Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
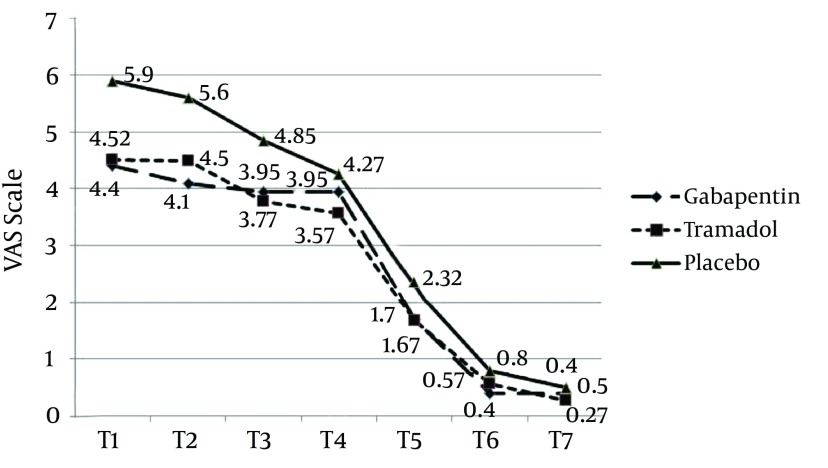
We investigated, in a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study, the efficacy and safety of gabapentin on pain after abdominal hysterectomy and on tramadol consumption in patients. The 50 patients were randomized to receive either oral placebo or gabapentin 1200 mg 1 h before surgery. Gabapentin reduced the need for additional postoperative pain treatment (PCA boluses of 50 microg of fentanyl) by 40% during the first 20 postoperative hours. Background: Gabapentin and ketamine are popular analgesic adjuvants for improving perioperative pain management. We designed this double-blind, placebo-controlled study to test and compare the preventive effects of perioperative ketamine and gabapentin on early and chronic pain after elective hysterectomy. Gabapentin and ketamine are popular analgesic adjuvants for improving perioperative pain management. We designed this double-blind, placebo-controlled study to test and compare the preventive effects of perioperative ketamine and gabapentin on early and chronic pain after elective hysterectomy. Purpose Gabapentin has demonstrated analgesic effects in some studies. This double blind randomized clinical trial (RCT) was conducted to evaluate whether the pre-emptive use of gabapentin 600 mg could reduce postoperative pain, nausea and vomiting, and meperidine consumption in patients after hysterectomy. Methods Between 2009 and 2010, a total of 170 patients who were candidates for 1. Introduction. Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) have an incidence of 40–90% especially after general anesthesia [Citation 1].Severe medical complications could be caused by PONV such as suture dehiscence, subcutaneous emphysema, esophageal rupture, or pneumothorax, which could dramatically increase the overall health care costs and boost patient quality and outcomes through its Pain scores after abdominal hysterectomy were reduced more with gabapentin alone (preoperative dosing) than when gabapentin was given both preoperatively and postoperatively. The benefits of gabapentin for minimally invasive hysterectomy (MIH) are not as well defined. Gabapentin is commonly indicated in the treatment of seizures. 27 Gabapentin, which acts on the nociceptive processes involved in central sensitization, has been shown to reduce hypersensitivity associated with nerve injury (hyperalgesia) and postoperative pain and inflammation in animal models. 28 Interestingly, gabapentin’s antiemetic Discussion. The results of our preoperative oral single-dose study investigating the acute postoperative analgesic effects of gabapentin in patients after total abdominal hysterectomy show that gabapentin decreased postoperative pain scores at rest and on movement, that gabapentin decreased postoperative tramadol consumption, and that gabapentin was not associated with more side effects when Would you want to take Lyrica (pregabalin) or Neurontin (gabapentin) for pain relief after a major surgery? Both drugs belong to a class of nerve medication called gabapentinoids that are increasingly being prescribed to patients perioperatively (after surgery) as an alternative to opioid medication. Pre-emptive use of gabapentin 600 mg orally, significantly decreases postoperative pain and PONV, and also rescues analgesic and anti emetic drug requirements in patients who undergo abdominal hysterectomy. Postoperative pain is an important factor affecting anesthesia and surgery. The present study assessed the effects of 1200 mg gabapentin, an anticonvulsant drug that acts through voltage-dependent calcium channels, for the control of postoperative pain in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. Gabapentin and the related, more potent compound pregabalin have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of neuropathic pain as well as postoperative pain following spinal surgery and hysterectomy. After accounting for stratification by surgery type, in our Cox multivariable regression analysis, perioperative gabapentin did not affect time to pain cessation. However, participants receiving gabapentin had a 24% increase in the rate of opioid cessation after surgery (HR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.00-1.54; P = .05) as reported in Table 3. Median time One of the methods for controlling postoperative pain is preemptive analgesia. Gabapentin and tramadol are both used for this purpose. Objectives: This study aims to compare the effects of tramadol and gabapentin, as premedication, in decreasing the pain after hysterectomy. Patients and Methods: However, the relationship between gabapentin and postoperative pain after open hysterectomy is still controversial. This meta-analysis was applied to assess the efficacy of pre-emptive use of gabapentin in open hysterectomy. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, has recently been suggested as an effective postoperative ‘analgesic’ agent. The objective of the present study was to examine the analgesic effectiveness, opioid-sparing effects and side effects associated with the use of gabapentin in a perioperative setting. Regimens designed to minimize postoperative opioid use also may include the use of scheduled acetaminophen, gabapentin, and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. For vaginal hysterectomy, paracervical nerve blocks or intrathecal morphine may be useful. Pain scores after abdominal hysterectomy were reduced more with gabapentin alone (preoperative dosing) than when gabapentin was given both preoperatively and postoperatively. The benefits of gabapentin for minimally invasive hysterectomy (MIH) are not as well defined. The primary outcome is prolonged use of gabapentin in the postoperative period, defined as a prescription refilled at 90-180 days after discharge from surgery, a time period based on definitions of prolonged use of opioids after surgical procedures. 20,25,26 We calculated the days’ supply and average daily dose. We defined which procedures
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |