Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
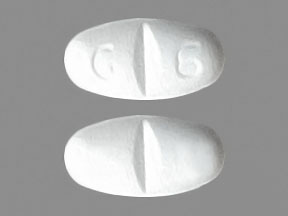 |  |
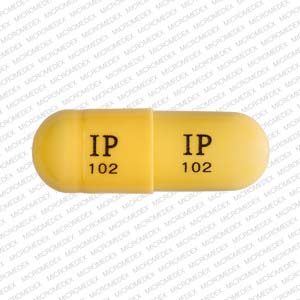
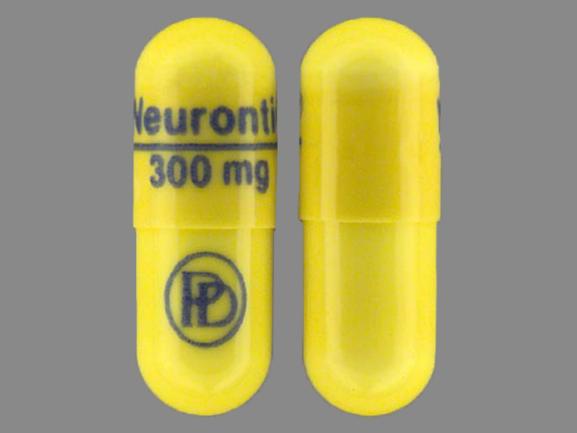
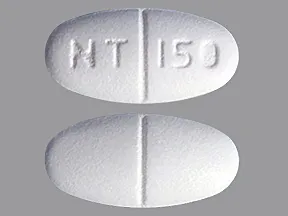
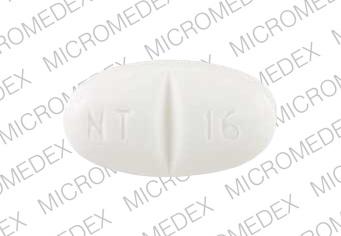
Gabapentin is a medication that is used to treat a variety of conditions‚ including seizures‚ nerve pain‚ and restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin is not a controlled substance‚ but it can be habit-forming in some people. People who abuse gabapentin may take it in high doses to get high. Gabapentin 600 mg is not a controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). Get help with Imprint Code FAQs. Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Pill with imprint 7 5 is White, Oval and has been identified as Gabapentin 600 mg. The dose may be adjusted and increased gradually based on the individual's response and tolerance. The maximum daily dose is usually not more than 1800 mg per day (600 mg three times per day).For individuals with impaired kidney function or undergoing hemodialysis, the gabapentin dosage may need to be adjusted. Gabapentin is used in the treatment of Back Pain; Postherpetic Neuralgia; Epilepsy; Chronic Pain; Seizures and belongs to the drug class gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs. Risk cannot be ruled out during pregnancy. Gabapentin 600 mg is not a controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). Images for 600 The number of individuals who have Gabapentin present in an accidental overdose is significant enough . to add Gabapentin dispensation into the CPRMS. Note: The Department is not changing the controlled substance scheduling of Gabapentin at this time. As such, the CPMRS look-up requirements do not apply to Gabapentin prescribing. Naloxone Gabapentin is chemically known as 2-[1-(aminomethyl) cyclohexaneacetic acid]. Gabapentin closely resembles pregabalin, a schedule V drug under the Controlled Substances Act in its chemical structure and pharmacological activity. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, and it is not classified as a controlled substance by the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA). However, this medication does share signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms of opioids like: Sweating. o Day 1: Single 300 mg dose o Day 2: 600 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg two times a day) o Day 3: 900 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg three times a day) •Epilepsy with Partial Onset Seizures (2.2) o Patients 12 years of age and older: starting dose is 300 mg three times daily; may be titrated up to 600 mg three times daily Some other states don't classify gabapentin (Neurontin) as a controlled substance, but they do keep close track of gabapentin (Neurontin) dispensing using a prescription monitoring program. If you have questions about controlled substance laws in your state, it's best to talk to a local healthcare professional. Gabapentin isn’t a controlled substance according to the federal government. But several states have passed their own laws classifying gabapentin a schedule V (schedule 5) controlled substance. Combining gabapentin and opioids can be extremely dangerous. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is not a narcotic or federally controlled substance by the DEA as of November 2022, but it is classified as a Schedule V controlled substance in certain states. Gabapentin is not currently listed as a controlled substance under federal law. However, some states classify gabapentin as a Schedule V substance or a drug of concern and mandate reporting to PMP. Furthermore, other states are considering similar actions due to increasing evidence of associated risks. Gabapentin isn’t a narcotic or federally controlled substance, but it is regulated and recognized as a controlled substance in certain states. Gabapentin is approved by the Food and Gabapentin 600 mg is not a controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). Note: Inactive ingredients may vary. Get help with Imprint Code FAQs. Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Gabapentin’s unscheduled status reflects its lower potential for abuse or dependency compared to controlled substances. However, the FDA monitors gabapentin for potential misuse, particularly when combined with other central nervous system depressants. Gabapentin isn’t a controlled substance or narcotic on the federal level, but several states have passed laws to make it a Schedule V controlled substance. Gabapentin has risks and adverse effects, especially when combined with some other substances. In a survey looking at abuse of gabapentin, it was found that patients were taking on average 3,000 mg/day, ranging from 600 mg to 8,000 mg/day. Withdrawal, when reported, occurred within 12 hours to 7 days of discontinuation of the medication. 2025 著作権. 不許複製 プライバシーポリシー Neurontin (gabapentin) is an immediate-release form used to treat seizures in adults and children who are at least 3 years old, in addition to nerve pain due to shingles. It comes as 100, 300, or 400 mg oral capsules; 600 mg and 800 mg oral tablets, and as a 250 mg per 5 mL oral solution. It is also available as a generic option. Absorption: Increasing gabapentin's dosage leads to reduced bioavailability; for example, daily doses of 900 mg, 1200 mg, 2400 mg, 3600 mg, and 4800 mg yield bioavailability of approximately 60%, 47%, 34%, 33%, and 27%, respectively. The impact of food is minor, resulting in a 14% increase in area under the curve (AUC) and Cmax.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |