Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
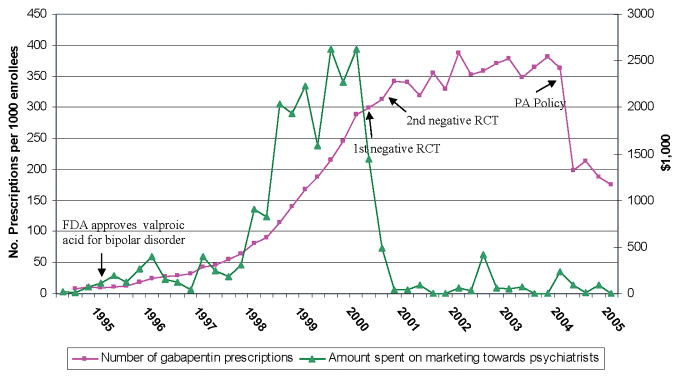
Researchers found that gabapentin does not help people with bipolar disorder. Learn more about the history of why some doctors prescribe gabapentin for bipolar as an adjunct therapy, even though there’s no evidence that it works for bipolar treatment or maintenance. Despite of the lack of evidence, reviews of gabapentin prescribing patterns in the United States show that this medication is still being used with alarming frequency for bipolar disorder. There are now five medications with specific, FDA approval for acute bipolar depression. A systematic search strategy employing different combinations of the keywords (bipolar, mania, hypomania, gabapentin, neurontin, gralise, gabarone, fanatrex, pregabalin, lyrica) was developed and performed in five databases namely OVID Medline, PubMed, ProQuest, PsychInfo and ScienceDirect from database inception to 7 June 2021. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. While gabapentin is frequently used in practice for a wide array of psychiatric diagnoses, its use is evidence-based for only a few indications. Multiple RCTs have shown gabapentin to be ineffective for bipolar disorder. There is insufficient evidence to recommend the use of gabapentin for MDD, GAD, PTSD, or OCD. If you've received a bipolar disorder diagnosis or were just prescribed a new medication, you may wonder what mood stabilizers are and if they have any side effects. gabapentin (Neurontin Gabapentin appears to have acute anti-manic and anti-depressant properties as an adjunctive agent for refractory bipolar illness. Prospective double-blind studies are needed to further delineate its acute efficacy when used as monotherapy and its prophylactic efficacy as monotherapy or in conjuction We identified 40 open-label studies on the use of GBP in at least 600 patients with bipolar disorder (BP), manic, depressed, or mixed episodes and unipolar depression and four controlled studies. is more gabapentin prescribed for bi-polar disorder than lamotrigine, even though there is little compelling evi-dence for gabapentin’s efficacy in bipolar disorder and the FDA has approved lamotrigine for the treat-ment of bipolar disorder.1,2 Thus, up to half of bipolar patients receiving combination therapy are given anti- There are claims that gabapentin was successful in helping with rapid cycling and mixed bipolar states in people who have not received relief from valproate or carbamazepine. Flowchart of included and excluded studies. Bipolar disorder (BD) Four DB-RCTs investigating the efficacy of gabapentin in BD were identified. 101 patients were randomised to receive gabapentin, 81 to placebo, 30 to lamotrigine and 19 to carbamazepine. Lithium and gabapentin. Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). The advantages of gabapentin include the lack of interactions with other drugs in the cytochrome P450 system and the lack of protein binding . Since there For bipolar disorder, four double-blind RCTs investigating gabapentin, and no double-blind RCTs investigating pregabalin, were identified. A quantitative synthesis could not be performed Gabapentin has an average rating of 8.5 out of 10 from a total of 138 reviews for the off-label treatment of Bipolar Disorder. 81% of reviewers reported a positive experience, while 9% reported a negative experience. 8.5 average rating out of 10. 138 ratings from 144 user reviews. Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. The use of gabapentin in bipolar disorder (BPD) treatment provides an informative case of off-label uptake and abandonment of a new medication. Gabapentin was patented by Warner-Lambert in 1977 and FDA-approved in December1993 for the adjunctive treatment of epilepsy and in 2002 for postherpetic neuralgia (see Appendix 1 for timeline). For bipolar disorder, four double-blind RCTs investigating gabapentin, and no double-blind RCTs investigating pregabalin, were identified. A quantitative synthesis could not be performed due to heterogeneity in the study population, design and outcome measures. A psychiatrist answers common questions about mood stabilizers for bipolar depression. Other medications, like topiramate (Topamax) or gabapentin (Neurontin), may be prescribed in some cases Gabapentin for Bipolar Disorder Reviews Understanding the Connection. Gabapentin, a medication commonly used to treat seizures and nerve pain, has been explored for its potential in managing symptoms of Bipolar Disorder. Some research suggests that Gabapentin may have a role in stabilizing mood and reducing symptoms of mania or depression.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |