Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
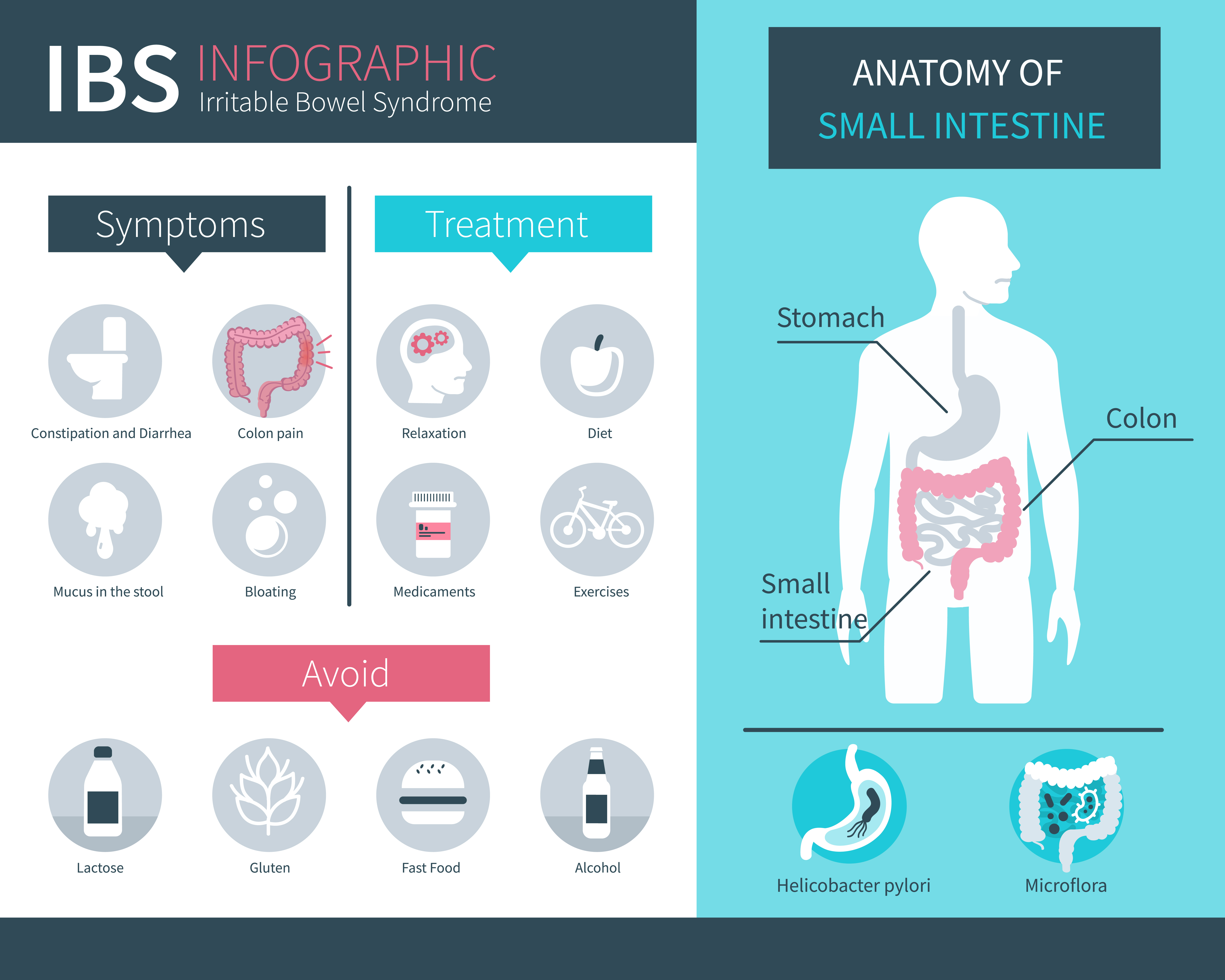
Anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs (Benzodiazepines, TCAs, SSRI and SNRI) can attenuate pain in IBS patients with relevant comorbidities. Clonidine, gabapentin and pregabalin can moderately improve IBS symptoms. Lubiprostone relieves constipation predominant IBS (IBS-C) while loperamide improves diarrhea predominant IBS (IBS-D). Our results of the present study showed that gabapentin attenuated rectal sensitivity to distension and raised rectal compliance, providing an evidence that it has a potential as a pharmacological agent for treatment of IBS. Duloxetine in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: an open-label pilot study. Hum Psychopharmacol 2009;24(5):423–428. [Google Scholar] 91. Kaplan A, Franzen MD, Nickell PV, Ransom D, Lebovitz PJ. An open-label trial of duloxetine in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and comorbid generalized anxiety disorder. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is associated with diverse pathophysiologic mechanisms. These mechanisms include increased abnormal colonic motility or transit, intestinal or colorectal sensation, increased colonic bile acid concentration, and superficial colonic mucosal inflammation, as well as epithelial barrier dysfunction, neurohormonal up-regulation, and activation of secretory processes Our results show that gabapentin reduces rectal sensory thresholds through attenuating rectal sensitivity to distension and enhancing rectal compliance in diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome patients. On the other hand, the evaluation of mean GI symptom scores obtained from GSRS questionnaire, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, indigestion, and reflux, showed that the two groups were matched in terms of the severity of GI symptoms mentioned, and there was no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05) However, during treatment (after the treatment relative to Context: Visceral pain is a leading symptom for patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) that affects 10% - 20 % of the world population. Conventional pharmacological treatments to manage IBS-related visceral pain is unsatisfactory. What is known and objective: The complexity and diversity of irritable bowel syndrome's (IBS) presentation make treatment difficult. Although there are reviews and guidelines for treating IBS, they focus on the efficacy of medications for IBS symptoms using high-priority endpoints, leaving those of lower priority largely unreported. For the purpose of treatment, IBS can be divided into four types, based on symptoms: constipation-predominant, diarrhea-predominant, mixed or unclassified. A healthcare professional also will likely explore whether you have other symptoms that might suggest another, more serious condition. How severe was Irritable bowel syndrome and when was it recovered: Irritable bowel syndrome in Gabapentin; Expand to all the drugs that have ingredients of gabapentin: Irritable bowel syndrome and drugs with ingredients of gabapentin (1,051 reports) More studies by gender and age: Female: 0-1 2-9 10-19 20-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 60+ Here we present the evidence supporting medication treatments for specific IBS symptoms, discuss evidence-based management of IBS with medications including dose regimens and adverse effects and review progress on research for new IBS treatments. Gabapentin is a medication that has been shown to be effective in treating Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) by reducing rectal mechanosensitivity and increasing rectal compliance. It is also used to relieve painful bowel spasms and treat diarrhea. Although all patients with IBS have symptoms of abdominal pain and disordered defecation, treatment needs to be individualized and should focus on the predominant symptom. This paper will review therapeutic options for the treatment of IBS using a tailored approach based on the predominant symptom. GABA agonists or analogues such as pregabalin or gabapentin could be useful for IBS treatment. As Zhang et al. proved, gabapentin improves pain and anxiety-like behaviours in mice, although the pharmacological use of this drug for the treatment of IBS should be limited due to its serious side effects (hepatotoxicity and neurotoxicity Summary: Currently, there is evidence to support improvements in specific IBS symptoms following treatment with loperamide, psyllium, bran, lubiprostone, linaclotide, amitriptyline, trimipramine, desipramine, citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, dicyclomine, peppermint oil, rifaximin, ketotifen, pregabalin, gabapentin and octreotide and there Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract of unknown etiology. Patients treated with gabapentin demonstrated Clonidine, gabapentin and pregabalin can moderately improve IBS symptoms. Lubiprostone relieves constipation predominant IBS (IBS-C) while loperamide improves diarrhea predominant IBS (IBS-D). Newer medications, such as alosetron, eluxadoline, rifaximin, lubiprostone, and linaclotide, can also help relieve symptoms. Always consult with your doctor to determine the most effective IBS treatment for your specific condition. The medications listed below are related to or used in the treatment of this condition. Activity ? Yes, Gabapentin can be used for the treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Many researchers have monitored the effects of gabapentin in the management of IBS and have observed positive results. What does research suggest? Overview of treatment options for abdominal pain in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). 5-ASA, 5-aminosalicylic acid; IBS, irritable bowel syndrome; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. (Courtesy of Dr. Douglas Drossman.)
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |