Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
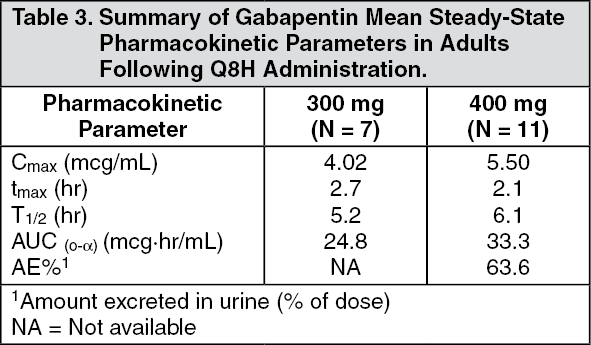
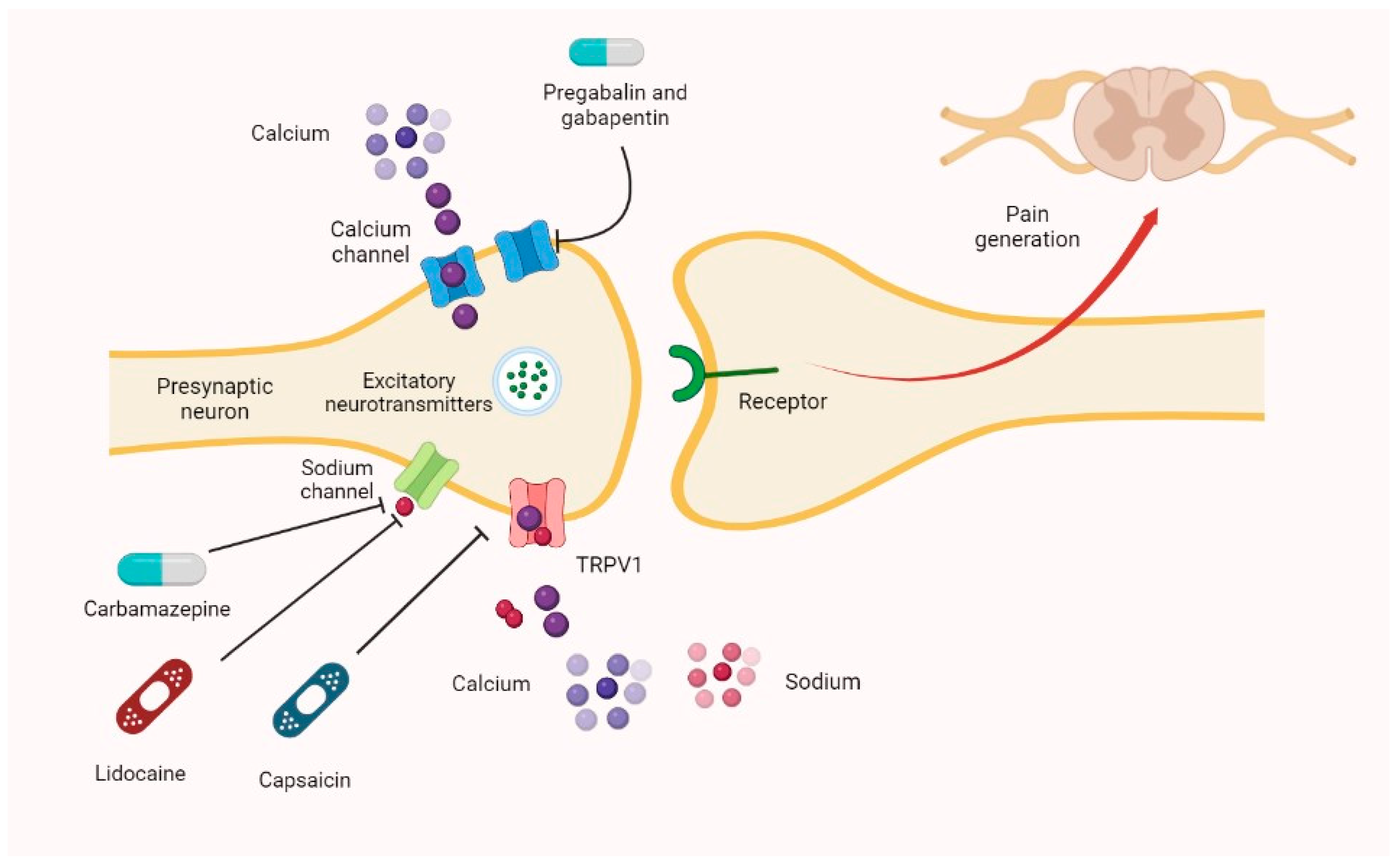
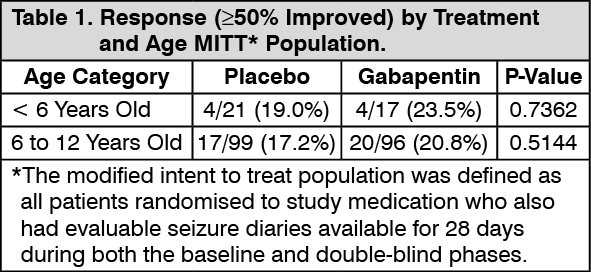
Gabapentin interacts with cortical neurons in the cerebral cortex at alpha 2-delta subunits of those voltage-gated calcium channel. By blocking these sites, Gabapentin is able to increase GABA synthesis. It does this by crossing lipid membrane barriers through system L-amino acid transporters. They bind to α2-δ calcium channels in the nervous system, reducing neurotransmitter release and decreasing pain sensation. Gabapentin is absorbed within 3 hours, has a 50% oral bioavailability, and is removed through renal excretion with a 5-9 hour half life. Pregabalin has similar mechanisms and indications as gabapentin but at lower doses. Gabapentin affects chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and some types of pain. The exact way that it works is unknown. Neurontin is used with other drugs in the treatment of some types of seizures and for the management of postherpetic neuralgia (nerve Gabapentin (Neurontin®) vs. Pregabalin (Lyrica ®) Similarities • Mechanism of action • Pharmacokinetics Differences • Pharmacokinetics – Absorption Di – Renal excretion – Dosing • Side effects • Easier to titrate pregabalin • Gabapentin is generic Bockbrader HN. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010;49:661-9. Gabapentin absorption 3600 It discusses drug mechanisms of action, classifications of seizures and epilepsy syndromes, and provides details on several newer drugs including their indications, mechanisms of action, dosing and side effects. These include drugs such as cannabidiol, everolimus, stiripentol, eslicarbazepine acetate, perampanel and brivaracetam. It discusses their mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses, side effects and interactions. It concludes with advice on properly diagnosing and treating epilepsy. ANTIEPILEPTIC_DRUGS in children amd usagepptx The mechanisms of the anti-allodynic effects of gabapentin proposed include: CNS effects (potentially at spinal cord or brain level) due to either enhanced inhibitory input of GABA-mediated pathways (and thus reducing excitatory input levels); antagonism of NMDA receptors; and antagonism of calcium channels in the CNS and inhibition of 2) It also discusses the mechanisms of action of barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and gabapentin as anti-convulsants. 3) For H1 and H2 receptor antagonists, it describes histamine receptors and classifications of H1 and H2 receptor antagonists. The document outlines metformin's mechanisms of action, pharmacological actions including its effects on weight, lipids, and insulin sensitivity, as well as its indications for treating conditions like diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome. It discusses: 1) Gabapentin's mechanism of action involves binding to voltage-gated calcium channels containing the alpha-2-delta-1 subunit, which may modulate the release of excitatory neurotransmitters involved in epilepsy and pain. 2) Gabapentin has variable oral bioavailability that is inversely related to dose due to saturable absorption. It discusses: 1) Gabapentin's mechanism of action involves binding to voltage-gated calcium channels containing the alpha-2-delta-1 subunit, which may modulate the release of excitatory neurotransmitters involved in epilepsy and pain. 2) Gabapentin has variable oral bioavailability that is inversely related to dose due to saturable absorption. Mechanism of Action Echinocandins exert their antifungal effects by selectively inhibiting the enzyme (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase, which is essential for the synthesis of β-glucan, a major component of the fungal cell wall. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The mechanisms of action are still unclear despite their widespread use. Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Results with human and rat brain NMR spectroscopy indicate that gabapentin increases GABA synthesis. It discusses gabapentin's mechanism of action, approved uses, dosing, pharmacokinetics, interactions, adverse effects and overdose treatment. It then summarizes a clinical study comparing the dose-response relationship of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with partial seizures, finding that pregabalin was more potent and effective at Title: Mechanism of action of Antiepileptic Drugs 1 Mechanism of action of Antiepileptic Drugs B. Gitanjali Gitanjali-1 2 Cellular Mechanisms of Seizure Generation. Excitation (too much) Ionic-inward Na, Ca currents ; Neurotransmitter glutamate, aspartate ; Inhibition (too little) Ionic-inward Cl outward K currents ; Neurotransmitter GABA This document summarizes information about the anti-seizure medications gabapentin and pregabalin. It discusses gabapentin's mechanism of action, approved uses, dosing, pharmacokinetics, interactions, adverse effects and overdose treatment. It discusses gabapentin's mechanism of action, approved uses, dosing, pharmacokinetics, interactions, adverse effects and overdose treatment. It then summarizes a clinical study comparing the dose-response relationship of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with partial seizures, finding that pregabalin was more potent and effective at This document discusses antiepileptic drugs, including their mechanisms of action, classifications, pharmacokinetics, indications, and adverse effects. It classifies antiepileptic drugs based on their actions on ion channels and neurotransmitter systems.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |