Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
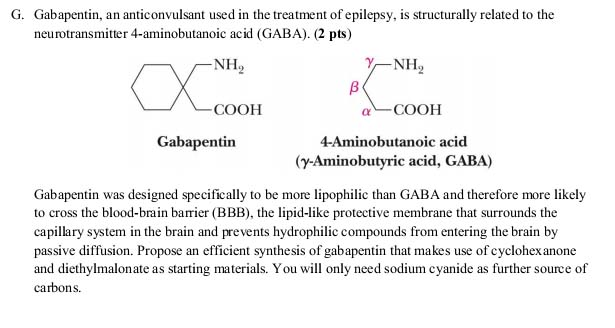
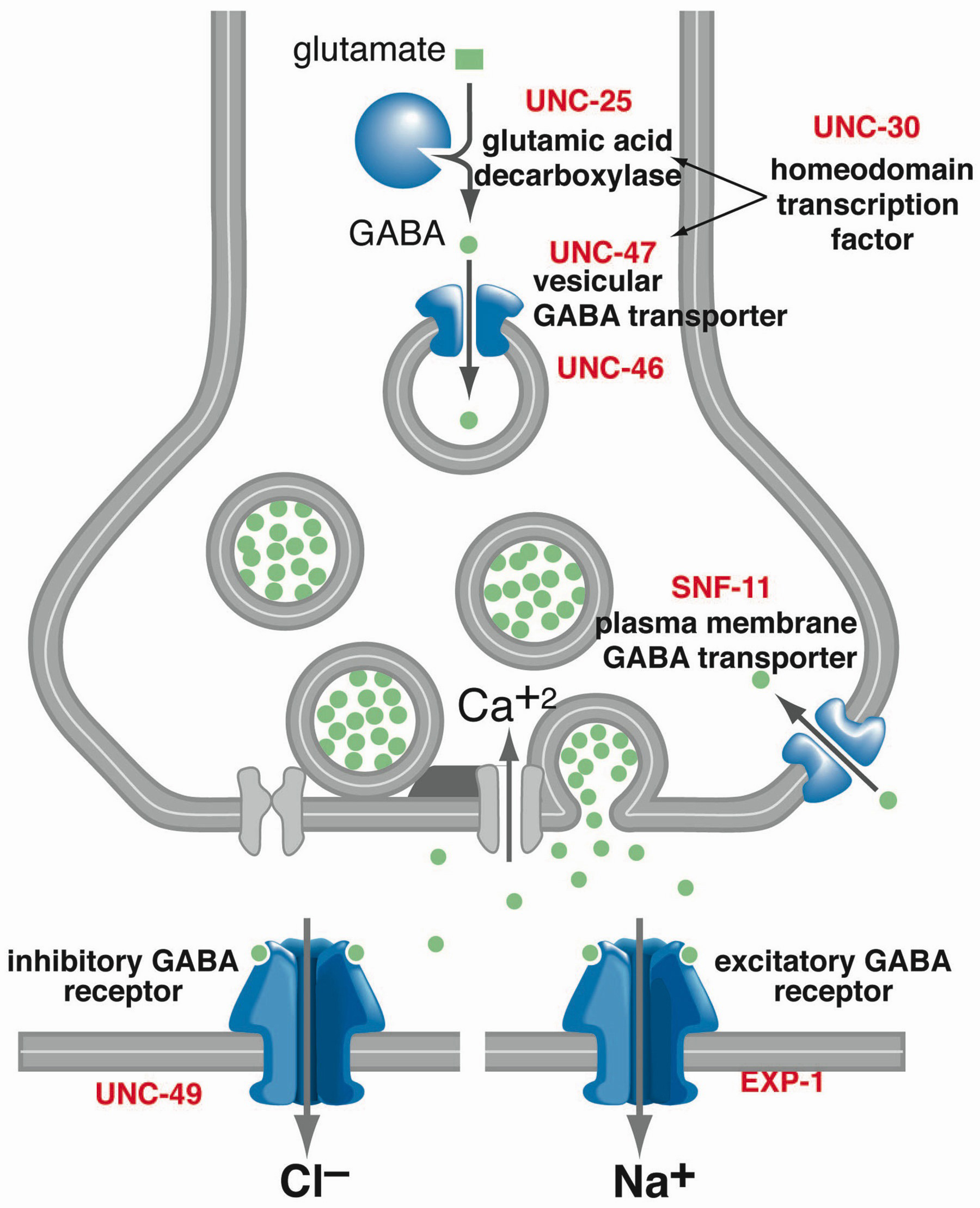
Fermented soy products like tempeh and miso Fermented grains, such as in the fermentation of rice to produce sake (Japanese rice wine) Vegetables. Vegetables such as tomatoes, spinach, broccoli, and peas have been found to contain GABA, although in lower concentrations compared to fermented foods. Tea. Certain types of tea, particularly The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. GABA is not the same as gabapentin. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter; gabapentin is a prescription medication. They are often used interchangeably (as you’ll read below) and should not be! GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both compounds that play important roles in the functioning of the central nervous system. While GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain, Gabapentin is a synthetic drug that is structurally similar to GABA. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. While both relate to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), they are fundamentally different in their origin, mechanism of action, and legal status. In short, over-the-counter (OTC) GABA is a dietary supplement, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. As nouns the difference between gaba and gabapentin is that gaba is while gabapentin is (medicine) a medication, originally used for the treatment of epilepsy but now used to relieve pain. If gabapentin does not work for you or believe the side effects are too severe, here’s a set of other drugs that do the same job. Pregabalin (Lyrica) This drug is also an anticonvulsant, and just like Gabapentin, you can take it for epilepsy, nerve pain, and anxiety. It differs from Gabapentin in terms of dosage and frequency of administration. GABA acts like a brake in a car and slows down nerve cells that are over-excited. Because it calms the nervous system, it is called an inhibitory neurotransmitter. GABA analogs are medicines that have a very similar structure to GABA but act in a different way, although experts aren’t exactly sure how they work. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. You can take 100 to 300mg sublingual GABA to treat pain flares, or 100 to 200mg of GABA simultaneously with an opioid medication or GABA surrogate for added pain relief. Forest Tennant is retired from clinical practice but continues his research on intractable pain and arachnoiditis. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin acts like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, which decreases the activity in your nervous system. However, it doesn’t work with GABA receptors in the same way. Although gabapentin’s mechanism of action isn’t entirely understood, it definitely has an effect on the brain. GABA is a neurotransmitter that directly inhibits neuronal activity, whereas gabapentin is a GABA analog that modulates calcium channels to achieve its therapeutic effects. Understanding these differences is crucial for their effective use in clinical practice. Take-home message: - gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a major neurotransmitter that regulates much of our brain function. It was previously thought that ingested GABA could not cross the blood-brain barrier, but new research suggests that it may be able to. - Drugs that mimic the action of GABA are numerous, work in a variety of ways, and can have effects ranging from treating epilepsy to Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Gabapentin, like other gabapentinoid drugs, GABA A and GABA B and also that baclofen was an agonist of GABA B receptors. Gabapentin was designed, Horizant (gabapentin enacarbil) is an extended release tablet used to treat restless legs syndrome and for the pain from having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). Generic brands of gabapentin capsules, USP are used for postherpetic nerve pain and for add on therapy for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Warnings
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |