Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
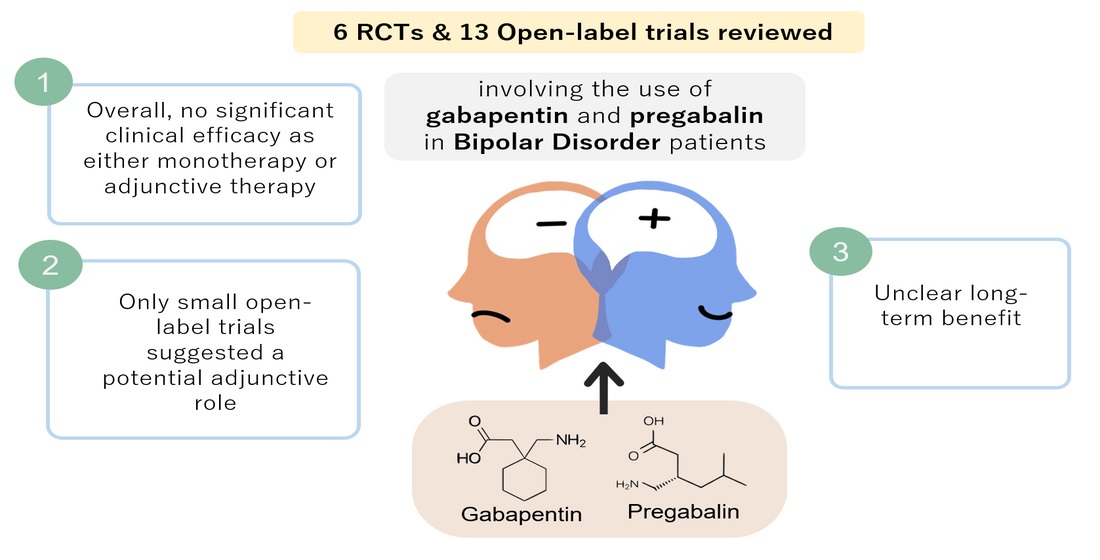
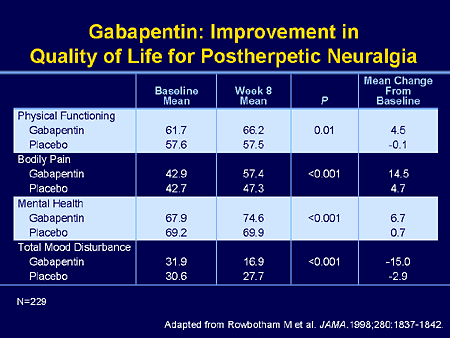
Gabapentin, also known as Gralise and Neurontin, is an anticonvulsant medication typically used in the treatment of epilepsy, along with various other physical and mental health treatments. Always use this medication exactly as prescribed and consult with your doctor prior to starting any other medications (prescribed or over the counter) while Objective: Gabapentin (GBP) is an anticonvulsant medication that is also used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS) and posttherapeutic neuralgia. GBP is commonly prescribed off-label for psychiatric disorders despite the lack of strong evidence. Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Balancing the benefits and risks of gabapentin use for mental health is an ongoing process. As with any medication, it’s about weighing the potential improvements against the possible side effects. It’s a delicate balance, but one that can lead to significant improvements in quality of life for many individuals struggling with mental health Gabapentin isn’t the main treatment option for anxiety, but it can be an effective alternative when other medications haven’t worked. Doctors may prescribe gabapentin to treat various health The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. 1. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. This medication, often associated with nerve pain, is making waves in the mental health community for its potential benefits in alleviating anxious feelings. But is it the right choice for you? 🤔 In this article, we’ll unravel the ins and outs of gabapentin, highlighting its effectiveness and any potential drawbacks. How does Gabapentin work? Gabapentin works by mimicking a neurotransmitter in the brain called GABA. GABA has a calming effect on the brain and impaired functioning of GABA has been linked to various mental health conditions such as panic disorder and depression. Neurontin - also known as Gabapentin - is a drug that is sometimes prescribed to those who experience anxiety especially in situations where the anxiety is co-occurring with bipolar disorder. This article explores the usage of Neurontin, as well as the benefits, weaknesses, and side effects for those looking to learn more about this medication A 2015 systematic review concluded that further research is needed to better understand gabapentin's role in the treatment of mental health disorders. Before Taking Neurontin Before taking this medicine you should go over the list of active and inactive ingredients with your doctor to make sure you are not allergic to any ingredient in it. This study examined off-label use of gabapentin for psychiatric indications and its concomitant use with CNS-D prescription drugs in a nationally representative sample of ambulatory care office visits. Less than 1% of outpatient gabapentin use was for FDA-approved indications. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. But since it’s been available, gabapentin has also been used off-label in psychiatry to treat patients with treatment-resistant mood and anxiety disorders as well as alcohol-withdrawal and We call on NICE to re-evaluate their support for use of pregabalin in anxiety in light of its known harms. The use of gabapentinoids off-label for other psychiatric conditions should also be re-considered. In general, psychotropic medications require longer term efficacy and safety studies before allowing widespread use. In recent years, gabapentin has gained attention for its potential role in managing anxiety disorders, particularly for individuals who do not respond well to traditional anxiety medications like SSRIs or benzodiazepines. Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Explore gabapentin's psychological side effects, learn to recognize symptoms, and discover management strategies for improved mental well-being during treatment. Gabapentin, while initially developed for treating epileptic seizures, has become a valuable option in mental health care due to its unique benefits. Many healthcare providers consider it a good alternative to traditional psychotropic medications for specific conditions. RESULTS. Bipolar Disorder. The randomized controlled trials 19 –21 investigating gabapentin for treating bipolar disorder indicate it is likely to be ineffective. Data interpretation is difficult: dosing varies by trial, gabapentin is used as both monotherapy and adjunctive therapy, patients have heterogeneous diagnoses, and primary outcomes differ between studies.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |