Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
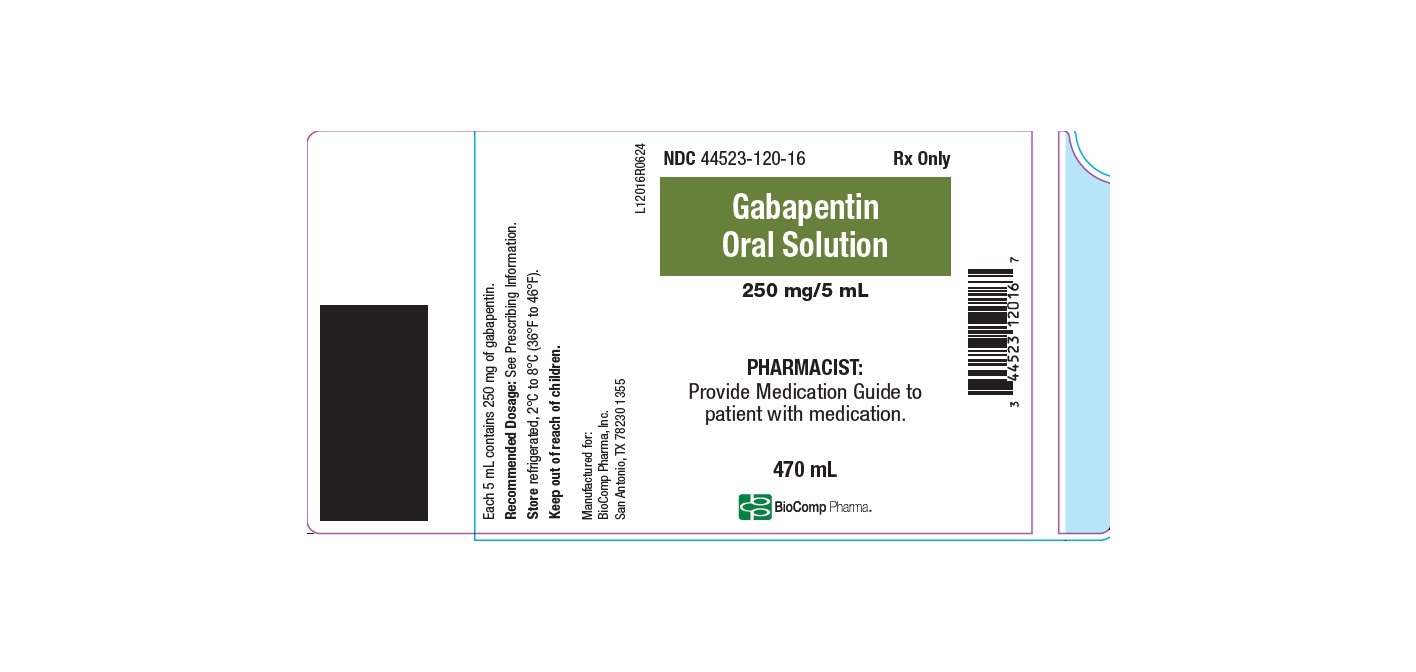
Gabapentin Oral Solution is a prescription medicine used to treat: •Pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults. •Partial seizures when taken together with other medicines in adults and children 3 years of age and older with seizures. Gabapentin Oral Solution is a prescription medicine used to treat: z Pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults. Gabapentin is taken by mouth and comes in capsule, tablet, and liquid form. Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin therapy may be initiated as a single 300-mg dose on Day 1, 600 mg/day on Day 2 (divided BID), and 900 mg/day on Day 3 (divided TID). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a daily dose of 1800 mg (divided TID). GABAPENTIN (GA ba pen tin) treats nerve pain. It may also be used to prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. It works by calming overactive nerves in your body. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an antiseizure medication. It’s also used for nerve pain from shingles. Other long-acting forms called Gralise and Horizant are also available. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. Gabapentin is an oral liquid medicine that’s used to treat Epilepsy. This page contains material targeted specifically to healthcare professionals based in the UK Login / Register Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). Use: Gabapentin oral suspension is used in the treatment of seizures, bipolar disorder, social phobia, and chronic pain. Packaging: Package in tight, light-resistant containers. Labeling: Shake well before taking. Stopping Gabapentin Oral Solution suddenly can cause serious problems. Gabapentin Oral Solution can cause serious side effects including: 1. Like other antiepileptic drugs, Gabapentin Oral Solution may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500. Neurontin and generic forms of Neurontin tablets may be broken into two pieces. You can take the second half for your next dose. Don't use the half-tablet beyond 28 days after the whole tablet was cut or broken. Carefully measure the liquid formulation of gabapentin using the measuring device that comes with the drug. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin oral solution may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Gabapentin oral solution is indicated for: Postherpetic neuralgia in adults ( 1) Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy ( 1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Postherpetic Neuralgia ( 2.1) Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Gabapentin oral solution is indicated for: • Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults - • Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |