Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
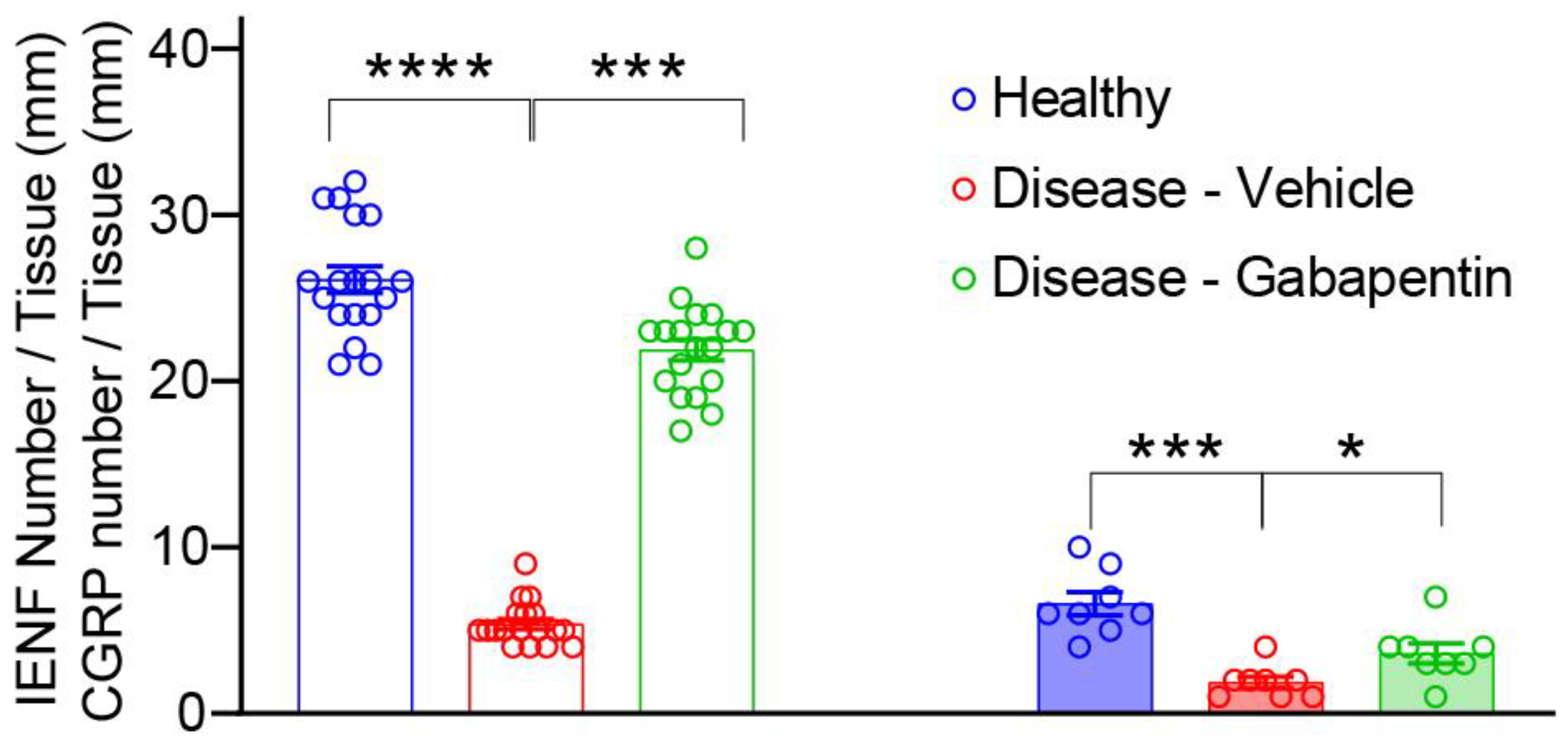 |  |
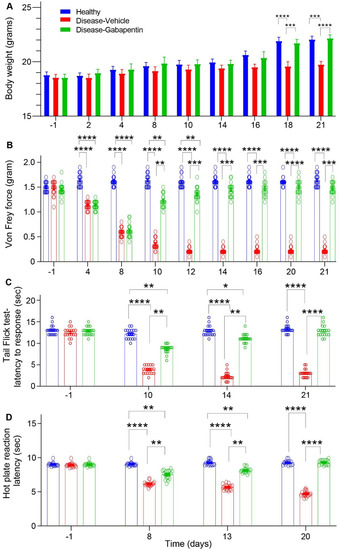
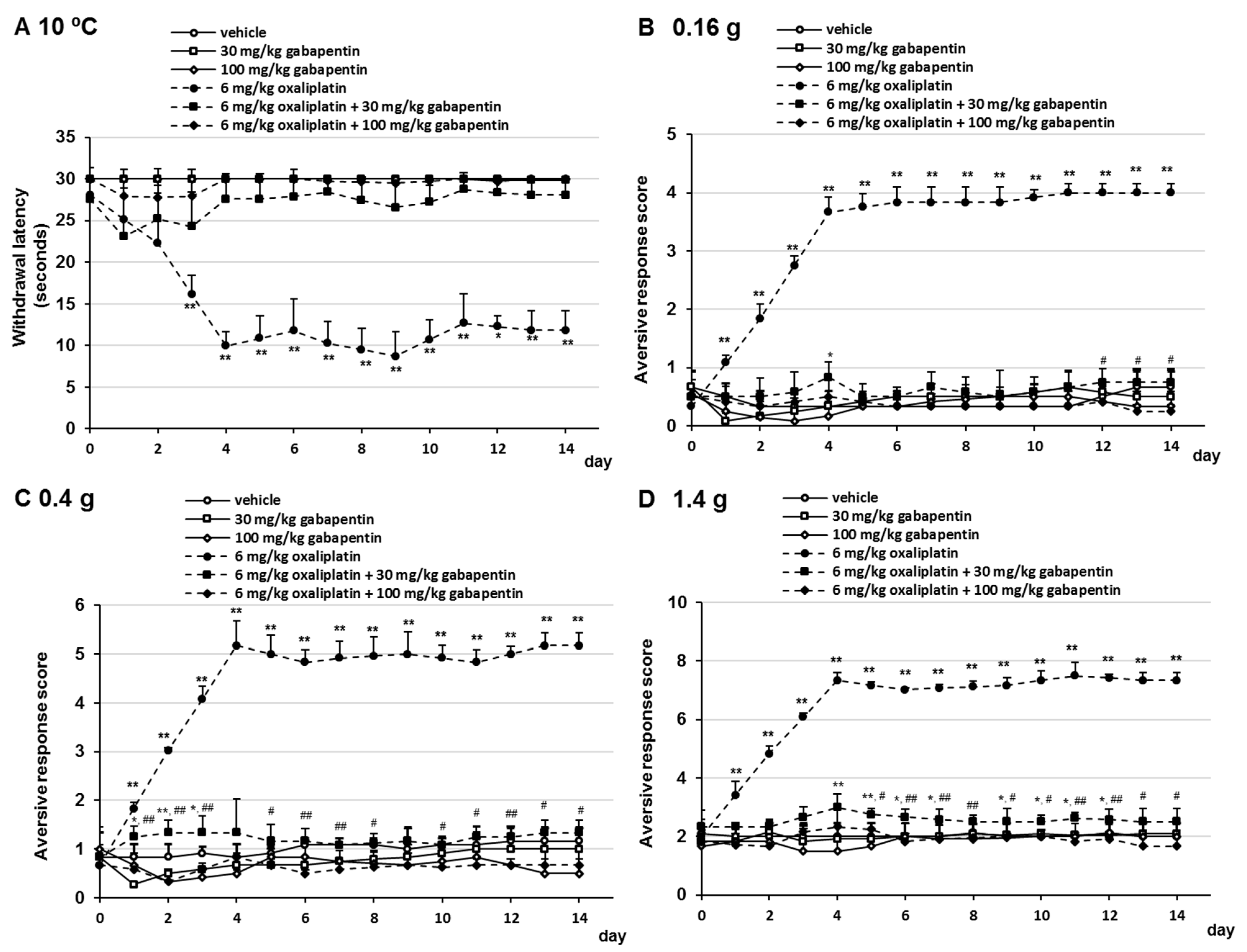
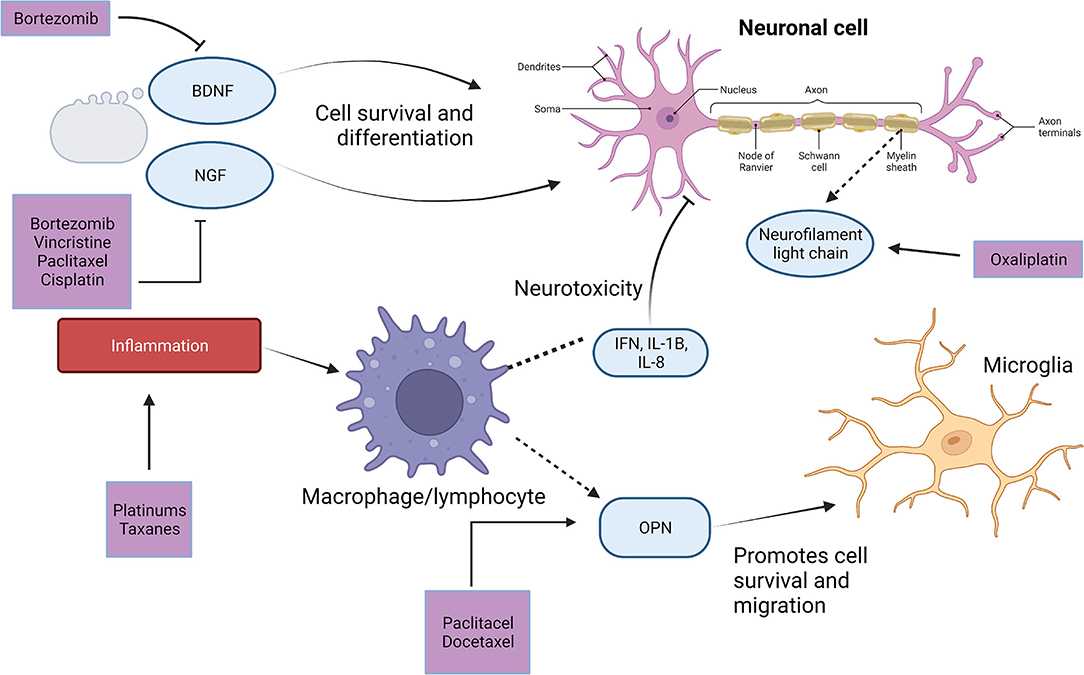
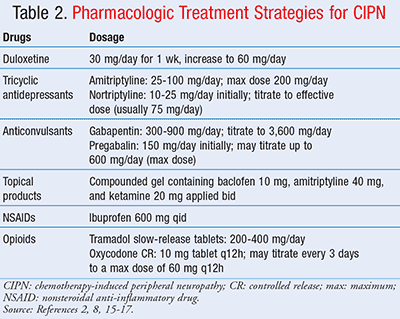
A powerful analgesic effect of both gabapentin and pregabalin on peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel and oxaliplation has been reported. However, gabapentin did not affect vinctistine-induced allodynia [ 51 , 52 ]. DIPN is often difficult to treat, however medications including duloxetine, and gabapentin are shown to reduce neuropathic pain. Advanced techniques of neuromodulation offer promise though further randomized and controlled studies are needed to confirm efficacy. The aim of our study was to assess the presence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in ovarian cancer patients treated with first-line paclitaxel and carboplatin chemotherapy and evaluate the effectiveness of gabapentin in treatment of this condition. Regarding gabapentin, research has demonstrated its efficacy in alleviating neuropathic pain in surgery-induced or trauma-induced peripheral neuropathy models in diabetic animals. Studies suggest that gabapentin reduces pain behavior and improves nerve function by modulating calcium channel activity and inhibiting excitatory neurotransmitter When peripheral neuropathy occurs due to chemotherapy treatment, it is referred to as chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Typically, symptoms are sensory rather than motor and include reduced feeling and heightened sensitivity to pressure, pain, temperature, and touch. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is one of the main dose-limiting side effects of neurotoxic anticancer drugs. The chemotherapy dose needs to be reduced or completely paused when CIPN develops. Rao RD, Michalak JC, Sloan JA, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin in the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial (N00C3). Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common toxicity associated with treatment with platinum-based agents, taxanes, vinca alkaloids, and other specific agents. The long-term consequences of this condition can result in decreased In addition, administration with gabapentin was improved paclitaxel-induced neuropathy symptoms, neuropathic pain, neurologic deficit, and quality of life in ovarian cancer patients . Our results showed that gabapentin and duloxetine prevented the development of oxaliplatin- and paclitaxel-induced neuropathy via inhibition of ERK1/2 activation Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common adverse effect of cancer therapy that can have a profound impact on quality of life and survivorship [1]. On the basis of these data, a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, randomized trial was conducted to evaluate the effect of gabapentin on symptoms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Alcohol-induced PN can be managed with antiseizure medication, which has an anticholinergic effect on the central and peripheral nervous systems and blocks the uptake of serotonin and norepinephrine to decrease pain perception. Gabapentin, pregabalin, and carbamazepine are commonly used to alleviate burning and stabbing dysesthesias. Compared with the control group, gabapentin therapy led to a statistically significant better response in patients of each baseline neurotoxicity group. Conclusions. Gabapentin monotherapy seems to be well tolerated and useful for the management of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. An ongoing phase III study is evaluating the efficacy of oral gabapentin in preventing paclitaxel-induced neuropathy.33 Some experts recommend integrated care approaches, such as acupuncture, exercise and scrambler therapy, for treatment and prevention. When peripheral neuropathy occurs due to chemotherapy treatment, it is referred to as chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Typically, symptoms are sensory rather than motor and include reduced feeling and heightened sensitivity to pressure, pain, temperature, and touch. Gabapentin, an antiepileptic drug that is structurally related to the neurotransmitter gamma- aminobutyric acid (GABA), has been shown to be effective in treating symptoms from several neuropathic syndromes. The combination of “chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy” and each of the following keywords were used to search for CIPN treatment: “calcium and magnesium”, “goshajinkigan”, “duloxetine”, “vitamin B12”, “pregabalin”, “gabapentin”, and “pancreatic cancer”. Introduction: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) affects patients' quality of life and treatment effectiveness. Gabapentinoids, like gabapentin and pregabalin, are often used for CIPN treatment, but their efficacy and safety remain uncertain. This study reviews and analyses randomised controlled trial data on this topic. In another study presented at ASCO (2005), 115 patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (for ≥ 1 month, with average pain rating of ≥ 4/10 or Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group [ECOG] sensory neuropathy ≥ 1/3) were randomized in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to either: gabapentin (target dose = 900 mg three Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy is a serious clinical problem caused by a substantial number of cytotoxic drugs, including taxanes, platinums, vinca alkaloids, epothilones, eribulin, and bortezomib; these drugs cause different pathologic insults to neurons.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |