Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 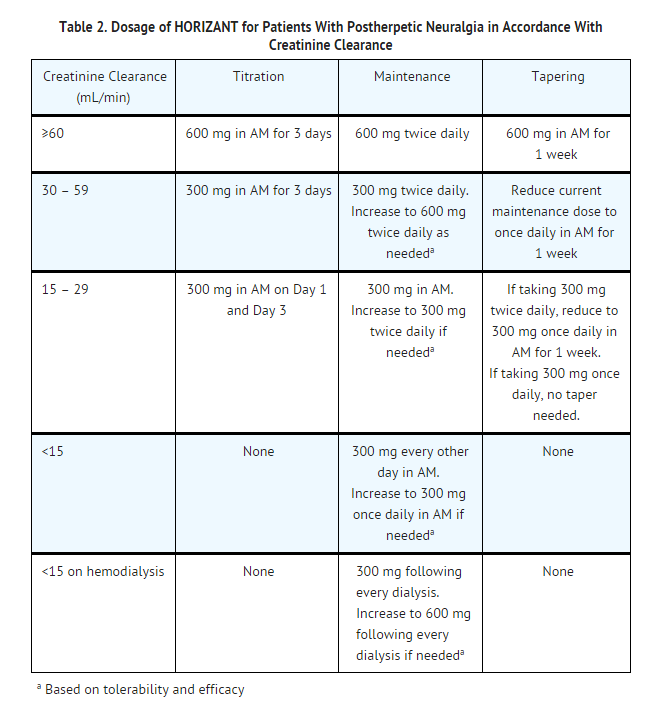 |
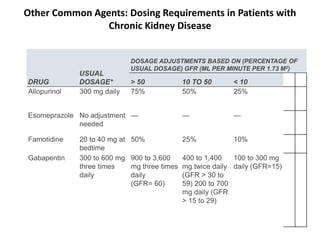
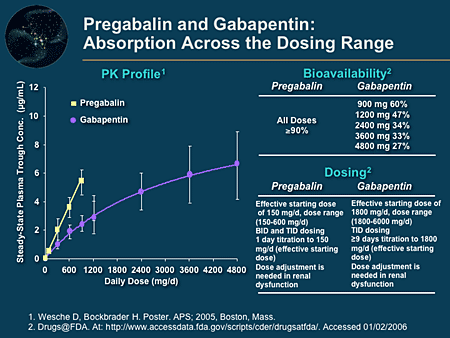
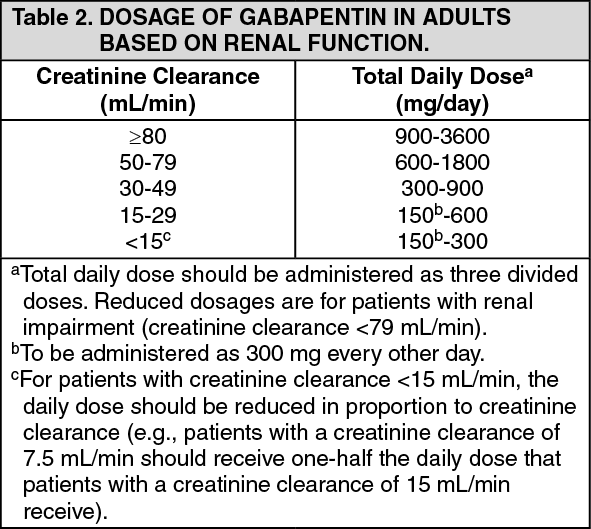
The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin; Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue; Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures. Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years <3 years: Safety and efficacy not established 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Mild Kidney Problems (CrCl 60-90 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg/day TID. How Often to Take: 3 times a day. Notes: Monitor for dizziness or double vision. Moderate Kidney Problems (CrCl 30-59 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the The typical effective daily dose range for immediate-release (IR) gabapentin is 1200 to 2400 mg/day on a three-times a day schedule, with a maximum daily dose of 3600 mg. As gabapentin can be sedating, the authors at times dose it asymmetrically with a larger dose at night to facilitate sleep. Dosages of drugs cleared renally should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance or glomerular filtration rate and should be calculated using online or electronic calculators. Recommended The usual dose for acamprosate is 666 mg three times daily. However, in individuals with moderate kidney dysfunction (creatinine clearance 30 to 50 mL/min) an initial dose of 333 mg three times daily is recommended. Additionally, in individuals with a body weight <60 kg we typically initiate treatment at a lower dose (eg, 333 mg twice daily). Disclaimer: This generalized information is a limited summary of diagnosis, treatment, and/or medication information. It is not meant to be comprehensive and should be used as a tool to help the user understand and/or assess potential diagnostic and treatment options. The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. As the dose of gabapentin increases, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) does not increase proportionally. Disclaimer: This generalized information is a limited summary of diagnosis, treatment, and/or medication information. It is not meant to be comprehensive and should be used as a tool to help the user understand and/or assess potential diagnostic and treatment options. Gabapentin can also be used in patients with renal function below 20 mg/dl (although a dosing adjustment is needed). A 2018 clinical review examined gabapentin and other drugs as anti-craving therapy in alcohol use disorder. 14-C Urea breath test: Drug information; Abacavir and lamivudine: Drug information; Abacavir, lamivudine, and zidovudine (United States and Canada: Not available): Drug information - Gabapentin versus pregabalin - Dosing and administration - Efficacy and adverse effects; Intravenous lidocaine - Dosing and administration - Efficacy - Adverse effects; Topical lidocaine; Ketamine - Dosing and administration - Efficacy - Adverse effects and contraindications; Glucocorticoids - Dosing - Efficacy and adverse effects; Alpha-2 Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg orally once Day 2: 300 mg orally 2 times day Day 3: 300 mg orally 3 times a day. Titrate dose as needed for pain relief; Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg/day orally in 3 divided doses Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day Extended-release: Gralise (gabapentin) 24-hour extended-release tablets: Initial dose: - NSAIDs and acetaminophen: Usual oral dosing for adults - Side effects of antidepressant medication - Topical analgesics - Opioids commonly used for acute pain In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and other conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and precautions. 2.3 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment. Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): TABLE 1. GABAPENTIN Dosage Based on Renal Function Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. - Principles for dosing and administration - Drug selection - Specific pain syndromes. Nociceptive pain - Acetaminophen - Opioids; Neuropathic pain - Gabapentin and pregabalin - Tricyclic antidepressants; Mixed nociceptive and neuropathic pain; DRUGS THAT SHOULD BE AVOIDED; SOCIETY GUIDELINE LINKS; SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS; REFERENCES; GRAPHICS
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |