Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
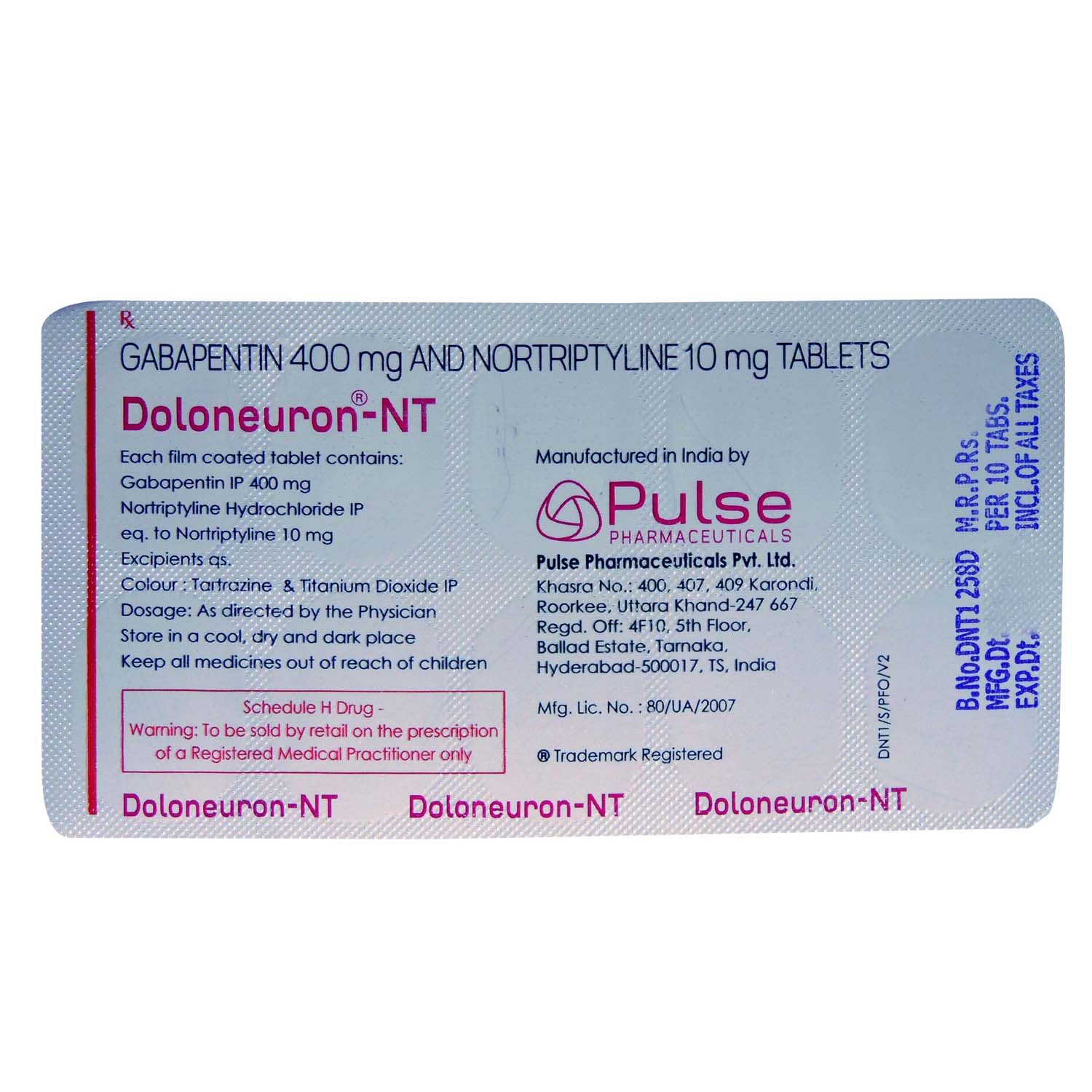
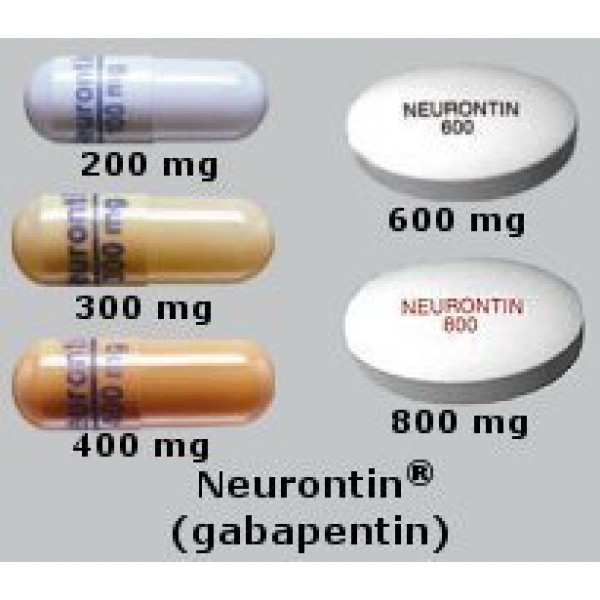
- Alpha-2 ligands (pregabalin and gabapentin) EVALUATING RESPONSE TO INITIAL TREATMENT; TREATMENT OF REFRACTORY SYMPTOMS. Clinical reassessment; Pharmacologic therapy for patients not responding to initial medications - Switching to an alternative pharmacologic therapy - Using combination drug therapy - Other medications; Nonpharmacologic therapies INTRODUCTION. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [].The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms []. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Gabapentin (1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid; Neurontin) is a novel anticonvulsant drug, with a mechanism of action apparently dissimilar to that of other antiepileptic agents. We report here the isolation and characterization of a [3H]gabapentin-binding protein from pig cerebral cortex membranes. UpToDate Comprehensive guide on nonopioid pharmacotherapy for managing acute pain in adults, including treatment options, efficacy, and safety considerations. 14-C Urea breath test: Drug information; Abacavir and lamivudine: Drug information; Abacavir, lamivudine, and zidovudine (United States and Canada: Not available): Drug information Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric Gabapentin — Gabapentin (sample brand name: Neurontin) is a medication that was developed to treat seizures. It also relieves hot flashes in some people. It also relieves hot flashes in some people. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and other conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and precautions. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentin and pregabalin — The gabapentinoids have proven efficacy versus placebo in several neuropathic pain conditions . Gabapentin has primarily been studied and found effective for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy; evidence for efficacy in other types of neuropathic pain is limited [ 45,46 ]. Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Comprehensive clinical resource tool providing information across various medical specialties. Disclaimer: This generalized information is a limited summary of diagnosis, treatment, and/or medication information. It is not meant to be comprehensive and should be used as a tool to help the user understand and/or assess potential diagnostic and treatment options. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost .table_layout tbody td{ font-size:0.95em;} Usual Gabapentin Dosing (Adults) Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg Gabapentin Renal Dosing [>60 ml/min]: Give usual dosage : Dosage range: 400-1400mg/day (divided doses - Usually bid) : Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. : 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL We conducted this population-based cohort study to understand the risk of acute altered mental status and mortality within 30 days of initiating a high versus low dose of gabapentin in older adults, a segment of the population at higher risk of adverse drug events. Chronic pain results from combined biologic, psychologic, and social factors, and most often requires a multifactorial approach to management. In addition to nonpharmacologic therapies, many patients require medications to manage pain. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |