Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |
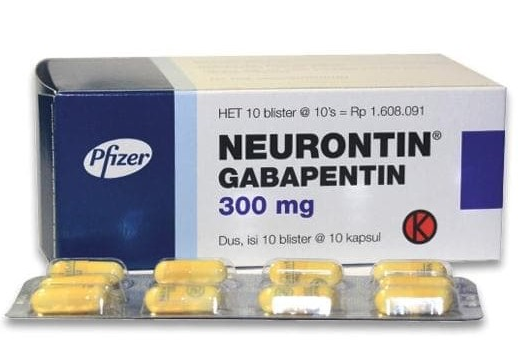
Stopping gabapentin, especially after prolonged use, can lead to a range of withdrawal symptoms, varying in intensity from mild discomfort to severe distress. The body becomes accustomed to the presence of the drug, and abruptly ceasing its intake can trigger a physiological response as it struggles to readjust. Rare but serious side effects of gabapentin include: rash, itching, or yellowing of the skin If you stop taking gabapentin suddenly, there is a chance of having Symptoms of stopping gabapentin can range from harmless to deadly depending on the dosage, duration of medication use, and any pre-existing medical conditions. While gabapentin is not a controlled substance, taking gabapentin without doctor supervision is just as dangerous, as is stopping the medication without consulting a physician. Gabapentin withdrawal happens when a person stops taking the medication abruptly, which may lead to symptoms such as confusion, disorientation, and seizures. The duration of these symptoms can vary, so it's crucial to take preventive steps. There are certain risks for someone who stops taking gabapentin. An individual who has been taking the drug to treat pain may feel increased pain when they stop the drug. A person with epilepsy Some people can become addicted to gabapentin. If this happens, you’ll have withdrawal symptoms after you stop taking the medicine. When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. If you want to stop taking gabapentin but have concerns about withdrawal symptoms and other side effects, talk with your doctor and create a plan that works for you. When the drug is stopped, your brain becomes temporarily disorganized. If you are starting to feel that you need a higher dosage of gabapentin to function, then you are most likely physically dependent on it and stopping suddenly will likely lead to withdrawal symptoms. Immediate side effects of stopping gabapentin can include anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. These symptoms occur as the body reacts to the absence of the medication, which it has become accustomed to over time. People who develop physical dependence to gabapentin may experience withdrawal symptoms when they try to come off it. Withdrawal symptoms can begin within 12 hours to 7 days after quitting the medication and last up to 10 days. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, and anxiety. What are the side effects of stopping gabapentin suddenly? A person who stops taking gabapentin or neurontin can expect to experience withdrawal symptoms within 12-48 hours after their last dose. 3. The following is a general gabapentin withdrawal timeline. The precise detox period and neurontin withdrawal symptoms will vary from person to person. Never stop taking gabapentin without talking to your healthcare provider first. Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems, including increasing your risk of seizures (if you are taking gabapentin to control seizures) or not improving your symptoms (if taking gabapentin for other indications). However, stopping gabapentin is not a simple process and requires careful management to minimize withdrawal symptoms and potential complications, including depression. Understanding Gabapentin Withdrawal. When a person stops taking gabapentin, especially after long-term use, they may experience a range of withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will help you stop taking the drug safely. Drug interactions. When using gabapentin, Speak with your doctor if you notice these side effects when taking gabapentin. When someone stops taking Gabapentin suddenly, they might experience symptoms like anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. This happens because the body has become used to the drug’s presence and needs time to adjust to its absence. If you’re thinking of stopping Gabapentin, it’s crucial not to do it abruptly. Side Effects Common side effects of gabapentin. Gabapentin can cause several common side effects, including dizziness, drowsiness, and fatigue. Other commonly reported side effects include headache, nausea, and blurred vision. These side effects are usually mild and tend to improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication. Some people may experience tremors, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, and insomnia when they stop taking gabapentin suddenly. Never stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor first. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. When discontinuing gabapentin (Neurontin), withdrawal symptoms can occur, so a gradual dose reduction is recommended. Read here for side effects, timeline, and treatment for gabapentin withdrawal.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |