Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
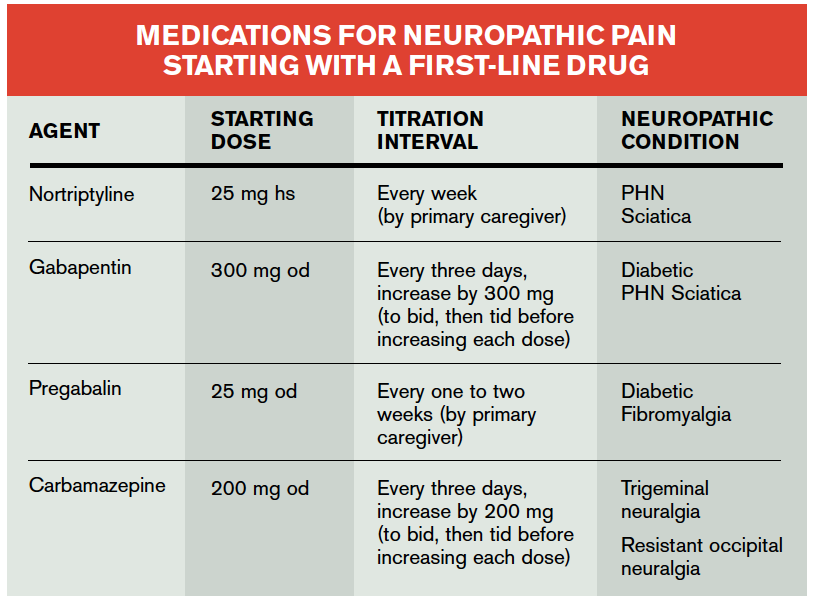
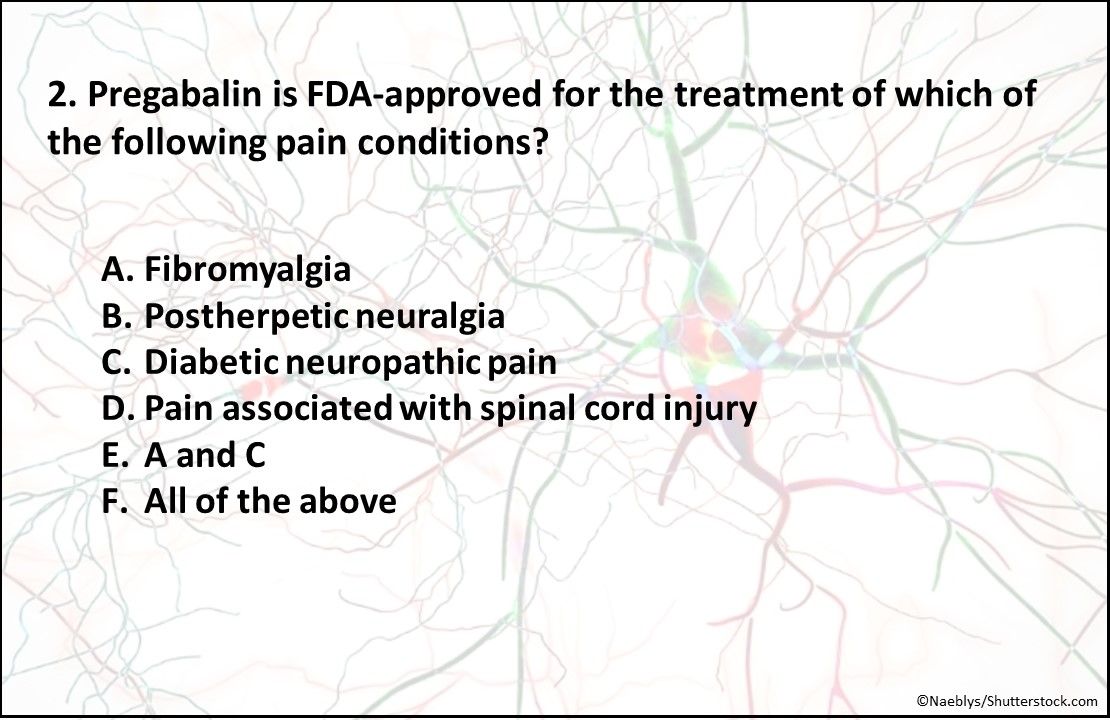
In particular, gabapentin prevents pain-related responses in several models of neuropathic pain in rats or mice (e.g. spinal nerve ligation models, streptozocin-induced diabetes model, spinal In 1993, the FDA approval of Neurontin, the original branded gabapentin, was for use as an adjunctive medication to control partial seizures. 9 Over the next several years, the manufacturer, Parke-Davis, a subsidiary of Warner-Lambert, engaged in a large marketing campaign to increase off-label prescribing of Neurontin for pain. 4 By the mid The authors concluded that gabapentin is associated with reduction in acute pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (the later indication is not approved by the FDA), and that there is limited evidence to support the use of gabapentin for other types of neuropathic pain and pain disorders. 1 This Editorial Gabapentin is FDA-approved for epilepsy and neuropathic pain caused by shingles, but is often prescribed off-label for depression, ADHD, migraine, fibromyalgia, bipolar disorder and postoperative pain. Gabapentin was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of seizures in 1993 and was subsequently approved for one pain indication, postherpetic Listen to an audio podcast of the December 19, 2019 FDA Drug Safety Communication warning that serious breathing difficulties may occur in patients using seizure and nerve pain medicines Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and is used to treat: postherpetic neuralgia, a nerve pain caused by the shingles virus (herpes zoster), FDA is warning that serious breathing difficulties may occur in patients using gabapentin or FDA-approved to treat a variety of conditions including partial seizures and nerve pain from spinal 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or Gabapentin is FDA approved for pain management of a limited number of neuropathic pain conditions; Gabapentin is widely used off-label for various chronic pain conditions and for the treatment of acute pain, making it now one of the most commonly described analgesic drugs Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Originally approved by the FDA for epilepsy in 1993, gabapentin was reviewed for a supplemental pain indication in 2001. Five trials with 1357 participants were submitted by Parke Davis and Pfizer and reviewed by the FDA for an indication of broad neuropathic pain. Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved for a variety of conditions, including seizures, nerve pain, and restless legs syndrome. Gabapentinoids are FDA-approved to treat a variety of Gabapentin is a prescription medication approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of neuropathic pain and epileptic disorders. This drug is currently marketed in capsule, tablet, and oral solution formulations. In recent years, however, gabapentin has been increasingly encountered by law enforcement, •Peripheral neuropathic pain may be chronic, therefore, a long-term plan to maximize quality of life is important – E.g., consider long-term adverse events of treatment Accordingly, the United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has permitted gabapentin treatment for postherpetic neuralgia, while pregabalin is approved for postherpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain associated with diabetes or spinal cord injury, and fibromyalgia [2]. Limited evidence suggests the possible use of gabapentin for neuropathic pain associated with Parkinsonism. Gabapentin has also been used off-label for antipsychotic-induced akathisia; propranolol is typically considered the first-line treatment. Pregabalin has got FDA approval for the management of neuropathic pain, whereas gabapentin has not. A systematic review of 83 RCTs have observed that amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, pregabalin and venlafaxine have the best available evidence as monotherapy, and oxycodone has the best available evidence as add-on therapy for the Oral gabapentin dosed at 1,200 mg or more daily demonstrated a 50% reduction in pain intensity, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of eight for postherpetic neuralgia and an NNT of six for Even with sufficient data supporting the use of gabapentin in the treatment of various neuropathic pain conditions, gabapentin only has Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for PHN. Dosing recommendations for off-label use of gabapentin can be somewhat ambiguous, if a recommendation exists at all.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |