Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
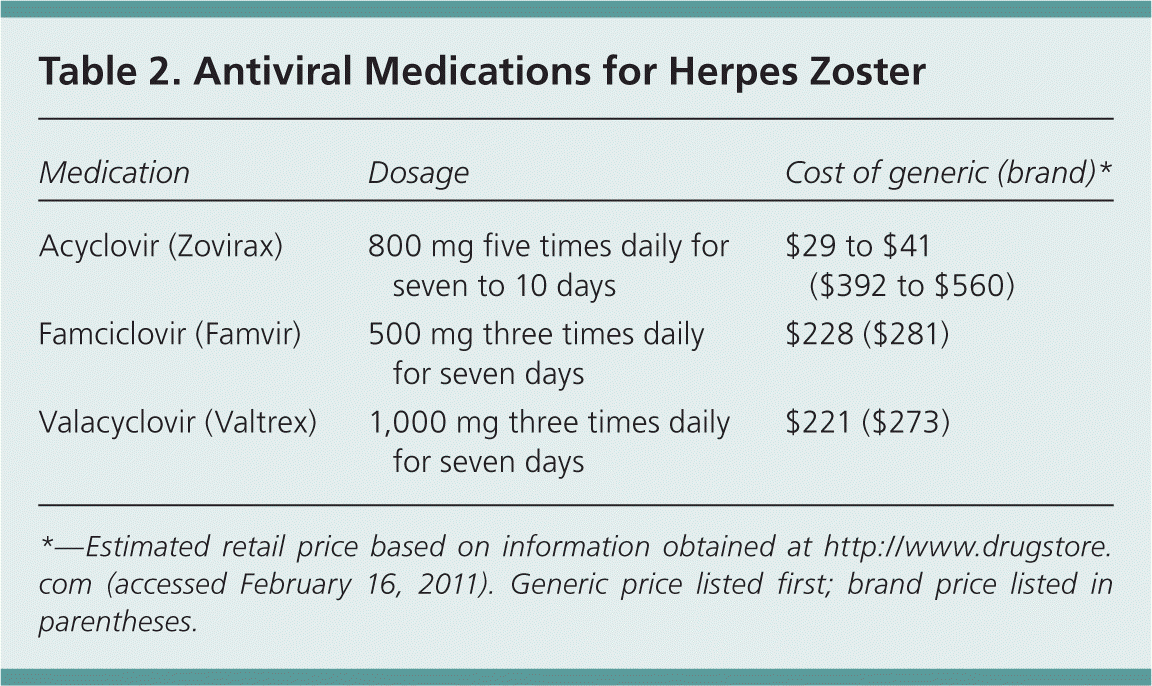
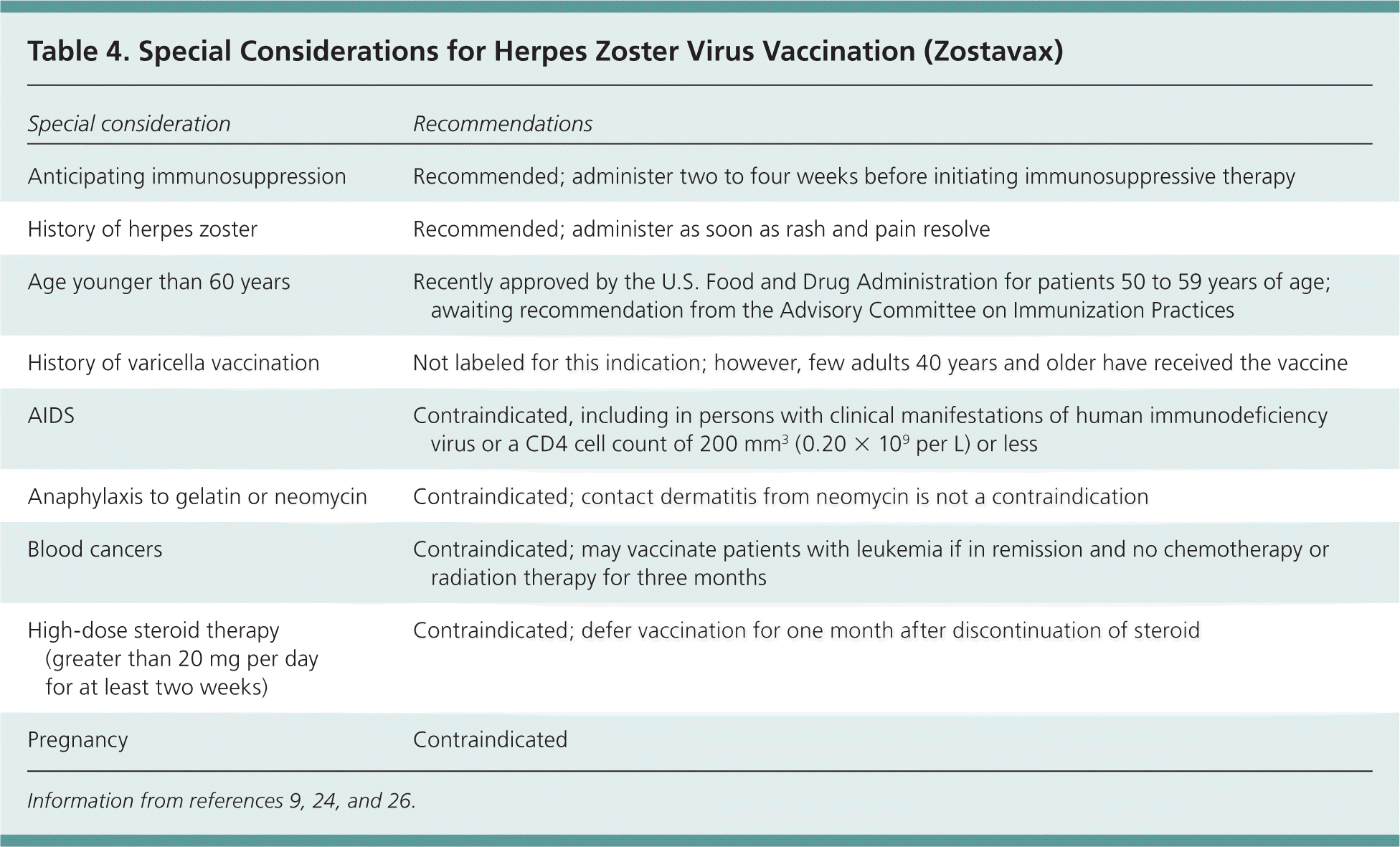
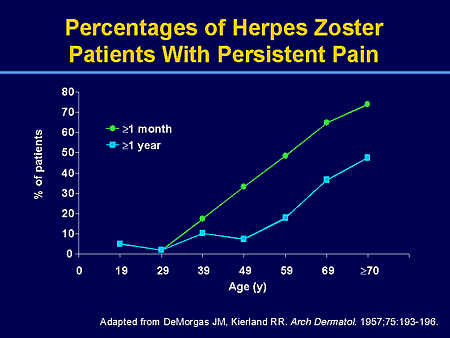
Context.— Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a syndrome of often intractable neuropathic pain following herpes zoster (shingles) that eludes effective treatment in many patients.Objective.— To determine the efficacy and safety of the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin in reducing PHN Subjects receiving gabapentin had a statistically significant reduction (P<0.0001) in visual analog scale (VAS) score as compared to placebo, emphasizing the efficacy of gabapentin in the treatment of acute pain associated with herpes zoster on each assessment (weeks 1, 2, 3, and 4). Gabapentin in doses of 600 mg/day and 900 mg/day was better Gabapentin is effective in reducing neuropathic pain due to post-herpetic neuralgia when given at least three times per day, due to its short half-life, resulting in demonstrable fluctuations in plasma levels. This study shows that elderly gabapentin-naive subjects no matter whether receiving 200, 400 or 600 mg/day of gabapentin benefited a moderate pain relief with minimal side effects at the first three days of treatment. Since starting with a minimal dose of 200 mg/day did not offer a better reduction Objective: This study aimed to systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy of gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of acute herpes zoster (HZ) neuralgia, including pain control and the occurrence of adverse effects. The Shingles Prevention Study found the herpes zoster vaccine to be 51.3 percent effective in preventing herpes zoster and 66.5 percent effective in preventing postherpetic neuralgia (when defined Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic neuropathic pain that results from alterations of the peripheral nervous system in areas affected by the herpes zoster virus. The symptoms include pain, paresthesia, dysesthesia, hyperalgesia, and allodynia. We performed a prospective randomized controlled study of 120 participants diagnosed with acute herpes zoster, aged 50 and over and complaining moderate to severe pain. All patients were treated with valacyclovir and acetaminophen. We do not know whether the use of dressings, oral opioids, or gabapentin during an acute attack reduces the risk of postherpetic neuralgia, as we found no studies. There is limited evidence that Shingles nerve pain, also known as postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), is the most common complication associated with shingles. Doctors can prescribe several different medications to help a person Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) can be used for treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Amitriptyline, nortriptyline (Pamelor), and desipramine can be used for pain relief in Gabapentin and Lyrica are generally considered 'first-line' agents for treating the pain associated with shingles (postherpetic neuralgia). Alternative treatment options include tricyclic antidepressants, lidocaine, anticonvulsants, SNRI antidepressants and tramadol. A recent Cochrane review reported that among patients taking gabapentin at doses higher than 1200 mg/day, there was a substantial effect on PHN-related pain (50% or more reduction in pain) in 32% of patients, and a moderately beneficial effect (30% or more reduction in pain) in 46% of patients. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregalbin (Lyrica) work directly through the nerves to decrease pain. Gabapentin causes much more drowsiness compared to pregalbin. Many of my patients who have difficulty with sleep at night due to the pain of post-herpetic neuralgia do well with Gabapentin. Objective: To assess the efficacy of a 5-week course of gabapentin on acute herpetic pain and on the prevention of PHN at 12 weeks in patients with acute HZ. Methods: This was a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in 17 primary care health centers in Mallorca, Spain. Background Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic neuropathic pain that results from alterations of the peripheral nervous system in areas affected by the herpes zoster virus. The symptoms include pain, paresthesia, dysesthesia, hyperalgesia, and allodynia. Despite the availability of pharmacological treatments to control these symptoms, no treatments are available to control the underlying How to take gabapentin for pain relief from nerve pain? Gabapentin comes in the form of a capsule, tablet, extended-release tablet, solution, and suspension to take by mouth. The usual dose of gabapentin for shingles (post herpetic neuralgia) in adults is a 300-milligrams (mg) single dose on day 1, 300 mg twice a day (total 600 mg) on day 2 complication of herpes zoster, is defined as pain in a dermatomal distribution that is sustained for at least 90 days after the rash. It occurs in approximately 20% of patients with herpes zoster Gabapentin does not work to treat the virus-causing shingles, but rather it is used to address the pain from nerve damage that can occur in certain individuals at higher risk of developing complications from shingles, termed postherpetic neuralgia. Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is the most common complication of herpes zoster (HZ). Previous trials have reported that gabapentin can relieve chronic neuropathic pain, but its effect on prevention of PHN is unclear.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |