Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | +and+Gabapentin+(Neurontin).jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
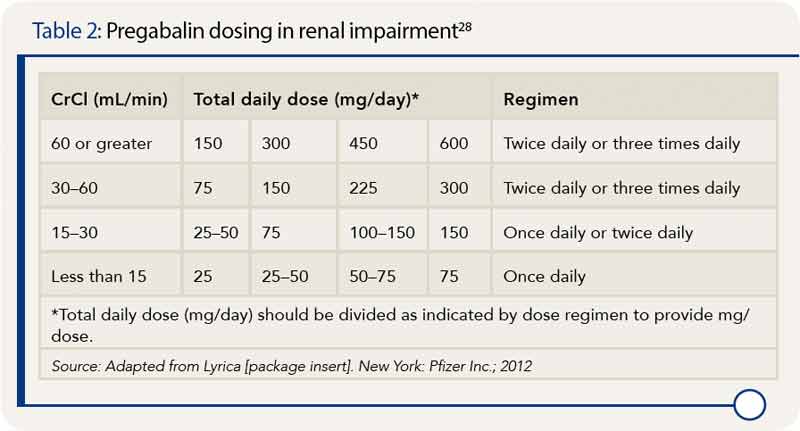
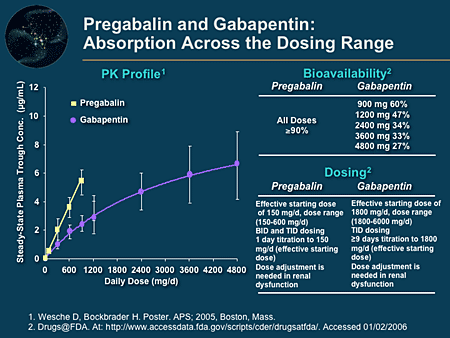
Conclusion: In conclusion, pregabalin demonstrated superior and faster efficacy in alleviating neuropathic pain than gabapentin did. Additionally, it improved patient-reported outcomes, resulted in lower opioid consumption, and led to fewer adverse events. Pregabalin and Gabapentin are both effective treatments for neuropathic pain and other conditions, but they differ in several key aspects. Pregabalin has faster absorption, onset of action, and greater potency, making it more effective for some patients. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are effective for neuropathic pain conditions. A network meta-analysis suggests pregabalin in patients offers better pain reduction, but gabapentin oral remains widely used. Studies have also shown both Lyrica and gabapentin to be effective for treating partial onset seizures in adults and some children, when used with other seizure medications. Find out how gabapentin and Lyrica are used for pain control and when they can be used together. and your doctor will gradually increase your dose until effective levels are reached. However Several studies have evaluated the efficacy of gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of neuropathic pain, yielding contradictory results. On one hand, it has been observed that gabapentin is more effective, especially at higher doses, compared to pregabalin (8, 9). What are gabapentin and pregabalin used for? Gabapentin and pregabalin are used to treat neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and other conditions such as fibromyalgia and generalized anxiety disorder. Which medication works faster, gabapentin or pregabalin? Pregabalin generally works faster, with patients often experiencing relief within a few days. The particular NNTs for pregabalin and gabapentin were 7.71 and 7.16, respectively. 10 A more recent meta-analysis in 2022 specifically focused on post-herpetic neuralgia and found greater efficacy with pregabalin in alleviating pain and improving global perception of pain and sleep. 15 Another meta-analysis published in 2021 reported similar Pregabalin works similarly to gabapentin. Like gabapentin, pregabalin is also thought to relieve nerve pain by lowering levels of substance P and excitatory chemicals in the nervous system. Pregabalin dosage for sciatica nerve pain. In studies, participants took a range of pregabalin dosages for sciatica. Pregabalin is licensed for peripheral and central neuropathic pain whereas gabapentin is licensed for peripheral neuropathic pain only. Use of gabapentin for central neuropathic pain is therefore off-label. Pregabalin and gabapentin are structurally related to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin, pregabalin, and GABA all modulate voltage-gated calcium channels. The mechanism of action of gabapentinoids like gabapentin and pregabalin in seizure treatment and pain management is not fully understood. However Gabapentin is indicated as adjunct therapy for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia. 4 Pregabalin is indicated for the same uses as gabapentin, plus the management of fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain associated with diabetes, specifically diabetic neuropathy. 5 We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Systematic reviews have found moderate quality evidence to support the use of gabapentin and pregabalin in people with peripheral diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia. 4 Approximately 40% of people taking pregabalin (600 mg, daily) and 30% of people taking gabapentin (≥ 1,200 mg, daily) for at least eight weeks achieved ≥ 50% Both Lyrica and gabapentin are used as anti-epileptic medications and to treat nerve pain. But there are several differences between them. The main differences between Lyrica and gabapentin are: Lyrica is a brand name for pregabalin. Gabapentin is a generic name - brands of gabapentin include Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are both approved to treat nerve pain. How are they different, and which one is preferred? Compare both meds here. For this study, a key measure was whether a medication reduced discomfort by 50%. The most effective treatment was nortriptyline. Of the study subjects taking this medication, 25% reported their discomfort improved by at least 50%. The least effective treatment was pregabalin: only 15% of study subjects reported that much improvement. However, in another study, it was shown that Pregabalin was not as effective as Gabapentin in reducing the frequency of seizures [5]. A review found no significant difference in the effectiveness of Gabapentin and Pregabalin for treating nerve pain after spinal cord injury [6]. Pregabalin and Gabapentin work by affecting nerve signals in the brain to reduce pain and prevent seizures. Both medications target calcium channels in nerve cells, slowing down excessive nerve activity. This helps to relieve nerve pain and control seizures. Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved to treat some of the same conditions, including postherpetic neuralgia in adults. Both drugs are also indicated to treat partial seizures in adults and certain children with epilepsy (a seizure disorder) when taken along with other medication.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | +and+Gabapentin+(Neurontin).jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |