Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 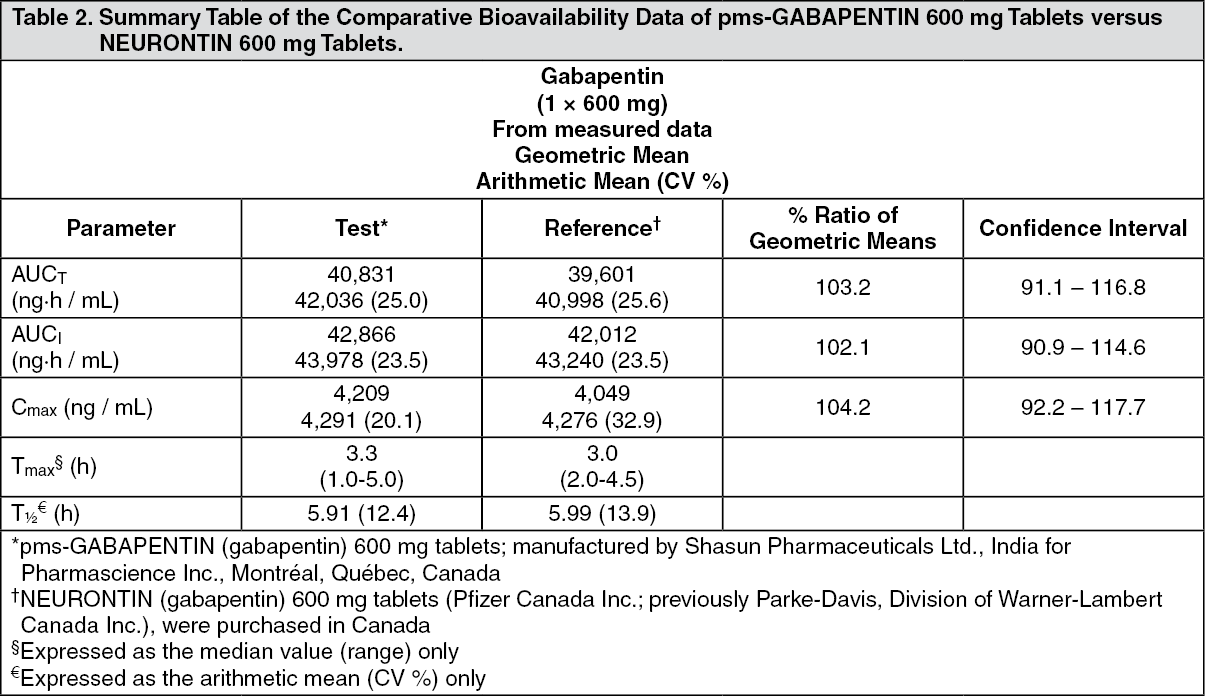 |
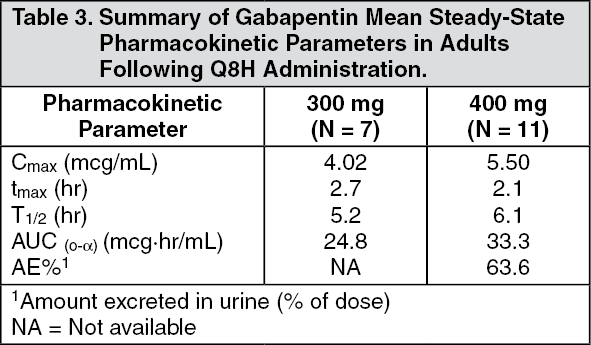
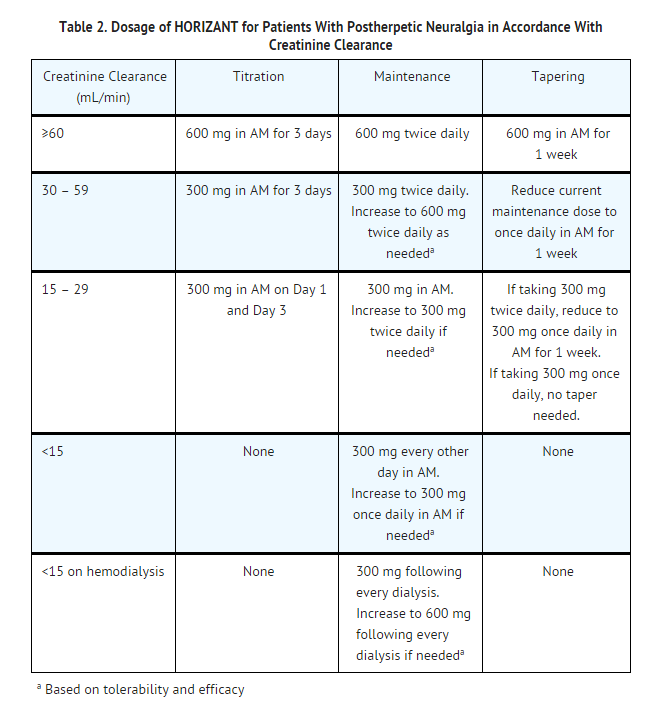
what is the mechanism of action of gabapentin enacarbil? Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin that is absorbed throughout the entire GI tract. The ability of gabapentin enacarbil to be absorbed in the large intestine differs from traditional gabapentin and contributes to its long-acting nature. Mechanism of action. Although the exact mechanism of action of gabapentin in RLS and PHN is unknown, it is presumed to involve the descending noradrenergic system, resulting in the activation of spinal alpha2-adrenergic receptors. Find patient medical information for Horizant (gabapentin enacarbil) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin, and its therapeutic effects are attributed to gabapentin, for which the precise mechanism of action in RLS is unknown . Gabapentin is structurally related to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GBP has been effective for RLS sufferers however its use remains questionable due to an unknown underlying mechanism of action and several pharmacokinetic limitations, including an unpredictable bioavailability and limited half-life. Mechanism of Action . Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin. In vitro studies have shown that gabapentin binds with high affinity to the α2gamma Multiple mechanisms of action have been postulated, including combined increased GABA synthesis, non-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonism, and an inhibitory action at the voltage gated calcium channel (α 2 δ subunit). Action of Gp has been demonstrated at spinal, supraspinal, and peripheral sites. Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin. Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. High affinity gabapentin binding sites have been located throughout the brain; these sites correspond to the Gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant (ER) (U.S. Tooltip United States), Regnite (in Japan)) is an anticonvulsant and analgesic drug of the gabapentinoid class, and a prodrug to gabapentin. [1] It was designed for increased oral bioavailability over gabapentin, [ 2 ] [ 3 ] and human trials showed it to produce extended release of gabapentin with Gabapentin is available in 2 forms—gabapentin immediate release and the prodrug gabapentin enacarbil. Gabapentin is available in tablet form with strengths of 600 mg and 800 mg, capsules in strengths of 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg, as well as an oral solution of 250 mg/5mL. Gabapentin enacarbil is available in 300 mg extended-release tablets. Gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant®) is a prodrug of gabapentin which binds with high affinity to the α2δ subunit of voltage-activated calcium channels in vitro studies. It is unknown how the binding of gabapentin enacarbil (GEn) to the α2δ subunit corresponds to the treatment of restless leg syndrome (RLS) symptoms. Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is The mechanism of action of gabapentin in treating restless leg syndrome or postherpatic neuralgia is not known. Gabapentin structurally resembles the neurotransmitter, gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin structurally resembles the neurotransmitter, gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). After years of uncertainty, it now appears that the mechanism of action of gabapentin is inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels containing the α 2 δ subunit (Sills, 2006). Two agents from this class, pregabalin (Sommer et al., 2007) and gabapentin enacarbil (Kushida et al., 2009), are under investigation as treatments for RLS. Mechanism of Injury. Gabapentin enacarbil is hydrolyzed to gabapentin in the gastrointestinal tract. Gabapentin itself undergoes little subsequent metabolism and is excreted in the urine unchanged. Gabapentin and gabapentin enacarbil do not induce or inhibit the drug metabolizing, microsomal cytochrome P450 enzymes. 12.1 Mechanism of Action 12.3 Pharmacokinetics . 12.6 Cardiac Electrophysiology . 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY . 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility . 14 CLINICAL STUDIES . 14.1 Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) 12-Week Pivotal Studies 14.2 Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN) 12-Week Study 14.3 Effects on Driving Gabapentin is available in two extended-release formulations in addition to the immediate release: a gastric retentive formulation (GBP-GR) and a gastro-retentive prodrug gabapentin enacarbil that are approved for the management of postherpetic neuralgia. The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin in the management of restless legs syndrome (RLS) has been evaluated in small controlled trials, demonstrating benefits compared with placebo. Gabapentin enacarbil is FDA-approved for the treatment of RLS Garcia-Borreguero 2002, Saletu 2010. The . Social anxiety disorder, adjunct to antidepressants or monotherapy (alternative agent)c
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |