the most common daily dose. Depending on individual needs, this is usually taken once at bedtime or divided into 1–3 doses throughout the day. Do not take gabapentin daily doses of more than 3600 mg. Please consult with your doctor before adjusting any gabapentin dose. Long Term Use of Gabapentin for Sleep There is a need for more evidence-based research to conclude whether gabapentin for sleep is safe for long-term use as a sleep medication. The dosage of Gabapentin prescribed by doctors to treat the sleep disorder insomnia and improve overall sleep quality is generally between 100-400 mg. Gabapentin for primary insomnia will help you fall asleep quickly and even enjoy deep sleep for long hours. Most doctors prescribe around 100-400 milligrams of gabapentin medication to help those with sleep disorders. This gabapentin maximum dosage for sleep has to be taken once per day just before you go to bed. Gabapentin, an α 2 δ subunit ligand of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels, is indicated for the management of postherpetic neuralgia and restless legs syndrome, and as adjunctive therapy for partial seizures with and without secondary generalization (maximal dose: 600-1800 mg/day depending on indication and gabapentin formulation). 8 –10 Determining the Right Dose for Sleep. When it comes to using gabapentin for sleep, finding the right dose is crucial. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate your individual needs and suggest the appropriate dosage. Generally, a low to moderate dose of gabapentin is prescribed for sleep-related issues. Gabapentin is one sleep aid that’s available and can help many people achieve deeper and more restorative sleep. But for some, the risks outweigh the benefits. If you have a history of any of the following, please be sure to tell your doctor before starting a prescription: Gabapentin and sleep. Most studies show that gabapentin improves slow wave sleep (“deep sleep”) and total sleep time. Two small studies showed that gabapentin may help people with primary insomnia and occasional sleep disturbance improve total sleep time and wakefulness in the morning. Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin can attenuate insomnia, bolster sleep quality, and increase total sleep duration. Moreover, gabapentin has been shown to increase slow-wave sleep (SWS), promote sleep maintenance, and decrease unwanted awakenings throughout the night. When it comes to using gabapentin for sleep, determining the right dosage is crucial for maximizing benefits while minimizing potential side effects. The typical dosage range for sleep can vary widely, but most studies have used doses between 300mg and 600mg taken before bedtime. The optimal use of gabapentin for sleep involves careful consideration of timing, dosage, and integration with good sleep hygiene practices. Typically, taking gabapentin 1-2 hours before bedtime allows for its sleep-promoting effects to align with the desired sleep onset. Most doctors will prescribe between 100mg and 400mg of gabapentin for insomnia. Typically, a doctor will start you off with the lowest possible dose and then gradually increase it, as needed. When used for insomnia, gabapentin should be taken once a day shortly before bed. Always take it as directed by your doctor. Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous arousal. The results suggest that gabapentin may be beneficial in the treatment of primary insomnia. We found that regardless the type of sleep outcomes, gabapentin displayed stable treatment efficacy for sleep disturbance in patients with medical illness. However, when an average dose of approximately 1,800 mg/day was used, the risk of treatment discontinuation or drug withdrawal was relatively high. The initial dose of gabapentin was 300 or 600 mg/day; after the dose-increasing phase, the minimum dose was 600 mg/day and the maximum dose was 3,600 mg/day, with an average dose of 1,793.92 mg/day. Figure 1 presents the screening process used in the study, Table 1 lists the main characteristics of all included trials. A study of over 350 people with occasional insomnia found that taking gabapentin 250 mg and 500 mg doses increased the amount of time people slept. The 500 mg dosage helped people sleep for longer than the 250 mg dosage. But neither dosage shortened the amount of time it took to fall asleep. The appropriate dosage of gabapentin for sleep disorders and anxiety can vary significantly depending on the individual and the specific condition being treated. It’s crucial to emphasize that gabapentin should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as improper dosing can lead to suboptimal results or increased side
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |