Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
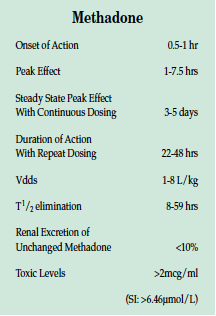
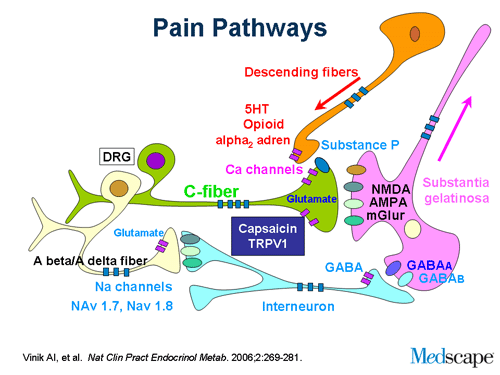
Gabapentin has been shown to be efficacious in numerous smaller clinical studies, case reports, and chart reviews in a variety of neuropathic pain syndromes. Two large multicenter studies, one in postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and one in diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), support preclinical findings. Gabapentin has been shown to be efficacious in numerous smaller clinical studies, case reports, and chart reviews in a variety of neuropathic pain syndromes. Two large multicenter studies, one in postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and one in diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), support preclinical findings. Gabapentin has been shown to be efficacious in numerous smaller clinical studies, case reports, and chart reviews in a variety of neuropathic pain syndromes. Two large multicenter studies, one in postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and one in diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), support preclinical findings. Gabapentin is a novel anticonvulsant that may have a unique effect on voltage‐dependent Ca2+channel currents at postsynaptic dorsal horn neurons that may interrupt an entire series of events, not just a single process, that lead to the development of neuropathic pain. The development of neuropathic pain involves a series of changes including primary and secondary hyperalgesia, peripheral and Gabapentin is a structural analog of the neurotransmitter g-aminobutyric acid (GABA) that it's beneficial effects on treating chronic pain conditions including neuropathic pain, regional pain Since gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with a proven analgesic effect in various neuropathic pain syndromes, we sought to study the efficacy of the anticonvulsant gabapentin as treatment for pain in patients with CRPS I. Case reports, pilot studies, and retrospective reviews also suggest efficacy for gabapentin in a variety of neuropathic pain syndromes (Wetzel and Connelly, 1997), including trigeminal neuralgia (Sist et al., 1997, Carrazana and Schachter, 1998, Valzania et al., 1998), complex regional pain syndromes (CRPS, Mellick et al., 1995, Mellick and Mellick, 1997), neuropathic pain associated with Gabapentin provides pain relief of a high level in about a third of people who take if for painful neuropathic pain. Adverse events are frequent, but mostly tolerable. We conducted a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to examine the safety and efficacy of gabapentin at doses of up to 2400 mg/day in a wide range of neuropathic pain syndromes. This study used a novel approach in which the inclusion criteria were based on the presence of specific symptoms, allowing patients with diverse This study shows that gabapentin reduces pain and improves some quality-of-life measures in patients with a wide range of neuropathic pain syndromes. A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled 8-week study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain, using doses up to 2400 mg/day. Despite its therapeutic role in neuropathic pain, gabapentin produces psychoactive effects and has an abuse liability. Gabapentin abuse typically involves taking higher doses in a single administration. Gabapentin has been shown to be efficacious in numerous smaller clinical studies, case reports, and chart reviews in a variety of neuropathic pain syndromes. Two large multicenter studies, one in postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and one in diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), support preclinical findings. Anticonvulsant drugs--including carbamazepine, phenytoin, and felbamate--have been used to treat neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is a novel anticonvulsant that may have a unique effect on voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel currents at postsynaptic dorsal horn neurons. Neuropathic pain is commonly defined as “pain caused by a disease or lesion which leads to damage or dysfunction of the somatosensory (pain) system.” 4 Neuropathic pain is maladaptive and can be fairly intense; pain impulses are often described by people as “lightning bolts” or “stabbing pain.” Components of neuropathic pain include Gabapentin (GBP) is a Health Canada approved antiepileptic drug. 5 In the UK, GBP is licensed for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults and in the US it is marketed for post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). 3 The mechanism of action for GBP relates to its ability to bind with high-affinity to the alpha-2-delta subunit of vo Objectives: Gabapentin was initially developed as an antiepileptic drug but was later discovered to be an effective treatment of neuropathic pain. Gabapentin has been successfully used for the treatment of multiple neuropathic pain syndromes such as diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled 8-week study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain, using doses up to 2400 mg/day. The study used a novel design that was symptom- rather than syndrome-based; an approach that aimed to reflect the realities of clinical practice. Most studies used oral gabapentin or gabapentin encarbil at doses of 1200 mg or more daily in different neuropathic pain conditions, predominantly postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. The purpose of this report is to review the clinical evidence on the efficacy, safety and guidelines for use of gabapentin in adults with neuropathic pain, and to examine evidence on the misuse or abuse of gabapentin and other drugs for neuropathic pain. Brand names of gabapentin include Horizant®, Gralise® and Neurontin®. What is gabapentin approved for? Gabapentin is used to: Prevent and control partial seizures. Gabapentin can be used in adults and children age 3 and older who have partial seizures. Relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |