Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
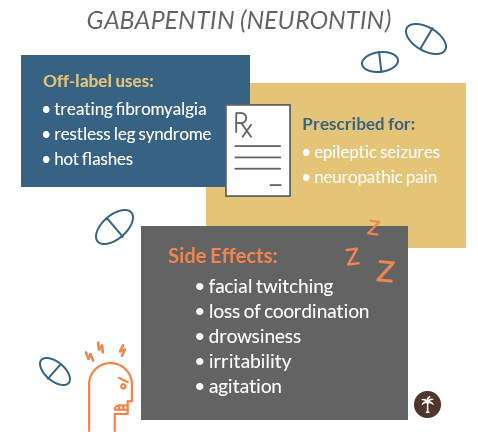
Generally, it is recommended to take gabapentin for at least four to six weeks or at the highest tolerated dose for at least two weeks. However, nerve pain can be a long-term issue, lasting for three or more months. If gabapentin provides relief, your healthcare provider may have you continue taking it daily. A neurologist prescribed 800 mg three times a day, and I took this for about 15 years. As I got older, it became 800 mg four times a day for the past 20 years. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. I don’t often see doses as high as you are taking, but they are certainly used. In a seminal trial on pain following shingles (post-herpetic neuralgia), the target dose of gabapentin was 900 mg Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Along with its needed effects, gabapentin (the active ingredient contained in Neurontin) may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. This is the 2-year interim report of results from a multicenter, open-label study evaluating the long-term efficacy and safety of gabapentin (Neurontin) as add-on therapy in patients with refractory partial seizures who had had a therapeutic response to gabapentin in a preceding 12-week double-blind For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. Gabapentin is a medication that is primarily used to treat seizures and neuropathic pain. It works by modulating calcium channels and reducing excitatory neurotransmitter release. While gabapentin can be very effective for these conditions, many people wonder if it is safe for long-term use. Is gabapentin addictive? Gabapentin and pregabalin are medicines that are used to treat epilepsy. The neural mechanisms of epilepsy and nerve damage pain have some commonality so the medicines are also prescribed for the treatment of neuropathic (nerve damage) pain such as pain after shingles, diabetes nerve pain and sciatica. Long-Term Effects of Gabapentin Use. When considering the long-term use of gabapentin, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects and risks involved. While gabapentin is generally safe when used as prescribed, it can have various adverse effects on the body. Gabapentin can be an effective option for long-term treatment of chronic nerve pain when taken under medical supervision. While it is generally safe for extended use, be cautious of risks like dependence, tolerance, and side effects. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that doctors often prescribe to manage seizures related to epilepsy. It is not a cure for epilepsy, but it can help people manage the condition. In this In this blog, we’ll explore the long-term effects of gabapentin, its benefits, and what to watch for if you or a loved one is using it for an extended period. What Is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that affects the brain and nervous system by calming overactive nerve signals. A further effect of long-term gabapentin use arises when a person who has been taking the medication for a long period of time tries to abruptly discontinue use. This places a lot of stress on the brain because it has gotten used to relying on the augmented GABA neurotransmitter production for improved functioning in the central nervous system. Gabapentin can be highly beneficial to individuals who are prescribed it and who take it as directed, however the misuse of this substance can be dangerous and even deadly. This page will discuss gabapentin misuse in further detail, including the long-term effects of gabapentin, gabapentin side effects, and possible withdrawal symptoms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |