Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 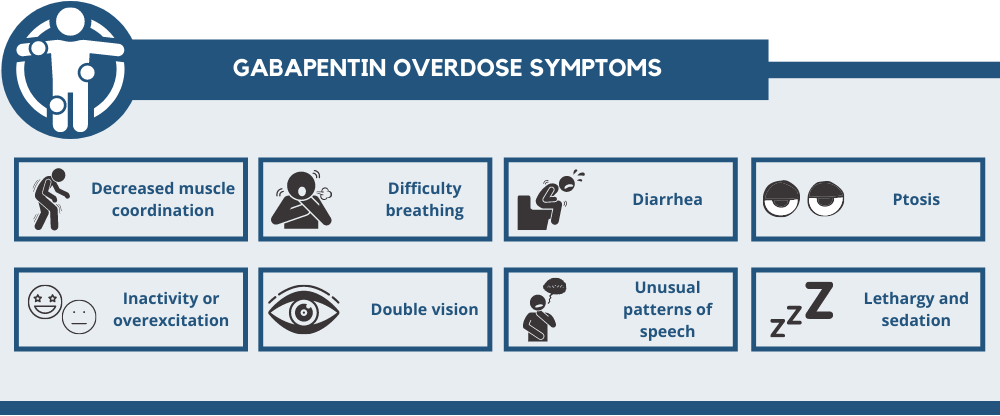 |
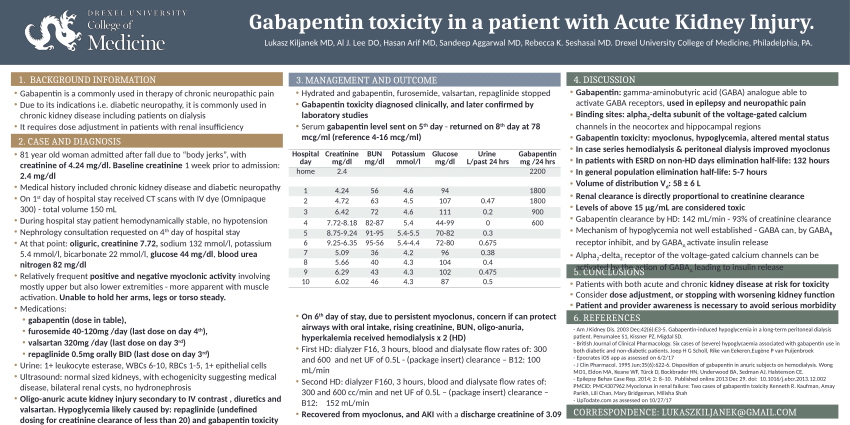
We report a case of gabapentin toxicity in a patient on long-term PD who was treated with continuous automated cycling PD. We find that continuous PD provides significant clearance of gabapentin. Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance. 24 In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (without dialysis), 30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. We report 2 cases of myoclonic activity associated with gabapentin toxicity in the setting of renal disease which resolved with discontinuation of gabapentin and treatment with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Introduction. Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (). 1, 2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Neuropathic pain, pruritus, and restless legs syndrome are commonly experienced symptoms among patients receiving hemodialysis 1,2 and have been associated with poor quality of life. 3–5 The anticonvulsant medications gabapentin and pregabalin have been shown to be efficacious treatments for these symptoms in several small, short-term randomized trials conducted in patients on hemodialysis A 38-year-old man with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on chronic hemodialysis was admitted for nonhealing, infected lower leg wounds and underwent a below-knee amputation. He suffered from postoperative pain at the operative stump and was treated for four days with regional nerve blocks, as well as gabapentin, intermittent intravenous Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. To inform safe gabapentinoid prescribing, we conducted a population-based study to examine the risk of serious adverse events in older adults with CKD (excluding those receiving dialysis) who started gabapentin at >300 mg/d or pregabalin at >75 mg/d versus at lower doses. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Myoclonus is a well-reported complication of gabapentin toxicity especially in patients with renal impairment. As gabapentin is solely excreted by the kidneys, renal dose adjustment is recommended in the literature. Gabapentin is not hepatically metabolized and is cleared solely by renal excretion; dosing requires consideration of the patient's renal function, especially in the context of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [3], [6], [7]. We report 2 cases of myoclonic activity associated with gabapentin toxicity in the setting of renal disease and address Renal Dosing; CrCl>60 mL/min: 300-1200mg PO TID CrCl 30-60 mL/min: 200-700mg q12hr CrCl 15-29 mL/min: 200-700mg qDay CrCl<15 mL/min: 100-300mg qDay HD: 125-350mg posthemodialysis after each 4h dialysis interval. Hepatic Dosing Adult: no modifications; Pediatric: no modifications; Contraindications. Allergy to class/drug; Adverse Reactions Serious Toxicity from gabapentin and pregabalin overdose is commonly encountered. Treatment is supportive, and the use of extracorporeal treatments (ECTRs) is controversial. The EXTRIP workgroup conducted systematic reviews of the literature and summarized findings following published methods. We report a case of gabapentin toxicity in a patient on long-term PD who was treated with continuous automated cycling PD. We find that continuous PD provides significant clearance of gabapentin. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin toxicity should be considered one of the differential diagnoses of altered consciousness in patients with compromised renal function, even after a single dose. We report a 57-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus and uraemia on regular Discussion: Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. We found that patients with chronic kidney disease had elevated serum gabapentin concentrations, in some cases leading to gabapentin toxicity; those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities were more prone to the toxicity, and the toxicity tended to be underrecognized. While gabapentin itself does not directly cause kidney damage, its accumulation due to impaired renal function can lead to increased side effects and potential toxicity. This makes it crucial for healthcare professionals to monitor patients on gabapentin closely, especially if they already have kidney disease.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |