Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
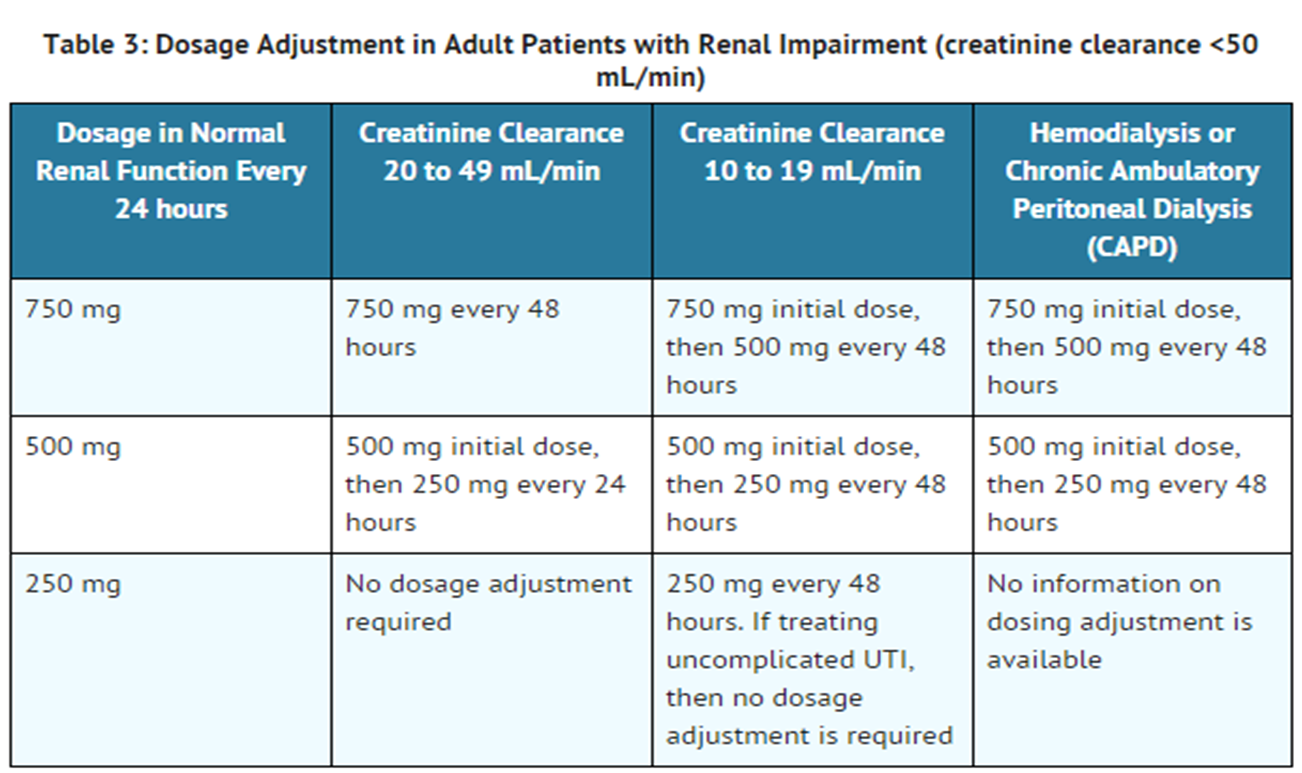
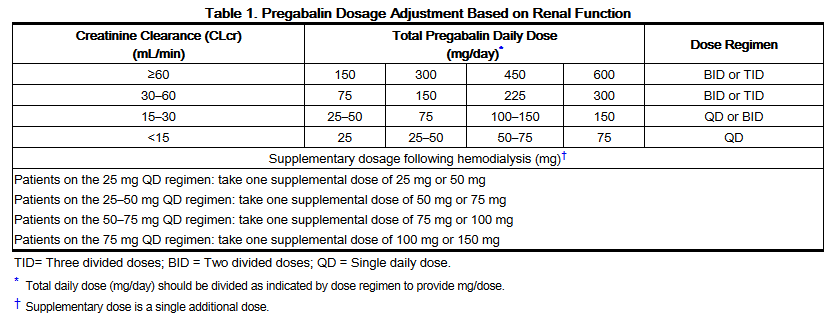
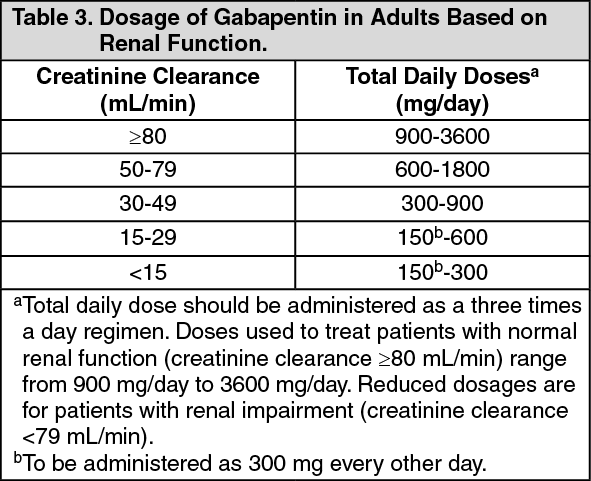
Notwithstanding, most reports of toxicities were associated with concentrations higher than 15 mg/L for gabapentin and concentrations higher than 13 mg/L for pregabalin, whereas individuals with normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of ~5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 200–300 mg after each HD : session and increase according to tolerability. Use: For the treatment of moderate-to-severe primary RLS in adults. Maximum dose: 2400 to 3600 mg/day; doses up to 2400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term studies; doses of 3600 mg/day have be used in a small number of patients for a relatively short duration and have been well tolerated. Renal clearance of gabapentin may vary in different dialysis patients depending on residual renal function and a lower starting dose is recommended for patients who are anuric. From the adverse events that were reported, they often subsided over 5–10 days [ 17 , 19 ]. Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function Renal Function Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) Total Daily Dose Range (mg/day) Dose 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Mild Kidney Problems (CrCl 60-90 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg/day TID. How Often to Take: 3 times a day. Notes: Monitor for dizziness or double vision. Moderate Kidney Problems (CrCl 30-59 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the Drug dosing requirements for antihypertensives in patients with chronic kidney disease are listed in Table 4. 4, 5 Thiazide diuretics are first-line agents for treating uncomplicated hypertension INTRODUCTION. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [].The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms []. Renal Dosing; CrCl>60 mL/min: 300-1200mg PO TID CrCl 30-60 mL/min: 200-700mg q12hr CrCl 15-29 mL/min: 200-700mg qDay CrCl<15 mL/min: 100-300mg qDay HD: 125-350mg posthemodialysis after each 4h dialysis interval. Hepatic Dosing Adult: no modifications; Pediatric: no modifications; Contraindications. Allergy to class/drug; Adverse Reactions Serious Ishida and colleagues examined data from the United States Renal Data System for patients receiving hemodialysis and stratified the groups by gabapentinoid dose. Patients on hemodialysis should receive maintenance doses based on estimates of creatinine clearance as indicated in the upper portion of the table and a supplemental post-hemodialysis dose administered after each 4 hours of hemodialysis as indicated in the lower portion of the table. The recommended dose of gabapentin in dialysis patients is 100 to 300 mg/per day, but on dialysis day an additional dose is given after the session, due to drug clearance through the dialysis membrane. We prescribed 300 mg/day (in a capsule), the minimum available dose of gabapentin in Greece. normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of 5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and ~ 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The elimination half-lives of gabapentin and pregabalin are prolonged with renal impairment leading up to accumulation with repeated dosing. The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. The recommended dose of gabapentin in dialysis patients is 100 to 300 mg/per day, but on dialysis day an additional dose is given after the session, due to drug clear-ance through the dialysis membrane. We prescribed 300 mg/day (in a capsule), the minimum available dose of gabapentin in Greece. However, on dialysis day we gave The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 Maximum dose: 75 mg/day. Dose to be given post-HD on HD days. No data to support use of pregabalin in gabapentin resistant or intolerant patient. THC:CBD (Sativex®): 1 spray under tongue or toward inside of cheeks daily to bid. May increase by 1 spray/day q2-4 days. Maximum dose: 12 sprays/day. Limited data in renal failure patients. It is recommended that patients with end-stage renal disease maintained on hemodialysis receive an initial 300-mg to 400-mg gabapentin loading dose. Plasma gabapentin concentrations can be maintained by giving 200 to 300 mg of gabapentin after every 4 hours of hemodialysis. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Gabapentin is not metabolized, and it is solely eliminated by renal excretion; pregabalin is not appreciably metabolized, and it is over 90% renally eliminated. 2,46,47 Accordingly, clinical practice recommendations and published reviews for the management of neuropathic pain in ESRD recommend conservative dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |