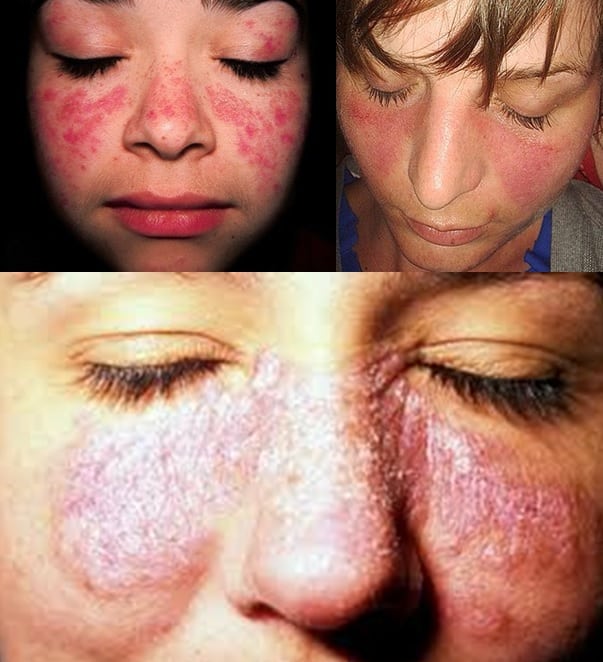
Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature. We suggest caution when considering gabapentin for patients with preexisting low platelet counts, as there seems to be a risk for worsening thrombocytopenia with this antiepileptic in the presence of HIV infection. Many antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are associated with hematological disorders that range from mild thrombocytopenia or neutropenia to anemia, red cell aplasia, until bone marrow failure. Fortunately, potentially fatal hematological disorders such as aplastic anemia are very rare. This review investiga We report a case of a patient who had thrombocytopenia with the dose of 2400 mg/day of gabapentin. The causal relationship between gabapentin and thrombocytopenia was revealed by dramatic increase in thrombocyte count following the cessation of the gabapentin treatment. Adverse Gabapentin Effects in pregnant women. Gabapentin (Neurontin) has been assigned a pregnancy category of c. C is typically classified as a passing grade. Not so with pharmaceuticals. What this grade implies is that the drug has been demonstrated as Teratogenic (deformity promoting), and fetotoxic (dangerous to the foetus) A 33-year-old man developed thrombocytopenia during treatment with gabapentin for complex partial seizures [duration of treatment/time to reaction onset not stated]. The man, who had been diagnosed with epilepsy at the age of 15 years, had received many different medications, none of which had successfully controlled his seizures. Analgesic therapy using small doses of gabapentin gave a pronounced, stable positive effect (pain intensity statistically significantly decreased by an average of 50%). After 7 days of gabapentin therapy, a decrease in the opioid dose was noted in 52% of patients. Side effects were dominated by drowsiness 67% ( n = 16), dizziness 32% ( n = 8). Gabapentin, a structural analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid, is used to treat peripheral neuropathic pain. Here we report the first case of platelet function disorder associated with gabapentin treatment in a 44-year-old woman without a history of bleeding. Despite the statistical associations and the pathophysiological hypotheses suggested here, this list of suspected drugs has to be considered with caution given the alternative causes that can be responsible for thrombocytopenia, and particularly for the rarest associations. Good questions, but your diagnosis suggests that no one, not even your doctors and specialists have yet to figure out the root cause of your thrombocytopenia. Wishing you best of luck. Wishing you best of luck. Thrombocytopenia may be associated with a variety of conditions, with clinical presentations ranging from asymptomatic to life-threatening bleeding (eg, in immune thrombocytopenia [ITP]) or thrombosis (eg, in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia [HIT]). Here we discuss our approach to the adult with unexpected thrombocytopenia. Drug-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia Results of the Testing for Drug-Dependent Platelet-Reactive Antibodies by the BloodCenter of Wisconsin Data are from 1995-2018, provided with the permission of Daniel Bougie PhD, Janice McFarland MD, Brian Curtis, PhD and Richard Aster, MD Many antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are associated with hematological disorders that range from mild thrombocytopenia or neutropenia to anemia, red cell aplasia, until bone marrow failure. Fortunately, potentially fatal hematological disorders such as aplastic anemia are very rare. This review investigates hematological effects associated with classic and newer AEDs: a PubMed search indexed for To provide a resource for diagnosis of DITP and for drug safety surveillance, we analyzed 3 distinct methods for identifying drugs that may cause thrombocytopenia. INTRODUCTION. Unexplained thrombocytopenia is a common clinical problem, and the possibility of drug-induced thrombocytopenia must be considered, especially in hospitalized patients, in whom new drugs are commonly administered. Many drugs have been implicated in drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia (DITP). Patients with DITP develop a drop in platelet count 5 to 10 days after drug administration with an increased risk of hemorrhage. Thrombocytopenia is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Revlimid, and have Multiple myeloma. Five clinical criteria have been proposed to help physicians to determine the diagnosis of DITP 1: 1) exposure to new drugs 5-10 days before onset of thrombocytopenia; 2) recovery from thrombocytopenia after discontinuing the candidate drug; 3) other drugs were continued or reintroduced after discontinuation of the candidate drug with a We report a case of a patient who had thrombocytopenia with the dose of 2400 mg/day of gabapentin. The causal relationship between gabapentin and thrombocytopenia was revealed by dramatic
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |