Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
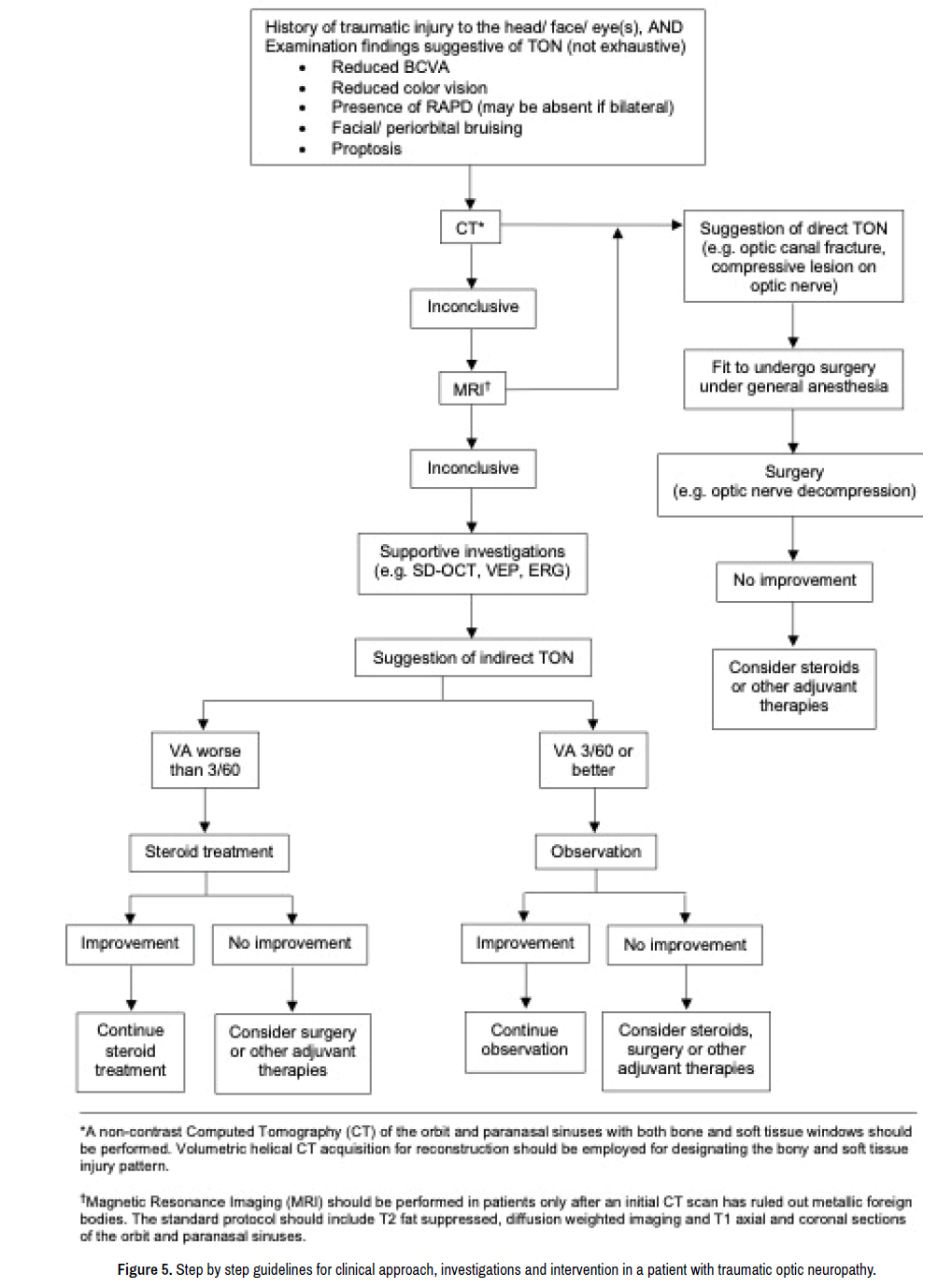
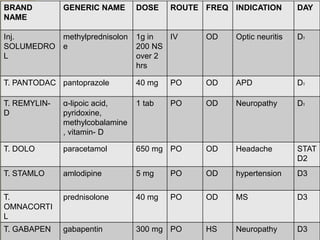
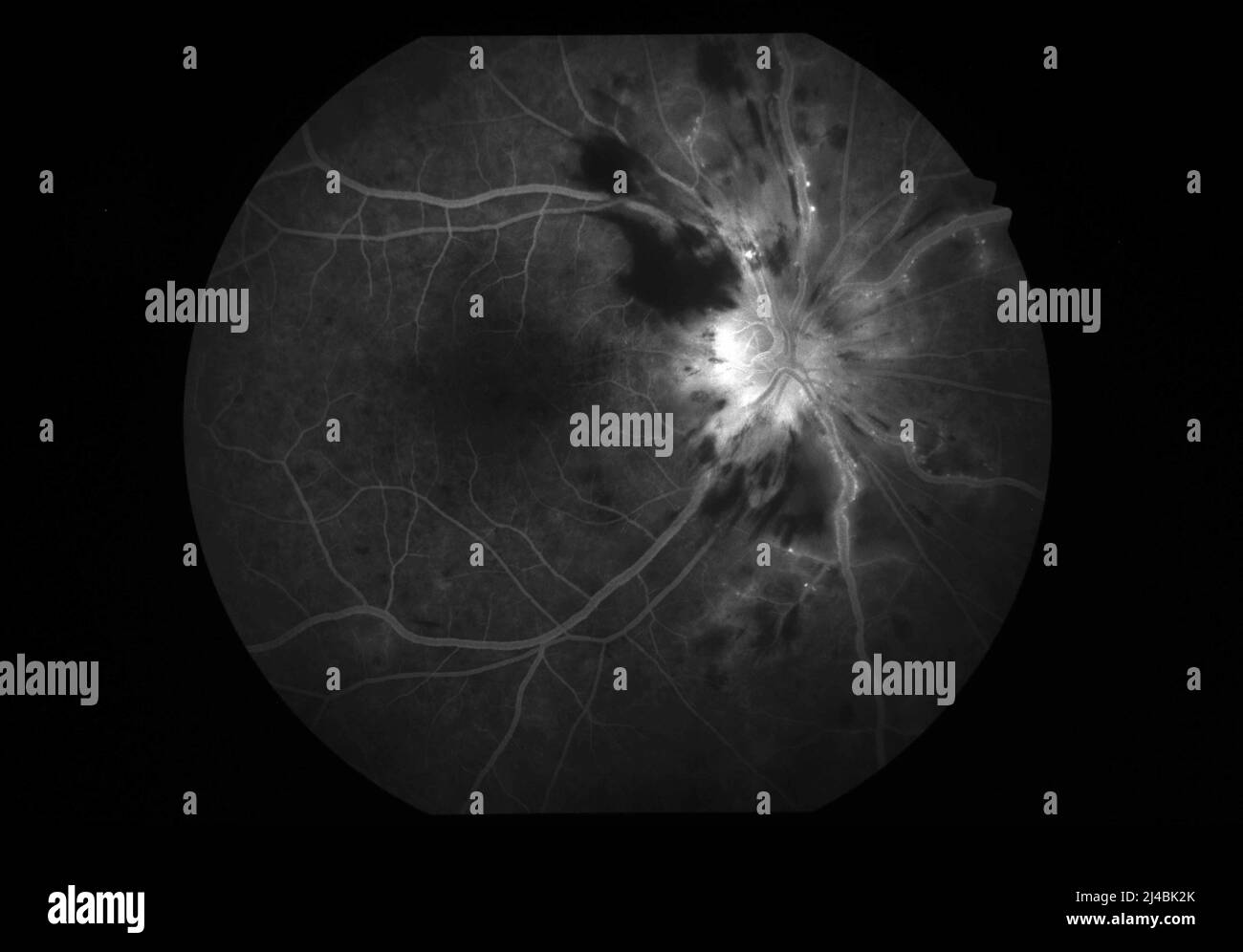
Background and ObjectivesMyelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease optic neuritis (MOGAD-ON) and nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) can cause acute optic neuropathy in older adults but have different managements. One review summarized the reported ophthalmologic adverse effects caused by the currently available AEDs from 1970 to 2019, and these included ocular motility dysfunction, retinopathy, maculopathy, glaucoma, myopia, optic neuropathy, and impaired retinal vascular autoregulation [1]. However, the results were limited by the statistical analyses. Gabapentin may be an underutilized medication in the treatment of chronic ocular pain. The pathophysiology of neuropathic ocular pain remains poorly understood. Clinical evaluation often reveals minimal ophthalmic exam findings, leading to an underdiagnosis of the condition by ophthalmologists. A recent study reported that oral gabapentin may be able to successfully treat DED patients with neuropathic ocular pain—as opposed to pain mainly caused by mechanical and chemical influences—who have systemic comorbidities, including rheumatological, neurological and psychological disorders. There is strong evidence that gabapentin is also effective in diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia [1]. To the best of our knowledge, macular edema after use of gabapentin has not been reported to date. Therefore, we report a case of macular edema after gabapentin. Optic nerve. Amiodarone may rarely induce optic neuropathy.3 This is characterised by swelling of the optic discs in addition to the typical symptoms of optic neuropathy . The main differential diagnosis is non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy, which is more common in patients with vasculopathy and is associated with an altitudinal retinopathy, maculopathy, glaucoma, myopia, optic neuropathy, and impaired retinal vascular autoregulation [1]. However, the results were limited by the statistical analyses. Eye disorders associated with AEDs should raise public concern. Due to the limited quantity and quality of current studies, the risk of Purpose: To investigate the response to gabapentin treatment in patients with dry eye (DE) accompanied by features of neuropathic ocular pain (NOP), and to analyze the differences between clinical manifestations of the groups according to treatment response. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of gabapentin treatment in dry eye disease (DED) and neuropathic ocular pain. Our study was performed with 72 patients. The painDETECT questionnaire was used for neuropathic pain screening. After 3 weeks of treatment with gabapentin 300 mg BID, the patient reported complete resolution of the ocular pain. The pathophysiology of neuropathic ocular pain remains poorly understood. Clinical evaluation often reveals minimal ophthalmic exam findings, leading to an underdiagnosis of the condition by ophthalmologists. Another factor that likely contributed to our patient's optic neuropathy is his history of smoking. Tobacco smoke can cause optic nerve damage, also called "tobacco optic neuropathy," through intrinsic toxicity and vasospastic effects. Tobacco contains small amounts of cyanide, which is thought to be the source of its neurotoxic properties. Optic nerve injury is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for 6 - 12 months also take Aranesp, and have Post procedural complication. Gabapentin and pregabalin. Gabapentin is FDA-approved for postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and epilepsy. Pregabalin is approved for PHN, fibro-myalgia, diabetic neuropathy, and certain seizure disorders. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic used for neuropathic pain treatment. Glaucoma can be conceptualized an optic neuropathy associated with characteristic structural damage to the optic nerve and associated visual dysfunction. Drugs That Can Cause Optic Neuropathy. Many commonly prescribed drugs have been implicated in optic neuropathy. Discussed here are the agents that have the most supporting information: phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, amiodarone, linezolid, ethambutol, and isoniazid. Other drugs reported to cause optic neuropathy are listed in TABLE In a small study of the electrophysiological consequences of gabapentin, three out of seven patients treated exhibited abnormal VEPs and one patient presented with an abnormal pattern ERG 143. It was suggested that an individual disposition to toxic effects on the transmitter function of the optic nerve might be responsible.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |