Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
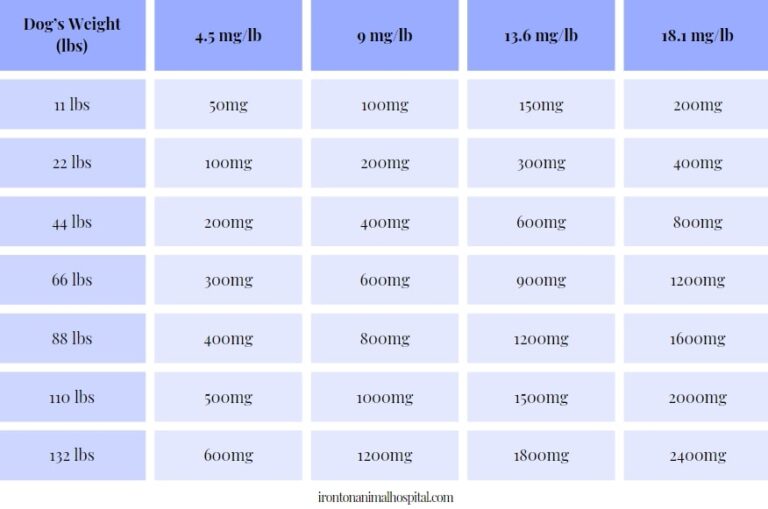
Gabapentin is used off-label for the treatment of severe knee osteoarthritis and typically when all other treatment options have failed to provide adequate relief. The rationale behind its use is based on the types of pain that OA causes, namely nociceptive pain (pain caused by damage to tissues) and nociplastic pain (pain caused by altered Yes, gabapentin can be a useful medication for managing arthritis pain in dogs, although it’s important to understand that it’s not a traditional painkiller like NSAIDs. Gabapentin is primarily an anticonvulsant and neuropathic pain reliever, which means it works differently than drugs designed to reduce inflammation. 1. Is gabapentin a strong painkiller for dogs? 2. How long does gabapentin take to work in dogs? 3. Can gabapentin make a dog unable to walk? 4. Is gabapentin hard on a dog’s kidneys? 5. What organs can gabapentin damage in dogs? 6. Can gabapentin make dogs sleepy? 7. What is better than gabapentin for dogs? 8. How does gabapentin make a dog Yes, gabapentin can be a valuable tool in managing arthritis pain in dogs, although it’s important to understand its role and limitations. While not a primary treatment for arthritis, which often involves anti-inflammatory drugs, gabapentin offers significant benefits as an adjunct analgesic. Osteoarthritis (OA), sometimes referred to as degenerative joint disease or DJD, affects approximately 1 in 5 adult dogs in the United States and is the number 1 cause of chronic pain in dogs.1 Statistics from 2016 estimate that about 10 million to 12 million dogs in the United States show signs of OA, When your dog is suffering from pain, whether due to arthritis, surgery, or injury, you’ll likely hear about medications like Carprofen and Gabapentin. Both drugs are widely prescribed by veterinarians, but they work in different ways and are suited for different types of pain. Understanding the key differences between Carprofen and Gabapentin can help you make informed decisions about managing Gabapentin No clinical studies evaluating gabapentin—as a single agent or an adjunct to NSAIDs—for the treatment of OA have been conducted in humans, dogs, or cats. However, a neuropharmacologic rationale exists for gabapentin’s ability to diminish central and peripheral sensitization, which is supported by a number of rodent studies. 17,18 Originally developed as an anticonvulsant (anti-seizure) medication for humans, gabapentin is commonly prescribed to dogs for pain relief, anxiety, or seizures. Like many human medications, In dogs with osteoarthritis, gabapentin was over 50% more effective than placebo for pain management. For separation anxiety, gabapentin reduced signs by 50-75% in most dogs, according to clinical research. Canine osteoarthritis is a significant cause of pain in many dogs and can therefore compromise animal welfare. As the understanding of the biology and pain mechanisms underpinning osteoarthritis grows, so do the number of treatments available to manage it. Gabapentin. Gabapentin prevents the release of the neurotransmitter glutamate and may reduce neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain may be experienced in some dogs with arthritis. Gabapentin may also decrease anxiety. Improvement in clinical signs of OA with CBD treatment. Of 23 dogs, 21 receiving concurrent gabapentin were comfortable reducing or stopping gabapentin: III: Brioschi et al. Randomised clinical study. Clinical cases of dogs with OA. NSAID plus gabapentin plus amitriptyline with or without CBD oil: 21: 12 weeks: CMI: CBPI Thus, gabapentin can be a useful way to relieve arthritis pain in dogs. Your vet may sometimes prescribe it in conjunction with other pain-relieving medications such as NSAIDs or tramadol for dogs. Gabapentin may also help control pain associated with cancer in dogs. If your dog has chronic pain from arthritis, spondylosis, tumors, herniated discs, or other conditions, they might benefit from Gabapentin. What is Gabapentin used for? During its use as a treatment for seizures in humans, gabapentin was found to be a useful medication for chronic pain, especially nerve pain. Gabapentin for dogs and cats, along with amantadine, are used as analgesics for chronic pain relief in dogs and cats. Here's how to choose which is best. Gabapentin: q8h to q12h PO (q8h is generally most recommended based on pharmacokinetics data). Starting dose is 10 mg/kg, potentially up to 40 mg/kg. 11,12 Gabapentin undergoes more hepatic than renal clearance in dogs compared to cats; thus, the dose reduction recommended for cats with renal disease is not generally necessary in dogs. Gabapentin: q8h to q12h PO (q8h is generally most recommended based on pharmacokinetics data). Starting dose is 10 mg/kg, potentially up to 40 mg/ kg.11,12 Gabapentin undergoes more hepatic than renal clearance in dogs compared to cats; thus, the dose reduction recommended for cats with renal disease is not generally necessary in dogs. What Is Gabapentin for Dogs? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic drug that is commonly prescribed by veterinarians to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. How gabapentin works is not completely understood; however, it is thought to block stimulation of the nerve cells. Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common conditions in dogs and can result in issues such as lameness and decreased joint range of motion. Veterinary practitioners should understand the process for early identification of OA in order to develop a multimodal treatment plan that aims to delay disease progression, decrease inflammation, and For dogs with arthritis, Gabapentin is usually part of a long-term treatment plan. It may take some time to see noticeable improvements, so patience is crucial. Your vet may also adjust the dosage based on your dog’s response to the treatment.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |