Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
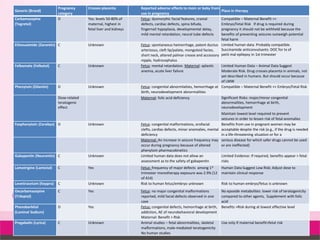
The literature includes a few cases suggesting an association between gabapentin use and urinary incontinence. This case focuses on a previously unrecorded association between gabapentin and increased urinary frequency, which was dose dependent. Gabapentin is often used to treat neuropathic pain and has been linked to potential urinary incontinence risks. Recent studies indicate significant symptom improvements in overactive bladder patients treated with gabapentin. Following administration of gabapentin, the patient's paresthesia was greatly reduced; however, 10 days after starting the therapy, she experienced daily urge urinary incontinence. Incontinence was mix type urinary incontinence. ing essential tremor. Case Report We present a case of an elderly woman diagnosed with essential tremor, in which GBP was initiated. In the following day, she complained of urinary incontinence with the absence of dysuria and urgency. It was not worse with movement, coughing, sneezing, or laughing. The vaginal parity of the patient was one. Laboratory tests and urinalysis were within normal Detrusor overactivity is a well-recognized and distressing medical condition affecting both men and women, with a significant prevalence in the population and with a higher incidence rate in people older than 70 years. Overactive bladder (OAB) is a symptomatic complex condition characterised by frequent urinary urgency, nocturia, and urinary incontinence with or without urgency. Gabapentin is an effective Overactive bladder syndrome with and without urinary incontinence and related conditions, signs, and disorders such as detrusor overactivity, neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction, underactive bladder, stress urinary incontinence, and nocturia are common in the general population and have a major impact on the quality of life of the Overactive bladder (OAB) is a symptomatic complex condition characterised by frequent urinary urgency, nocturia, and urinary incontinence with or without urgency. Gabapentin is an effective Bladder pain syndrome is a chronic disease that manifests as bladder pain, frequency, nocturia, and urgency. Gabapentin, amitriptyline, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are efficacious treatments for bladder pain syndrome. Fol-lowing administration of gabapentin, the patient’s paresthesia was greatly reduced; however, 10 days after starting the therapy, she experienced daily urge urinary incontinence. Incontinence was mix type urinary incontinence. Neurolog-ical and systemic physical examination, laboratory tests, and urinalysis were normal. This pathological condition is characterized by irritative symptoms: urinary urgency, with or without incontinence, and urinary frequency, often seriously compromising the quality of life of the people who have it. Benefits of Using Gabapentin for Urinary Symptoms. Gabapentin is seen as a good choice for those with urinary issues like overactive bladder (OAB). It offers benefits of gabapentin that traditional meds can't match. Studies show it helps with urgency, frequency, and nighttime urination. Reduction of Common Symptoms. Gabapentin is effective in Gabapentin is a first-line agent for neuropathic pain management and has a favorable safety profile. The literature includes a few cases of gabapentin-induced incontinence, and most of them involved patients with epilepsy who were between the ages of 12 and 43 years. Herein, we present three patient Exploring the Link Between Gabapentin and Urinary Incontinence. The link between gabapentin and urinary incontinence is an interesting topic in neurology. Some studies suggest gabapentin might affect bladder control. While it's seen as safe, some people with neurological conditions might find their gabapentin urinary function changed. Key Words: gabapentin, neurogenic detrusor overactivity, treatment of neurogenic overactive bladder (Clin Neuropharmacol 2006;29:206Y214) The overactive bladder is a well-recog-nized, chronic, and distressing medical condition characterized by urinary urgency and frequency, with or without inconti-nence.1 In the United States, overactive Yes, gabapentin can cause urinary incontinence, though it is considered a rare side effect. While the medication is primarily known for treating nerve pain, seizures, and restless legs syndrome, some individuals may experience a disruption in their bladder control while taking it. Introduction: We reviewed our experience with the use of gabapentin to treat symptoms of overactive bladder (OAB) and nocturia in patients who have failed conventional anticholinergic therapy. Methods: Thirty-one patients referred to us with refractory (OAB) and/or nocturia were treated with oral gabapentin. following six weeks of gabapentin treatment. • There was a significant decrease in mean scores for urgency, frequency, nocturia, and urgency incontinence. • These findings suggest that gabapentin has the potential to be an effective treatment option for individuals with OAB, resulting in symptom improvement. In the following day, she complained of urinary incontinence with the absence of dysuria and urgency. It was not worse with movement, coughing, sneezing, or laughing. The vaginal parity of the patient was one. Laboratory tests and urinalysis were within normal limits. Gabapentin can contribute to overactive bladder symptoms by relaxing the external urethral sphincter. And interestingly, gabapentin also can actually help decrease overactive bladder symptoms in some women. I take 100 mg of gabapentin at night for nerve pain. I also take Gemtesa, which is one of the newer overactive bladder medications on the
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |