Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
/GettyImages-1282121992-c55c996e5d4049a882fc973800abdf90.jpg) |  |
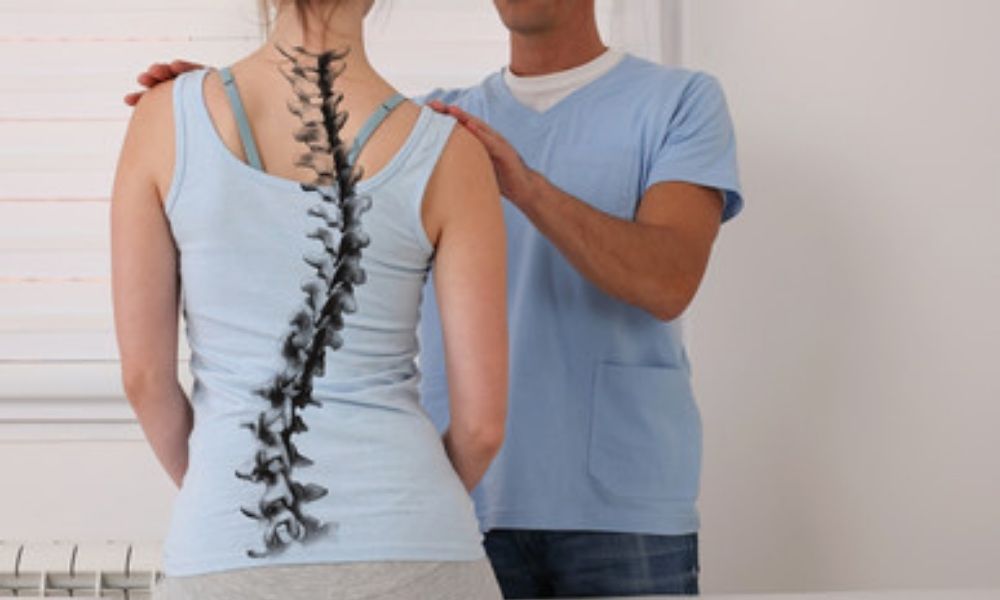
Risk of delirium -- the primary outcome of the study -- was 3.4% for older patients who received gabapentin within 2 days after major surgery and 2.6% for those who did not, with a relative risk Neuropathic pain after spinal surgery, the so-called failed back surgery syndrome (FBSS), is a frequently observed troublesome disease entity. Although medications may be effective to some degree, many patients continue experiencing intolerable pain and functional disability. Much of the literature regarding gabapentin’s benefits in treating postoperative pain have focused on patients undergoing general surgery. Few studies have focused on the spine surgery population, and of those that have been performed, evidence suggests that gabapentin is beneficial. 27-29 However, given this Opioid Management. Opioids remain a mainstay therapy for patients undergoing spine surgery. However, opioid therapy can also result in a number of adverse effects including nausea, vomiting, constipation, ileus, urinary retention, sedation, and respiratory depression. 5 Given increased attention to opioid-related adverse effects including persistent postoperative opioid use, opioid misuse, and Gabapentin is commonly indicated in the treatment of seizures. 27 Gabapentin, which acts on the nociceptive processes involved in central sensitization, has been shown to reduce hypersensitivity associated with nerve injury (hyperalgesia) and postoperative pain and inflammation in animal models. 28 Interestingly, gabapentin’s antiemetic The total fentanyl consumed after surgery in the first 24 h in the gabapentin group (233.5±141.9) was significantly less than in the placebo group (359.6±104.1; p<0.05). Turan et al., 2006 22 Turkey: Prospective: 40 patients Lower extremity surgery: Gabapentin (n= 20) 1.2 g 1 day before and for 2 days after surgery Similarly, aside from 24 h after surgery, gabapentin significantly reduced pain with movement (25–27,31,34,35,37,38) by 18% to 28% (VAS 8.2 mm to 10.2 mm) after surgery . The pooled effects on VAS pain scores displayed significant heterogeneity, which was not explained by subgroup analyses based on surgical procedure, gabapentin dose or study The Cleveland Clinic study had patients take a preemptive dose of three drugs: acetaminophen, the nerve pain medication gabapentin and the NSAID celecoxib (Celebrex). “Giving non-opioid pain medications before may help prevent the cascade of pain-causing chemicals that comes from your central nervous system after surgery,” explains Memtsoudis. The most common symptoms of nerve damage after surgery are usually numbness, tingling, burning, muscle weakness or atrophy. Many times the symptoms are temporary, for example, many patients have nerve problems after surgery that only last for a few weeks to months (2,3). Gabapentin and the related, more potent compound pregabalin have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of neuropathic pain as well as postoperative pain following spinal surgery and hysterectomy. We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. Preoperative oral gabapentin decreased pain scores in the early postoperative period and postoperative morphine consumption in spinal surgery patients while decreasing some morphine-associated side effects. They found that gabapentin resulted in a 35% reduction in total analgesic consumption in the first 24 hours following surgery. Gabapentin also resulted in 27% to 39% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in the first 24 hours postoperatively. In addition, a high dose (≥900 mg/d) of gabapentin is more effective than a low dose (<900 mg/d). The number of included studies is limited, and more studies are needed to verify the effects of gabapentin in spinal surgery patients. Keywords: gabapentin, meta-analysis, spine surgery. 1. Introduction Oral gabapentin was efficacious in the management of postoperative pain at all time points during the first day after surgery (SMD, -1.91 at 0-6 hr, -1.30 at 6-12 hr, -1.05 at 12-24 hr, respectively). Perioperative gabapentin, 1200 mg, administered preoperatively plus 600 mg every 8 hours continued for 72 hours after surgery did not affect time to pain cessation, the rate of pain resolution, or the proportion of patients with chronic pain at 6 months or 1 year following surgery. Background: Pain management after spinal surgery has been studied for years. Gabapentin is a third-generation antiepileptic drug that selectively affects the nociceptive process and has been used for pain relief after surgery. However, the relationship between gabapentin and postoperative pain in spinal surgery is still controversial. Would you want to take Lyrica (pregabalin) or Neurontin (gabapentin) for pain relief after a major surgery? Both drugs belong to a class of nerve medication called gabapentinoids that are increasingly being prescribed to patients perioperatively (after surgery) as an alternative to opioid medication. Gabapentin was efficacious in the reduction of postoperative pain, total morphine consumption, and morphine-related complications following spine surgery. In addition, a high dose (≥900 mg/d) of gabapentin is more effective than a low dose (<900 mg/d).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
/GettyImages-1282121992-c55c996e5d4049a882fc973800abdf90.jpg) |  |