Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
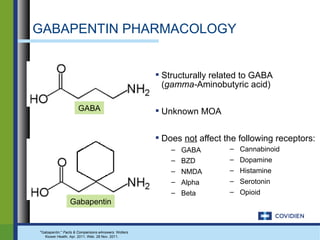
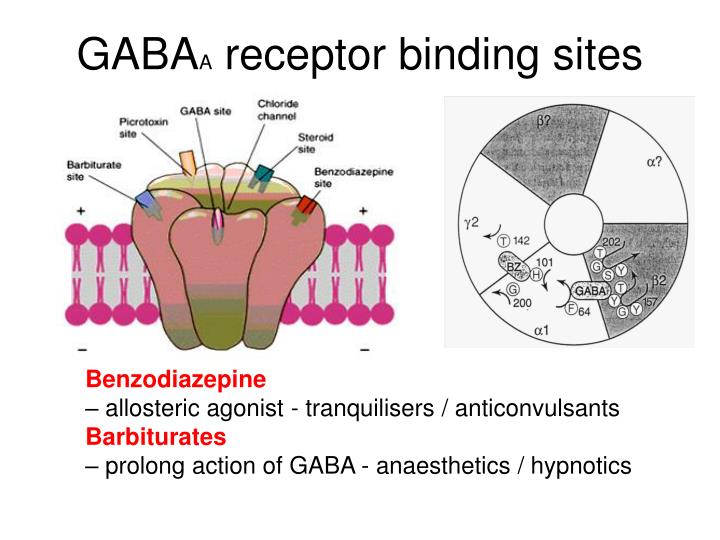
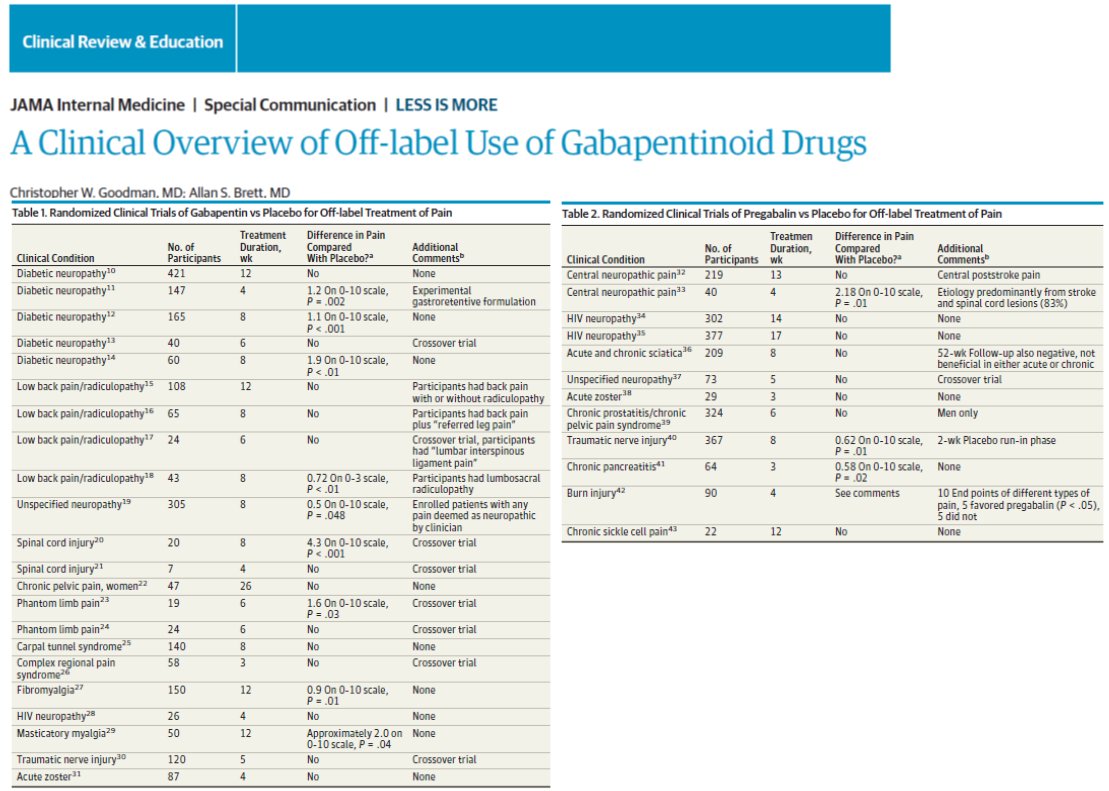
Gabapentin does not alter radioligand binding at GABA A or GABA B receptors at concentrations up to 100 μM (Taylor, 1995) nor does it alter [3 H]GABA uptake into neuronal or glial cultures (Su et al., 1995). In addition, gabapentin does not alter neuronal responses to the application of GABA in electrophysiological experiments (Rock et al., 1993). At clinically therapeutic doses (900-3600 mg/day), gabapentin does not bind to GABAA or GABAB receptors, nor does it bind to benzodiazepine sites. Despite the fact that gabapentinoids are GABA analogues, gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors, do not convert into GABA Tooltip γ-aminobutyric acid or GABA receptor agonists in vivo, and do not modulate GABA transport or metabolism. [15] [16] Conversely, GABA does not bind appreciably to the α 2 δ protein. [17] Pregabalin is a structural derivative of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA); however, it does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Pregabalin binds to the alpha 2-delta site of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system (CNS) tissues. 4 Gabapentin, a novel anticonvulsant and analgesic, is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue but was shown initially to have little affinity at GABA(A) or GABA(B) receptors. It was recently reported to be a selective agonist at GABA(B) receptors containing GABA(B1a)-GABA(B2) heterodimers, although Addition of the 3β-methyl group on ganaxolone does not alter binding to GABA A Rs, but prevents further metabolism of the 3α-OH group and thus prolongs its GABA A R-modulating actions. 100 Ganaxolone enhanced GABA and BZ binding via positive allosteric modulation of GABA A R activity, and at nanomolar concentrations potentiated GABA-evoked Although it is known that gabapentin and pregabalin do not act on GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) receptors, it is unclear whether these side effects are due to an action of these drugs Although gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not bind to GABA receptors. 19 The mechanism of action of gabapentin is not fully understood, although it is likely that gabapentin produces analgesia by binding to and inhibiting the presynaptic voltage-dependent Ca 2 Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). 19 VGCCs are composed of multiple subunits: α 1, β, γ and α 2 δ. Gabapentin has no activity at GABAA or GABAB receptors of GABA uptake carriers of brain. Gabapentin interacts with a high-affinity binding site in brain membranes, which has recently been identified as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. It binds to specific receptors in the brain, known as GABA receptors, which then open chloride channels, leading to a hyperpolarization of the cell membrane and a decrease in neuronal activity. Gabapentin, on the other hand, does not directly interact with GABA receptors. Although it is rapidly absorbed, readily crosses the blood–brain barrier and is orally active in several animal models of epilepsy, gabapentin neither binds to GABA A or GABA B receptors nor is it metabolized to GABA (Goa and Sorkin, 1993; Kammerer et al, 2011; Taylor et al, 1992). In the present study, we examined whether gabapentin is an agonist at native GABA(B) receptors using a rat model of postoperative pain in vivo and periaqueductal gray (PAG) slices in vitro; PAG contains GABA(B) receptors, and their activation results in antinociception. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are key front‐line therapies for various neuropathies of peripheral and central origin. Originally designed as analogs of GABA, the gabapentinoids bind to the α 2 δ‐1 and α 2 δ‐2 auxiliary subunits Gabapentin (GBP) was originally developed as a potential agonist for Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid (GABA) receptors, aiming to inhibit the activation of pain-signaling neurons. Contrary to initial expectations, it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it exhibits several distinct pharmacological activities, including: (1) binding to the alpha-2-delta protein subunit of voltage-gated calcium Despite its structural similarity to GABA, GBP does not bind to GABA receptors, is not converted metabolically into GABA, and is neither a substrate for, nor a direct inhibitor of, GABA transport [20]. Nevertheless, inhibitory neurotransmission remained a principal focus in early attempts to unravel the pharmacology of GBP. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Gabapentin binds preferentially to neurons in Gabapentin (GBP) was originally developed as a potential agonist for Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid (GABA) receptors, aiming to inhibit the activation of pain-signaling neurons. Contrary to initial expectations, it does not bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin (Trade name: Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant.It is commonly also used off-label for anxiety disorders, restless leg syndrome, and in alcohol use disorder.It is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin robustly increases cell-surface expression of δGABA A receptors and increases a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This enhanced δGABA A receptor function contributes to the ataxic and anxiolytic but not antinociceptive properties of gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |