Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
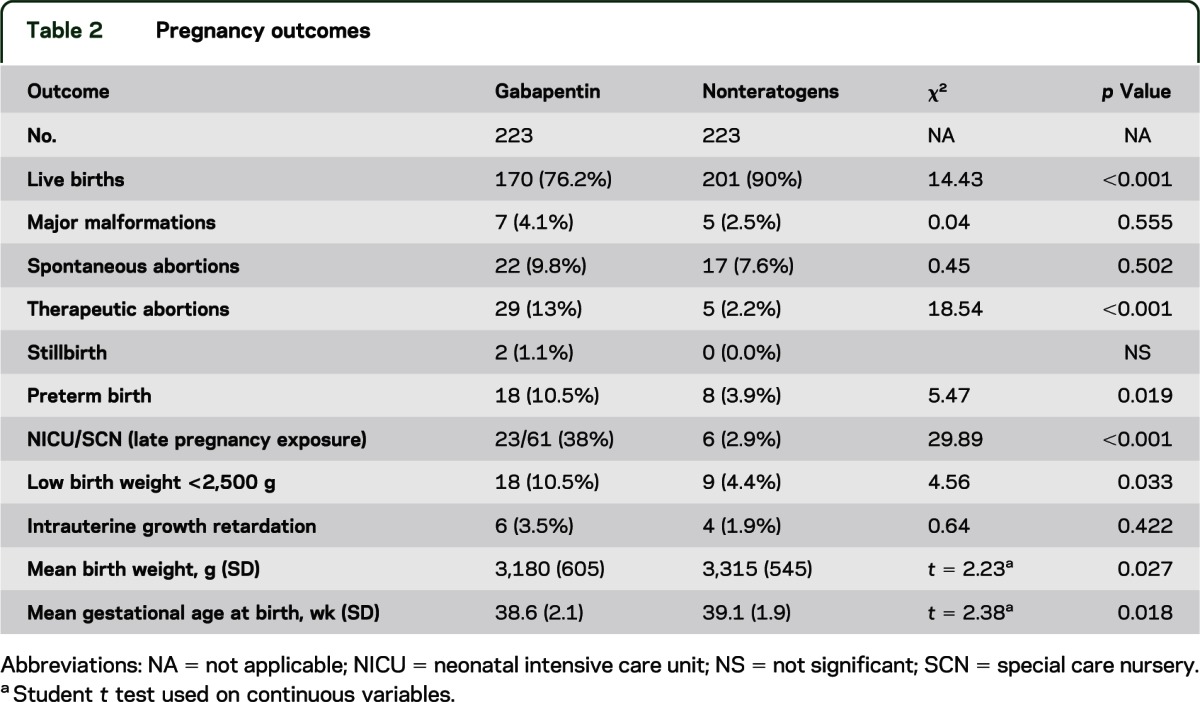
Gabapentin is a γ-aminobutyric acid analog formally indicated for the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain that is gaining increased popularity. Gabapentin has been historically considered a safe medication, including during pregnancy and lactation, with low reported concerns for misuse and us Advice and warnings for the use of Gabapentin during pregnancy. FDA Pregnancy Category C - Risk cannot be ruled out In our study, only 28% of the women continued taking gabapentin throughout pregnancy as two-thirds of the women (66%) discontinued in the first trimester, most following pregnancy confirmation between 6 and 8 weeks’ gestation. Despite the widespread use, only sparse information is available on the safety of gabapentin during pregnancy. We sought to evaluate the association between gabapentin exposure during pregnancy and risk of adverse neonatal and maternal outcomes. We examined the risk of major congenital malformations and cardiac defects associated with gabapentin exposure during the first trimester (T1), and the risk of preeclampsia (PE), preterm birth (PTB), small for gestational age (SGA), and neonatal intensive care unit admission (NICUa) associated with gabapentin exposure early, late, or both early While gabapentin (Neurontin) is now used in a wide variety of clinical settings — for epilepsy, pain management, restless leg syndrome, anxiety, and sleep disturbance – there is relatively little information regarding its reproductive safety. Most recently, a prospective study from researchers at the Motherisk program reports on the outcomes of 223 pregnancies exposed to gabapentin Safety of Gabapentin during Pregnancy. When considering the safety of using gabapentin during pregnancy, it is essential to weigh the potential risks against the benefits. Although gabapentin is generally considered safe for pregnant women, it is still important to consult with a healthcare provider before using this medication. The majority of the available epidemiological data relate to gabapentin use in pregnancy for the treatment of maternal epilepsy. A few case reports/series describe use of gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain or hyperemesis gravidarum but studies have not assessed fetal outcomes following use in pregnancy for these indications. Are there any risks of taking gabapentin during pregnancy? Gabapentin use in pregnancy is not very well-studied. While the available information does not strongly suggest that it causes problems for the baby, further research is required to prove that gabapentin is safe. It is not known if gabapentin can make it harder to get pregnant. Sexual dysfunction (including loss of desire to have sex and loss of ability to have an orgasm) has been reported among women who take gabapentin. Five studies reported significant findings with increased risks of overall congenital anomalies, specific anomalies (nervous system, eyes, oro-facial clefs, urinary and genital system), miscarriage, stillbirth and specific neurodevelopmental outcomes after exposure to pregabalin during pregnancy. Does taking gabapentin increase the chance of birth defects? Every pregnancy starts out with a 3-5% chance of having a birth defect. This is called the background risk. Small, controlled studies on gabapentin have not suggested an increased chance of birth defects. In a cohort study of pregnant women included in the US Medicaid Analytic eXtract (MAX) dataset, Elisabetta Patorno and colleagues investigate neonatal and maternal outcomes associated with gabapentin exposure during pregnancy. Despite the fact that gabapentin (Neurontin) is now used in a wide variety of clinical settings -- for epilepsy, pain management, anxiety, sleep disturbance – there is relatively little information regarding its reproductive safety. A prospective study from researchers at the Motherisk program reports on the outcomes of 223 pregnancies exposed to gabapentin and 223 unexposed pregnancies. Selected References: Blotiere PO, et al. 2020. Risk of early neurodevelopmental outcomes associated with prenatal exposure to the antiepileptic drugs most commonly used during pregnancy: a French nationwide population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 10(6). Brannon GE, Rolland PD. Anorgasmia in a patient with bipolar disorder type 1 treated with gabapentin. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2000;20(3):379 Pregnancy-related problems, such as preterm delivery (birth before week 37) or low birth weight (weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces [2500 grams] at birth) have been reported in some studies looking at the use of gabapentin during pregnancy. When treating neuropathic pain in a woman who is pregnant, the use of gabapentinoids (e.g. gabapentin) or an antiepileptic drug (AED) (e.g. levetiracetam, lamotrigine) is a last line option. This is due to the limited availability of data for safe use during pregnancy. Other options should be trialled first. Data on gabapentin use in pregnancy are mixed—some studies suggest it can result in increases in birth defects and other pregnancy complications, while other studies suggest it’s safe. Since decisions about gabapentin use in pregnancy are complex, it’s important to talk with your doctor about whether starting or continuing use is right Gabapentin is not generally recommended in pregnancy as there is not enough information about whether it's safe for your baby. However, from the small amount of information that is available, there's no clear evidence that it's harmful.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |