Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
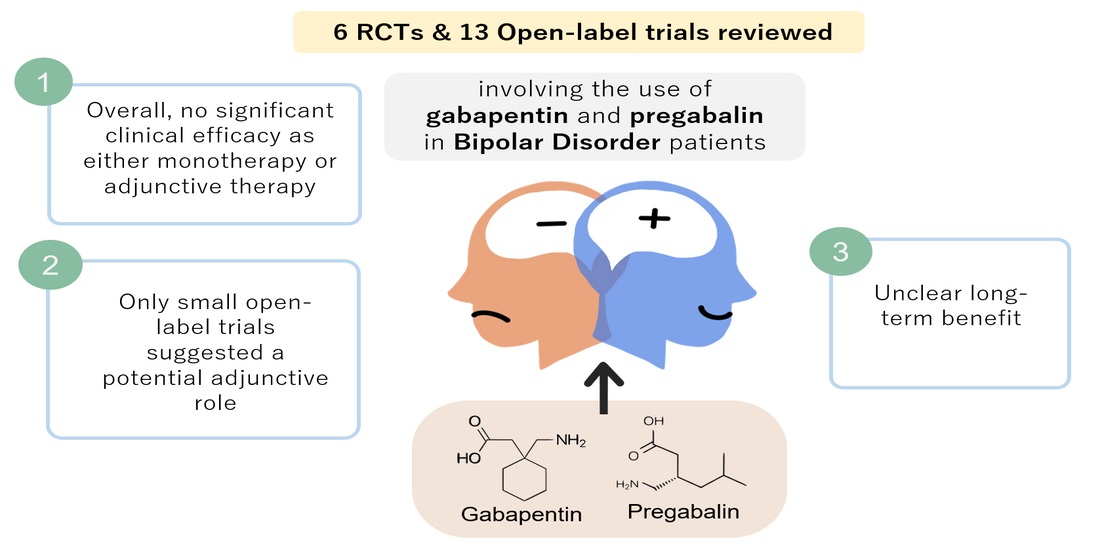
There’s good evidence that gabapentin is helpful for certain types of nerve pain and anxiety. But what about bipolar disorder? Not so much. The truth is, according to research studies, gabapentin is not an effective treatment for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. 2002: In one study analyzing the efficacy of Gabapentin as an adjunct treatment for bipolar disorder, it was discovered that improvements were most notable on anxiety-somatization measures of the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D). Results of the study suggest that those with bipolar disorder who attained the most benefit from Gabapentin is a prescription drug or medication that is FDA-approved to treat nerve pain and seizure disorders. It also has other uses—including treating anxiety disorders—though it has not been FDA-approved to be used for this purpose. The drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are sometimes prescribed for people with bipolar disorder or insomnia. Research found little evidence that they are effective. The drugs have side effects and can be addictive; the team calls for further trials. Gabapentin and pregabalin (collectively known as gabapentinoids) are licensed in the UK to treat pain and seizures. Gabapentin appears to have some benefit for anxiety disorders but failed to show benefit in bipolar disorder trials. In the individual patient with a mixed psychiatric disorder, benefits are most likely due to anxiolytic effects. Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly We conclude that there is moderate evidence of the efficacy of gabapentinoids in anxiety states, but minimal evidence in bipolar disorder and insomnia and they should be used for these The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α<sub>2</sub>δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric indications, and there is increasing concern abou Two new anticonvulsants, lamotrigine and gabapentin, have been used increasingly for bipolar disorder in the past several years. Despite this array of options, bipolar disorder remains a difficult disorder to treat. Some subtypes, such as those characterized by rapid cycling or mixed episodes, have been especially resistant to lithium treatment. "I have bipolar disorder, chronic depression, and anxiety, and gabapentin has helped tremendously without the use of other narcotic medicines. Yeah, it makes you feel a little loopy for the first few weeks, but after that, it does a wonderful job calming the nerves. The lifetime prevalence of anxiety disorders is 45% when BD is present; patients with BD are 3 to 7 times more likely to meet criteria for diagnosis of an anxiety disorder than the general population.1,2 Panic, posttraumatic stress (PTSD), and generalized anxiety disorders (GAD) are the most common (13% to 60%), followed by obsessive compulsive We conclude that there is moderate evidence of the efficacy of gabapentinoids in anxiety states, but minimal evidence in bipolar disorder and insomnia and they should be used for these disorders Multiple RCTs have shown gabapentin to be ineffective for bipolar disorder. There is insufficient evidence to recommend the use of gabapentin for MDD, GAD, PTSD, or OCD. There is sufficient evidence to consider the use of gabapentin for social anxiety disorder and, potentially, severe panic disorder after other treatment options have failed. A recent survey using the US-based TriNetX electronic health records network showed that gabapentin had been prescribed at least once in 13.6% of patients with bipolar disorder (BD), 11.5% with anxiety disorders, and 12.7% with insomnia disorder; for pregabalin, the figures were 2.9%, 2.6%, 3.0% respectively (PJH, unpublished observations). Results: The 40 open-label studies and two of the controlled trials suggested that GBP may have a role as adjunctive agent in the treatment of patients with bipolar disorders particularly when complicated by co-morbid anxiety disorder or substance abuse. GBP is usually very well tolerated and has no pharmacological interference with other mood Abstract. Despite its prevalence and disease burden, several chasms still exist with regard to the pharmacotherapy of bipolar disorder (BD). Polypharmacy is commonly encountered as a significant proportion of patients remain symptomatic, and the management of the depressive phase of the illness is a particular challenge. Results: Gabapentin may have benefit for some anxiety disorders, although there are no studies for generalized anxiety disorder. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. Neurontin - also known as Gabapentin - is a drug that is sometimes prescribed to those who experience anxiety especially in situations where the anxiety is co-occurring with bipolar disorder. This article explores the usage of Neurontin, as well as the benefits, weaknesses, and side effects for those looking to learn more about this medication We conclude that there is moderate evidence of the ef cacy of gabapentinoids in anxiety states, but fi minimal evidence in bipolar disorder and insomnia and they should be used for these
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |