Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
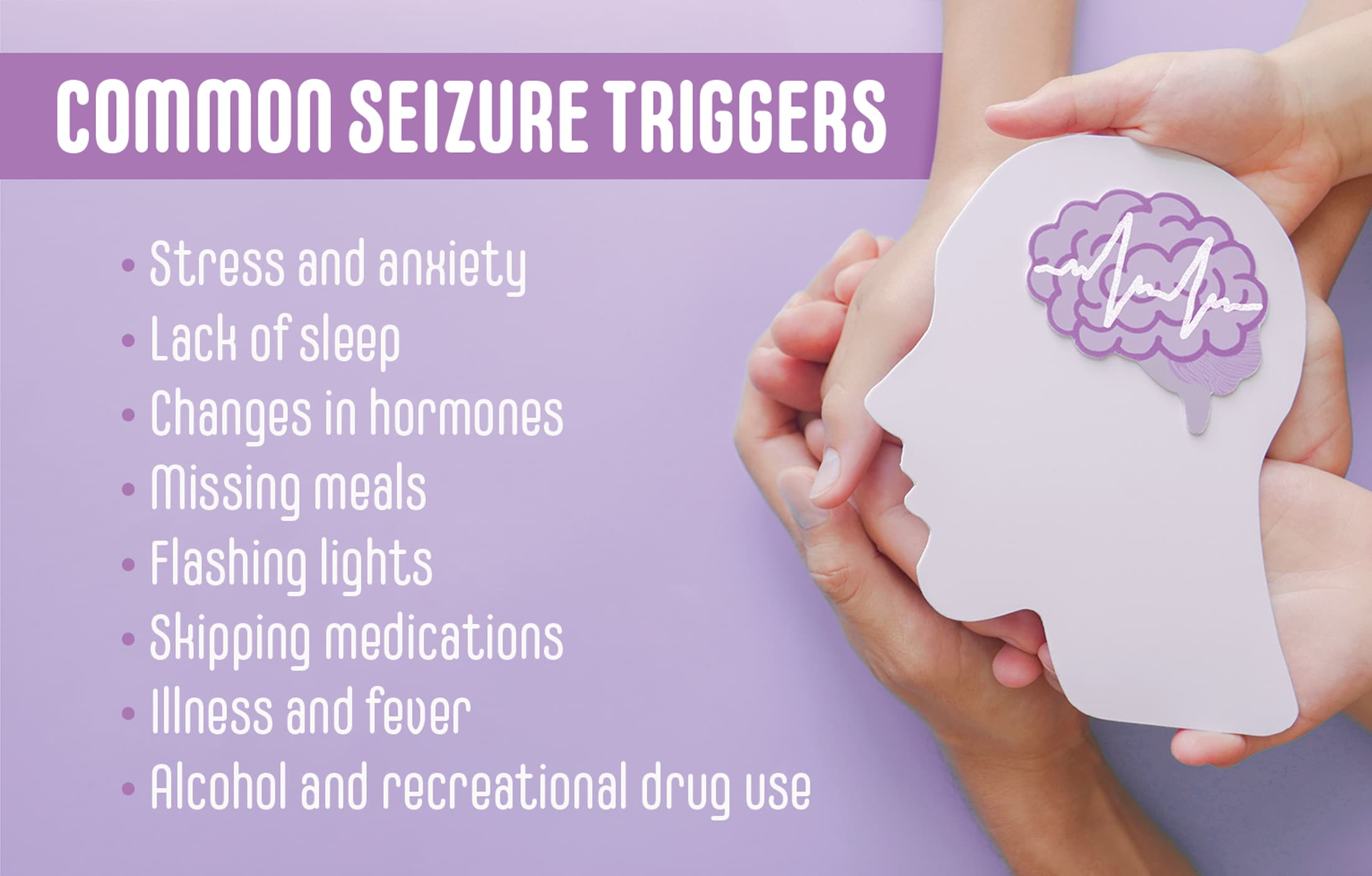
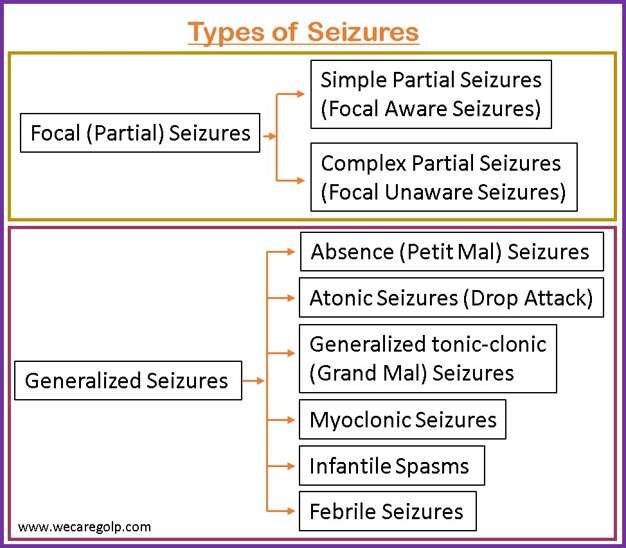
An antiepileptogenic effect has also been reported in the pilocarpine rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. In this model, treatment with NRP2945 (20 μg/kg, subcutaneously) for 7 days starting 24 h after cessation of pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus reduced the frequency of spontaneous recurrent seizures, but had no effect on seizure As with all antiseizure medications, gabapentin should be withdrawn gradually to minimize the risk of causing or worsening seizures or status epilepticus. You should not stop using gabapentin suddenly unless your healthcare provider tells you to stop the medicine because of a serious side effect. To help determine the potential place in therapy for gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy in adults, we sought to identify and summarize studies of the clinical- and cost-effectiveness of gabapentin as well as recommendations from evidence-based guidelines. • Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Clinical trials and retrospective studies have consistently demonstrated the beneficial effects of gabapentin in reducing seizure frequency and improving overall seizure control. Results: Our review of this literature suggests improved seizure control at higher gabapentin maintenance dosages (< or =3600 mg/d) than are used today in clinical practice (1800 mg/d) without an increase in the incidence of adverse reactions. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may The occurrence of a single seizure does not always require initiation of antiepileptic drugs. Risk of recurrent seizures should guide their use. In adults, key risk factors for recurrence are two Gabapentin is a Pfizer-made medication for focal aware and impaired seizures. For more information, visit the Epilepsy Foundation online. May be used in addition to other medication to reduce seizure frequency in adults and children aged three and older with partial-onset seizures. May be used in the management of postherpetic neuralgia (persistent nerve pain following Shingles infection) in adults. Direct comparison of gabapentin versus other antiepileptic drugs used for treatment of partial epilepsy showed that it was most likely to be associated with treatment failure due to inadequate seizure control and that carbamazepine was the least likely to be associated with treatment failure (gabapentin verus carbamazepine: hazard ratio (HR) 2. Seizures may increase if you stop using gabapentin suddenly. Ask your doctor before stopping the medicine. Avoid driving or hazardous activity until you know how gabapentin will affect you. Dizziness or drowsiness can cause falls, accidents, or severe injuries. Do not stop using gabapentin suddenly, even if you feel fine. Gabapentin is a prescription anti-seizure (anti-convulsant) drug that is used for preventing seizures and for treating post-herpetic neuralgia, the pain that follows an episode of shingles. Doctors do not know how gabapentin works (the mechanism of action). Gabapentin structurally resembles the neurotransmitter gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). Abstract. The new antiepileptic medications are prescribed for the treatment of patients with seizure disorders since 17 years ago. Gabapentin (GBP) was approved on January 1994 as adjunctive treatment in patients 12 years or older with partial seizures, with or devoid of secondary generalization. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Baseline seizure frequency was at least four seizures despite treatment (unclear over what time frame). The baseline period was time of enrolment. The trial period was 12 weeks. Treatment was gabapentin 300 mg on day one, 300 mg twice daily on day two and thereafter an increment of 300 mg/day until seizures were controlled or toxic effects Seizures occurred during withdrawal despite gabapentin treatment, but whether from an insufficient dose, patient susceptibility, or lack of gabapentin efficacy is not clear. Best results occurred at the 1,200-mg daily dose, but benefits may not apply to patients with severe withdrawal. Category 3. Brivaracetam, ethosuximide, gabapentin, lacosamide, levetiracetam, pregabalin, tiagabine, vigabatrin.For these drugs, it is usually unnecessary to ensure that patients are maintained on a specific manufacturer’s product as therapeutic equivalence can be assumed, however, other factors are important when considering whether switching is appropriate. Topiramate is a relatively newer drug used in the treatment of epilepsy in humans. 6 A 2013 study in 10 dogs showed that the drug was generally well tolerated, with side effects including ataxia, sedation, and weight loss. 28 This same study suggested that topiramate may be effective as an add-on medication for the treatment of idiopathic Background: Epilepsy is one of the most common chronic neurological disorders, affecting more than 50 million people globally. In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |