Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pinched-nerve-headache-treatment-1719581-5c04ae4146e0fb0001cc1846.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
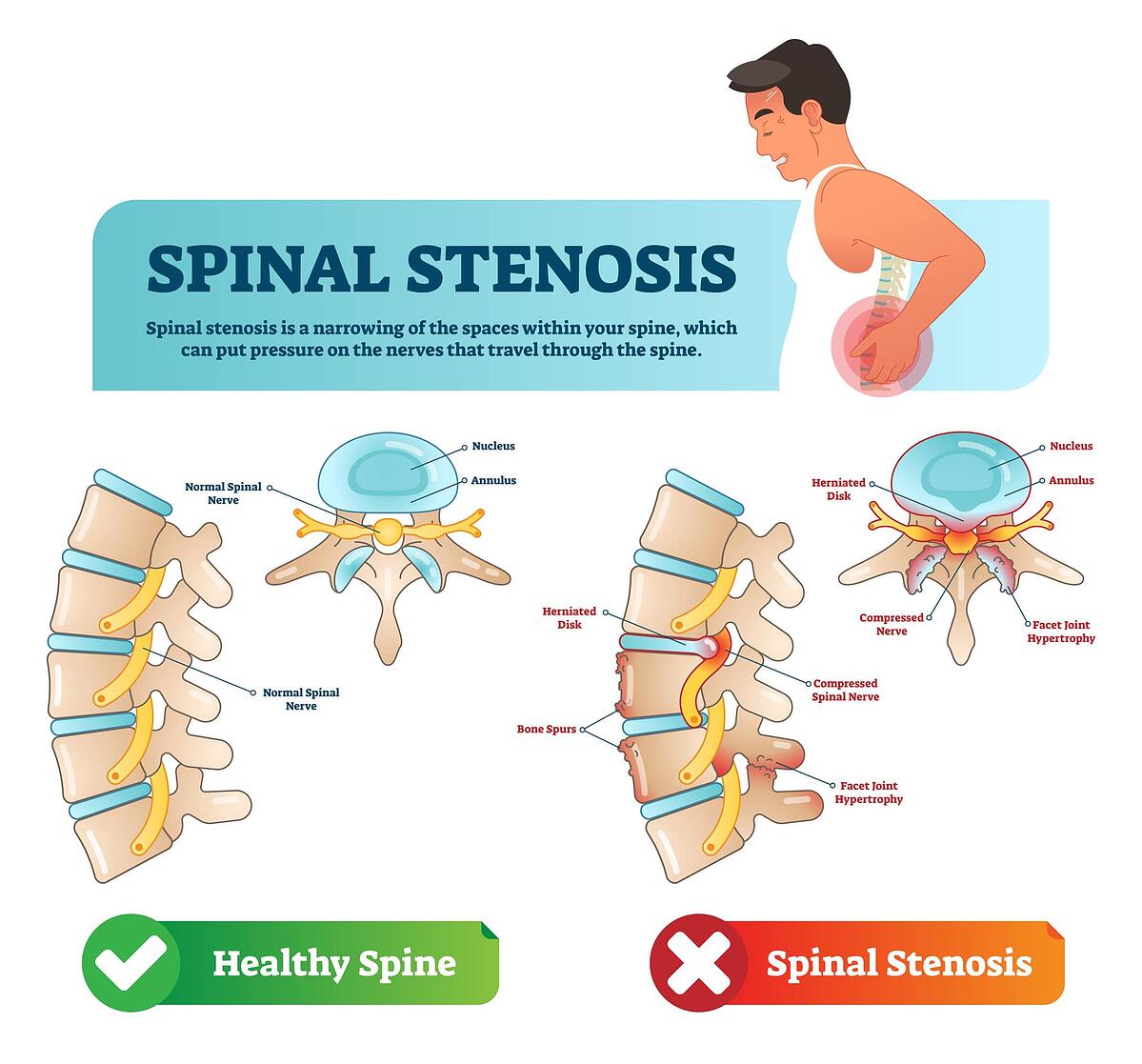
It is believed that gabapentin may reduce the release of inflammatory neuropeptides implicated in headache pain, such as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P; it could Gabapenten is more commonly used to treat nerve pain so using it to treat headache would be an off label use. 1. Identify gabapentin as a treatment option for post-dural puncture headache when other standard of care modalities have not been successful.2. Discuss advantages and disadvantages to using gabapentin in the treatment of post-dural puncture headache.A post-dural puncture headache (PDPH) is a common complication following trauma from spinal or epidural procedures. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Spinal stenosis is a degenerative condition typically seen in people over 60 that causes a narrowing of the lower spinal canal . Like spinal herniation, stenosis painfully pinches the nerves . Subjects in one study reported a significant improvement in their disk hernia pain after taking gabapentin for three months . The purpose of this report is to review the clinical evidence on the efficacy, safety and guidelines for use of gabapentin in adults with neuropathic pain, and to examine evidence on the misuse or abuse of gabapentin and other drugs for neuropathic pain. According to the 2018 definition by the International Headache Society (IHS), PDPH is a headache attributed to low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure occurring within 5 days of a lumbar puncture caused by CSF leakage through the dural puncture. 16 Headache is usually accompanied by neck stiffness and/or subjective hearing symptoms, remitting Gabapentin has been reported to be useful in the management of epilepsy, neuropathic pain and post-dural puncture headache. Seventeen obstetric cases are presented in which gabapentin was used either as a primary therapy for the management of severe headache following a diagnosed dural puncture or as an analgesic adjunct Objectives: To investigate the efficacy of treatment with gabapentin on the clinical symptoms and findings in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Summary of background data: LSS is a syndrome resulting from the narrowing of the lumbar nerve root canal, spinal canal, and intervertebral foramen, causing compression of the spinal cord. In this study, administration of gabapentin decreased the incidence and severity of post spinal anesthesia headache, postoperative pain and morphine consumption, without any significant differences in serious adverse effects. Lower back pain medication for severe spinal stenosis pain may include NSAIDs, antidepressants, anti-seizure medication, or corticosteroid shots. Medication can provide near-immediate relief from severe spinal stenosis pain, but may carry the risk of side effects and complications. NSAIDs; NSAIDs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are NSAIDs should be taken in the lowest effective doses to avoid side effects. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. Levendoglu F, Ogün CO, Ozerbil O, Ogün TC, Ugurlu H. Gabapentin is a first line drug for the treatment of neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury. Spine. 2004;29:743–751. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000112068.16108.3A. [Google Scholar] 14. Rekand T, Hagen EM, Gronning M. Chronic pain following spinal cord injury. Haghbin M. Therapeutic effect of propranolol on headache after spinal anesthesia. Pain 2012;150:63. [Google Scholar] Moghaddam 2011 {unpublished data only} Moghaddam MJ, Mirkheshti A, Yahyavi P. Comparison between analgesic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin in controlling delayed onset post dural puncture headache in non-pregnant patients. Gabapentin for spinal stenosis. Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the space between the bones of your back (vertebrae) and the spinal cord. This can happen as the spine collapses with age or from spine arthritis. As the space narrows, the bones or discs in the spine can compress the spinal cord and cause pain and nerve symptoms. We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. It is now considered to be an emergent treatment for pain syndrome. We delineate its pharmacological, laboratory and clinical profiles, with a review of the world literature. readmissions, timely consultation of the Pediatric Pain Service for performance of epidural blood patch, reduction of pain scores, and reduction in hospital length of stay. The protocol outlines a clinical continuum of care that begins upon identification of a patient with a post-dural puncture headache. The potential exists Neuropathic pain following an injury of the spinal cord can present above or below the level of injury. Symptoms include burning, tingling, or stabbing that is constant or intermittent. Patients may also experience hyperalgesia or allodynia in the same region [3] .
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pinched-nerve-headache-treatment-1719581-5c04ae4146e0fb0001cc1846.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |