Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |
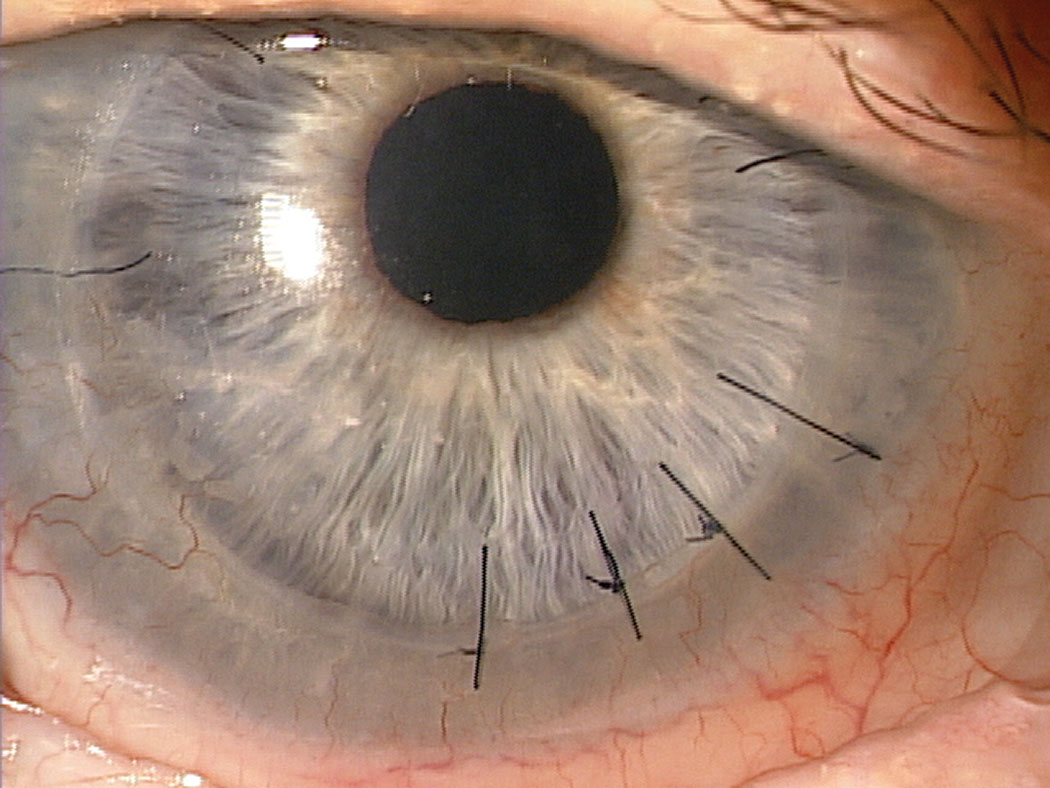
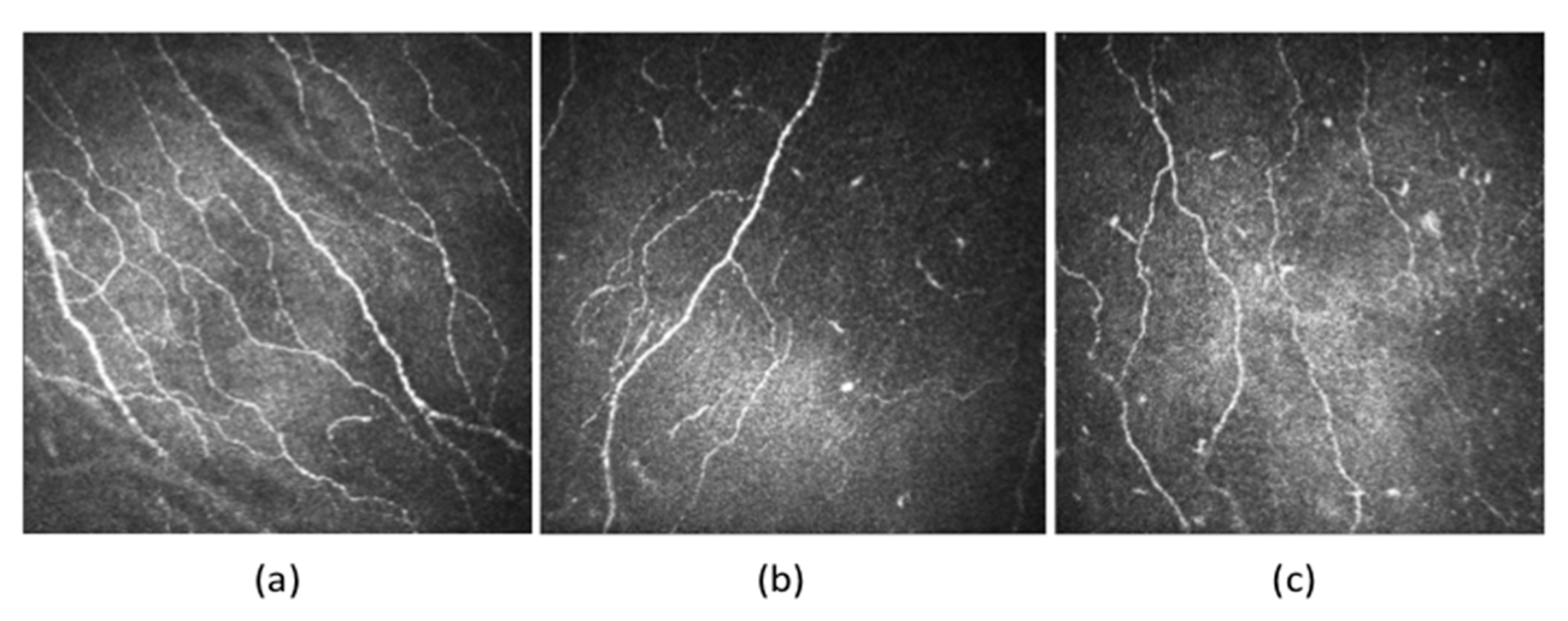
Triggers that lead to corneal nerve damage result in corneal neuropathy. Damage to nerves during refractive surgeries, ocular surface diseases such as chronic dry eye disease, recurrent corneal erosions, corneal neuropathic infections such as herpetic simplex and zoster, systemic neuropathic conditions such as diabetes, exposure to topical and systemic drugs, radiation keratopathy and 8. Aggarwal S, Kheirkhah A, Cavalcanti BM. Autologous serum tears for treatment of photoallodynia in patients with corneal neuropathy: Efficacy and evaluation with in vivo confocal microscopy. Ocul Surf 2015; 13:3:250-62. 9. Aggarwal S, Colon C, Kheirkhah A, Hamrah P. Efficacy of autologous serum tears for treatment of neuropathic corneal pain. Treatment might warrant other systemic anticonvulsants, like gabapentin, pregabalin or carbamazepine. But their effectiveness can be sporadic. Dr. Pflugfelder agreed. Gabapentin and similar drugs may be used to blunt sensory nerve stimulation or the perception of nerve stimulation, but it doesn’t always work and it has side effects. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines neuropathic pain as “pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction of the nervous system.” 1 The diagnosis of neuropathic pain requires confirmation of injury or disease affecting somatosensory pathways of the peripheral and/or central nervous systems (CNS). 2 Gabapentin is a potent blocker of nerve sensitization used to treat epilepsy and post-herpetic neuralgia; a related formulation (pregabalin) treats peripheral neuropathy. The research team from Korea found that this treatment may be even more effective in patients who have more severe corneal staining scores and no prior history of ocular These findings propose hypersensitivity within the corneal somatosensory pathways in patients with severe dry eye and ocular pain complaints as underlying pathology . In our study, first time in literature, we used gabapentin to ameliorate symptoms of neuropathic ocular pain in DED. Gabapentin and pregabalin, both originally designed as anticonvulsants are widely used as single agents for the treatment of diabetic neuralgia, PHN, and central neuropathic pain. 116,130,131 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the key inhibitory neuro-transmitter in the In a case series that included 8 patients, gabapentin was commenced at 300 mg orally daily and increased to 600–900 mg three times a day and pregabalin was commenced at 75 mg daily and increased Oral gabapentin is a first-line treatment for chronic systemic neuropathic pain. Although it has been used for ocular discomfort after refractive surgery and in severe, painful dry eye syndrome (DES), it can depress the central nervous system. Corneal neuropathic pain results from dysfunctional nerves causing perceptions such as burning, stinging, eye-ache and pain. Various inflammatory diseases, neurological diseases, and surgical interventions can be the underlying cause of corneal neuropathic pain. This is, to our knowledge, the first systematic review to investigate the efficacy and safety of therapies for corneal neuropathy. The primary aims were to: (i) extract the definitions, or other relevant information, used to define corneal neuropathy (and/or corneal neuropathic pain) in the study populations; (ii) summarize and synthesize data, including information about the outcome measures I have corneal neuropathy. Did anyone notice that their nerve pain got worse before better? I’ve been on Gabapentin for three days and have noticed each day that the pain has worsened, if anything, rather than improved. Just wondering how long to give the medicine a shot at turning things around as I’m scared of it worsening my pain The perception of neuropathic corneal pain (NCP), also called corneal neuralgia, corneal allodynia, keratoneuralgia, corneal neuropathy, or, more generally, ocular pain [5,6,7,8], can be highly A recent study reported that oral gabapentin may be able to successfully treat DED patients with neuropathic ocular pain—as opposed to pain mainly caused by mechanical and chemical influences—who have systemic comorbidities, including rheumatological, neurological and psychological disorders. Though Gabapentin remains well established as a first-line treatment for diabetic neuropathy, 14, 15 few randomized control studies have examined the utility of the drug in corneal neuropathic pain. 16 Ongun et al. showed a decrease in patient reported pain in a cohort of patients with chronic corneal neuropathic pain and dry eye disease Neuropathic pain is caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction of the nervous system and can occur in the cornea. However, neuropathic corneal pain (NCP) is currently an ill-defined disease. Patients with NCP are extremely challenging to manage, and evidence-based clinical recommendations for the management of patients with NCP are scarce. The objectives of this review are to provide guidelines of gabapentin falls from 60% to 33% as the total daily dosage increase from 900mg to 3600 mg. For safety reasons the Nottinghamshire APC guideline recommends that the maximum daily dose of gabapentin should NOT exceed 1800mg. Gabapentin in renal impairment (ref: Neurontin SPC): Creatinine Clearance (ml/min) Dose ≥80 300mg TDS to 600mg TDS Oral NSAIDs (e.g., diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen); antiepileptic agents (e.g., gabapentin and pregabalin), and analgesic antidepressants (e.g., duloxetine and nortriptyline) are good choices, according to Dr. Levitt. Ocular neuropathic pain, also called corneal neuralgia, is a spectrum of disorders of ocular pain which are caused by damage or disease affecting the nerves. Ocular neuropathic pain is frequently associated with damaged or dysfunctional corneal nerves, [ 1 ] but the condition can also be caused by peripheral or centralized sensitization. [ 2 ] Ocular neuropathic pain is a diagnosis of exclusion which refers to the heightened perception of pain in response to normally non-painful stimuli. It usually presents without any visible objective exam findings, making it extremely difficult to identify.[1] For this reason, it often gets misdiagnosed as dry eye disease.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |