Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 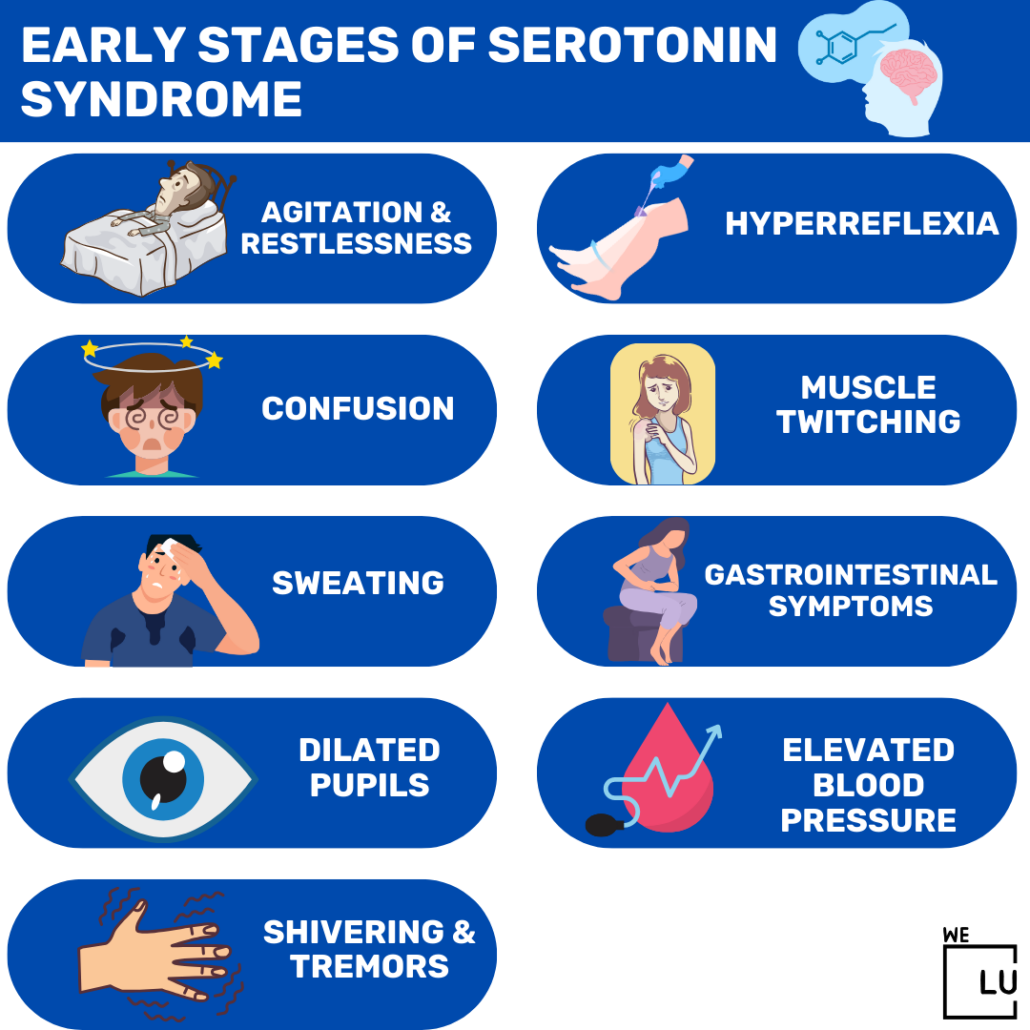 |
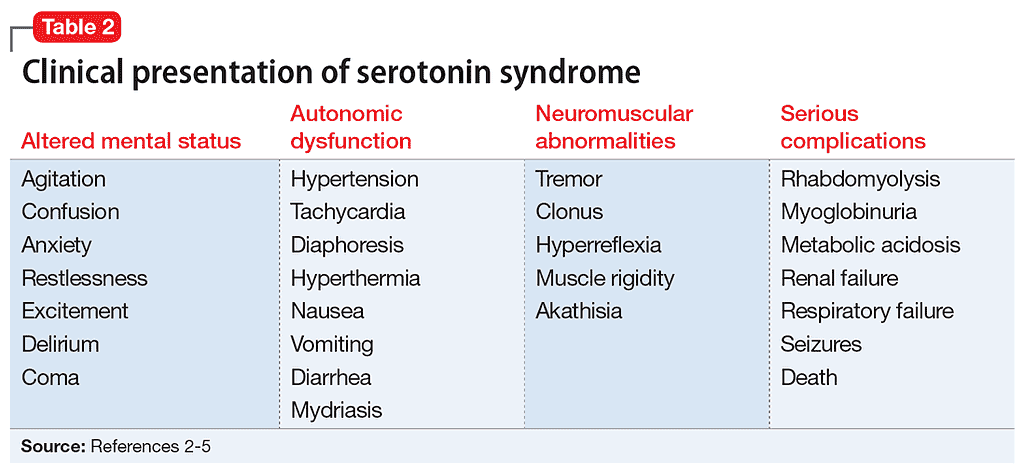
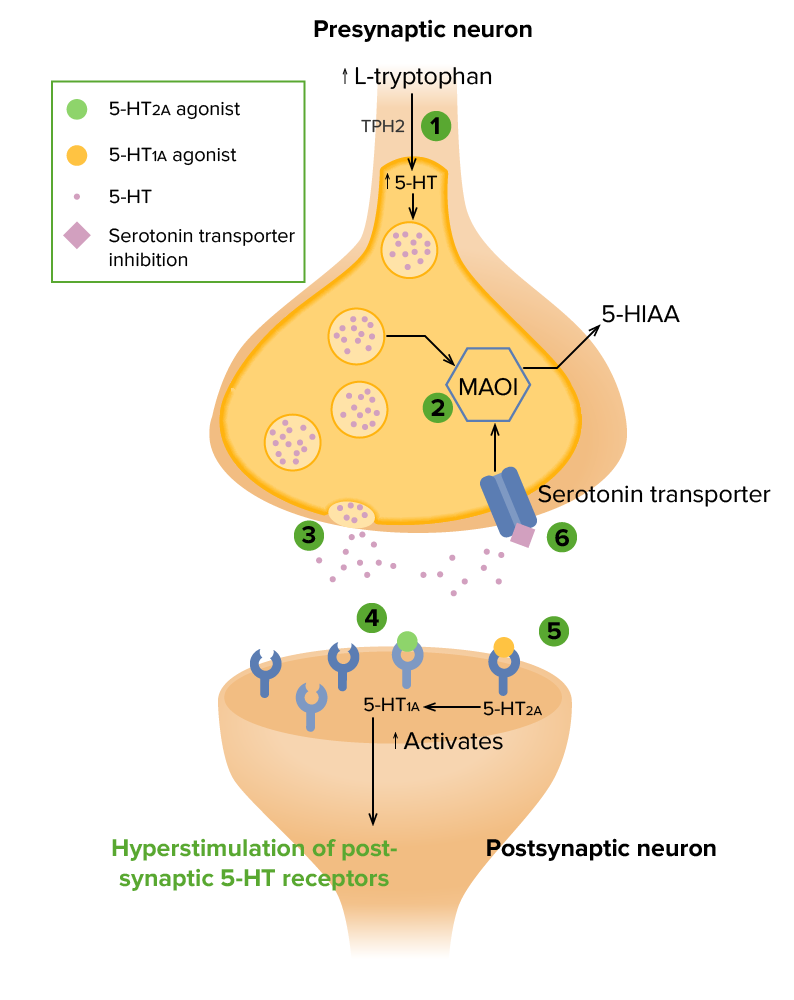
Serotonin syndrome is characterized by neuromuscular hyperreactivity (tremor, hyperreflexia, myoclonus), while NMS involves sluggish neuromuscular responses (rigidity, bradyreflexia). Hyperreflexia and myoclonus are rare in NMS . Excessive accumulation of serotonin in the body creates the symptoms of serotonin syndrome. Typically, nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord produce serotonin that helps regulate attention, behavior and body temperature. Gabapentin, 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid is an anticonvulsant medication and is used nowadays against neuropathic pain rather than for its anticonvulsant effect. 16 Gabapentin increases serotonin concentrations in human body. 16 SS due to concomitant use of tramadol and gabapentin has not been described in the English literature, to Because serotonin syndrome can be a life-threatening condition, seek emergency treatment if you have worsening or severe symptoms. If your symptoms aren't severe, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a drug‑induced, potentially fatal, clinical syndrome resulting from drugs that have serotonergic properties. Several antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are known to have serotonergic properties and it can be hypothesized that such AEDs can cause SS. This study aims to review the l Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition associated with increased serotonergic activity in the central nervous system (CNS). 1 While the highest concentrations of serotonin are found in peripheral tissues (platelets and the enterochromaffin cells of the gastrointestinal tract), 3 it plays a major role in the CNS, where it Antidepressants: Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. Bupropion Bupropion. Nefazodone Nefazodone. Trazodone Trazodone. Venlafaxine Venlafaxine. Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) Citalopram Citalopram. Escitalopram Escitalopram. Fluoxetine Fluoxetine. Fluvoxamine Fluvoxamine. Paroxetine Paroxetine A potentially lethal condition, serotonin syndrome (SS) is caused most often when certain antidepressant agents are taken concurrently with other drugs that modulate synaptic serotonin levels. 1,2 When patients take two or more antidepressants from different pharmacologic classes, drug-drug interactions may occur; these interactions may lead to Serotonin syndrome (SS) is an iatrogenic drug‑induced clinical syndrome characterized by a combination of altered mental activity, neuromuscular abnormalities, and autonomic disturbances. Serotonin syndrome typically results from the increased intrasynaptic concentration of serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT). There are seven types of 5-HT receptors (5-HT1 to 5-HT7), each with several Background: Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a common disease entity and could result in death if missed. The incidence of SS is underestimated due to misdiagnosis of many cases, especially the ones with less severe presentation. Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when you take medications that affect serotonin levels. Serotonin is a normal chemical in your body. Serotonin syndrome symptoms include agitation, blood pressure change, fever, rapid heart rate, seizures and twitching muscles. Additionally, gabapentin and pregabalin have also been implicated in an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. There are no laboratory studies to confirm the diagnosis of serotonin syndrome and thus diagnosis remains largely clinical. Clinical reports indicate that blood serotonin levels increase in healthy subjects treated with GBP (Rao et al., 1988); moreover, gabapentinoid usage for pain treatment with opioids causes serotonin syndrome (Prakash et al., 2021), suggesting that gabapentinoids facilitate serotonin secretion and serotonergic neurotransmission (Eksi et al., 2019). Research has indicated that gabapentin can cause serotonin syndrome, especially when taken with other drugs like tramadol. One study found that a 66-year old man who took a combination of tramadol and gabapentin after spinal surgery experienced serotonin syndrome. 1. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is similar to serotonin syndrome. This condition is rare but very serious. If it's not treated quickly, it can lead to death. But most people recover Serotonin syndrome is strongly suggested by the following constellation: (1) Bilateral ankle clonus and hyperreflexia. (2) Lack of another obvious explanation of clonus (no known chronic neurologic abnormality). We report a case of serotonin syndrome in a patient taking five agents that have known or reported serotonergic association. gabapentin 800 mg three times daily Serotonin syndrome is a potentially fatal and largely avoidable adverse drug reaction caused by serotonergic drugs. The steady increase in use of such drugs means all doctors need to be aware of what drugs increase serotonin and how to promptly recognise the syndrome and determine if it is potentially life threatening. What is serotonin syndrome? Serotonin Serotonin syndrome Serotonin toxicity Antiepileptic drugs Cyproheptadine ABSTRACT Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a drug‑induced, potentially fatal, clinical syndrome resulting from drugs that have serotonergic properties. Several antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are known to have serotonergic properties and it can Serotonin syndrome (SS) is an iatrogenic drug‑induced clinical syndrome characterized by a combination of altered mental activity, neuromuscular abnormalities, and autonomic disturbances. Serotonin syndrome typically results from the increased intrasynaptic concentration of serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |