Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
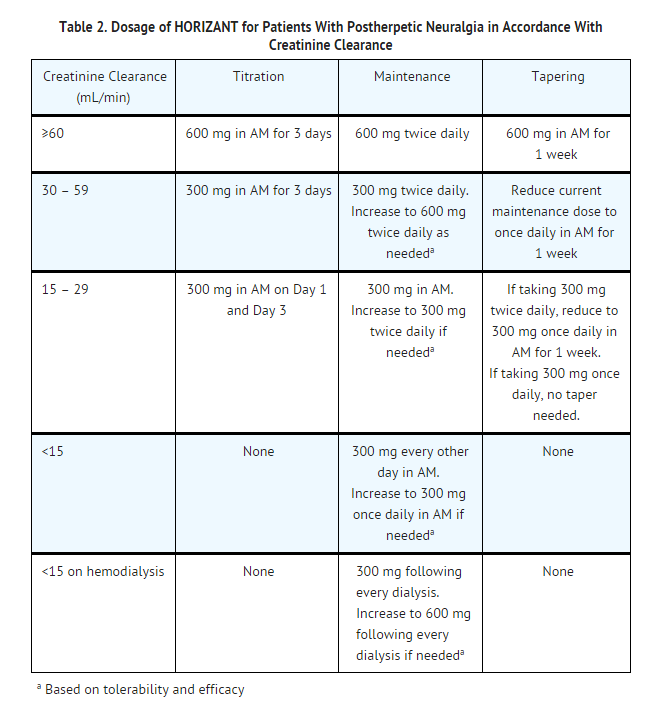
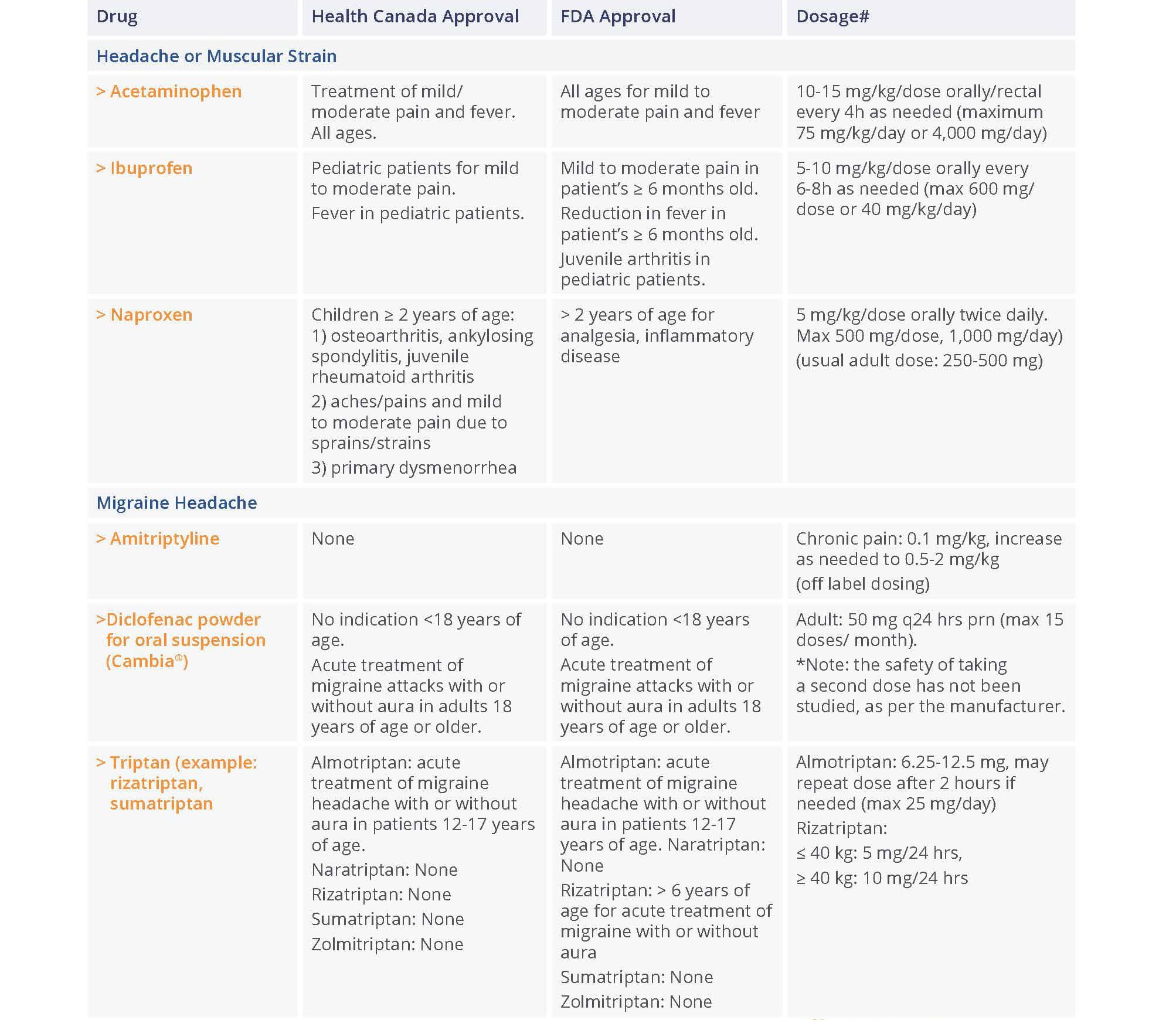
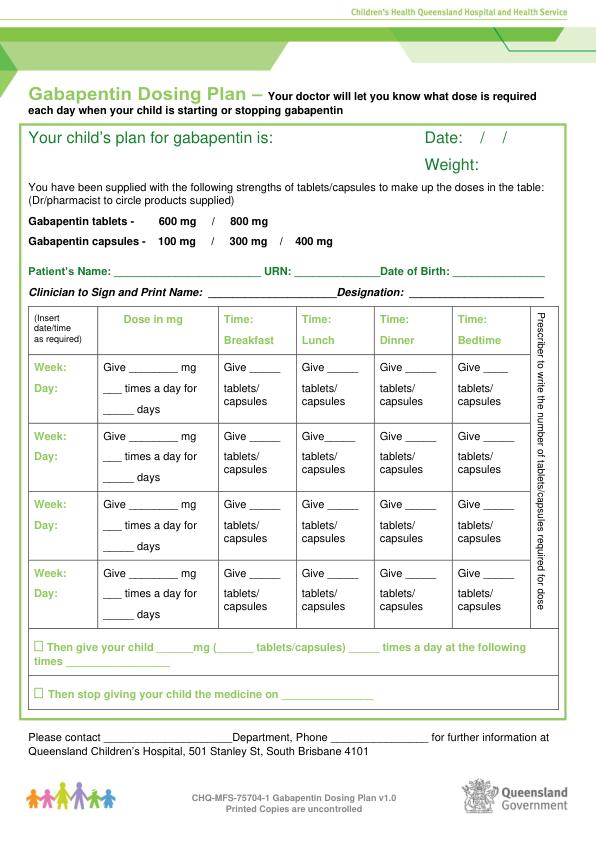
The most common locations for gabapentin initiation were in the cardiac (23%), pediatric (23%), and neonatal (11%) intensive care units. The most common indications for gabapentin use were neuro-irritability (80%), visceral hyperalgesia (6%), pain (6%), and gastroesophageal reflux (5%). The safety and effectiveness of gabapentin available under the trade name Gralise or Horizant have not been studied in pediatric patients and patients with epilepsy. Use: Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization in patients 3 years of age and older. 14-C Urea breath test: Pediatric drug information; Abacavir and lamivudine: Pediatric drug information; Abacavir, lamivudine, and zidovudine (United States and Canada: Not available): Pediatric drug information; Abacavir: Pediatric drug information; Abatacept: Pediatric drug information; AbobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport): Pediatric drug information When taken at the prescribed dosage, Gabapentin provides effective relief without causing significant harm or adverse reactions. Side Effects. The most common side effects of Gabapentin in children are mild and temporary, including drowsiness, dizziness, and nausea. These side effects usually subside as the body adjusts to the medication. These pharmacokinetic data indicate that the effective daily dose in pediatric patients with epilepsy ages 3 and 4 years should be 40 mg/kg/day to achieve average plasma concentrations similar to those achieved in patients 5 years of age and older receiving gabapentin at 30 mg/kg/day [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Gabapentin . Brand name: Neurontin. This leaflet is about the use of gabapentin for neuropathic pain (pain caused by nerve damage). Why is it important for my child to take Gabapentin? Gabapentin will help your child to feel less pain. What is Gabapentin available as? Tablets: 600 mg, 800 mg Gabapentin has shown benefits for a variety of pain etiologies in adult patients, with off-label use as an adjunctive agent in pediatric patients occurring more frequently. To summarize the studies which evaluate safety and efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of pediatric pain. Adjunctive therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization in patients older than 12 years of age with epilepsy; also indicated as adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in pediatric patients aged 3-12 years Eleven children (34%) had a 50% or greater reduction in seizure frequency during treatment. Another 4 children had at least a 25% reduction. Of the seven children who remained in the study at 6 months, two were seizure free, and four had only rare seizures. Three years later, Appleton and colleagues, publishing as the Gabapentin Pediatric Study Recent literature has shown an increased use of gabapentin in neonates and infants with similar indications to what we observed in our study. 1–7,9 Abdi et al 1 identified gabapentin use over an 11-year period from the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) at 0.13% (374/278,403) with 0% in 2005, 0.07% use in 2010, and 0.39% in 2016. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, NEURONTIN may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times These pharmacokinetic data indicate that the effective daily dose in pediatric patients with epilepsy ages 3 and 4 years should be 40 mg/kg/day to achieve average plasma concentrations similar to those achieved in patients 5 years of age and older receiving gabapentin at 30 mg/kg/day [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. gabapentin premedication on the frequency of emergence reactions and analgesic requirements following sevoflurane analgesia in children.8 A total of 46 children between 3 and 12 years of age undergoing tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy were randomized to receive either gabapentin 15 mg/kg orally 30 minutes of gabapentin with age can largely be explained by the decline in renal function. Reduction of gabapentin dose may be required in patients who have age related compromised renal function. (See PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) Pediatric: Gabapentin pharmacokinetics were determined in 48 pediatric subjects between the Medical information for Gabapentin on Pediatric Oncall including Mechanism, Indication, Contraindications, Dosing, Adverse Effect, Interaction, Renal Dose, Hepatic Dose. Card designed and compiled by the Stanford Pediatric Pain Service Pediatric Pain Assessment Tools FLACC Scale (Merkel, et al, 1997) Validated in Children < 3 years and Children with Developmental Disabilities Categories 0 1 2 Face No particular expression or smile Occasional grimace or frown, withdrawn, disinterested Frequent to constant Both gabapentin and pregabalin are approved for use in children, but the indications are limited to the JG, et al. Gabapentin use in pediatric spinal fusion What is this drug used for? It is used to help control certain kinds of seizures. It may be given to your child for other reasons. Talk with the doctor. If your child has been given this form of this drug, talk with the doctor for information about the benefits and risks. ty in neonates. Gabapentin is a potential drug of abuse and dependence in adults.(1) The effects of both gabapentin and pain on the neonatal neurodevelopment. nial pressure). Gabapentin should not be started without a full and thorough review by a senio. People over the age of 12 should be started on 300 mg gabapentin taken three times a day. The dose can be increased up to a total of 1,800 mg per day. In some instances, doses of up to 3,600 mg per day have been tolerated. Children should receive a dosage of 10–15 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into three equal doses.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |