Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/hip-prosthesis--surgery-586033988-5bec4193c9e77c0051f4746b.jpg) | 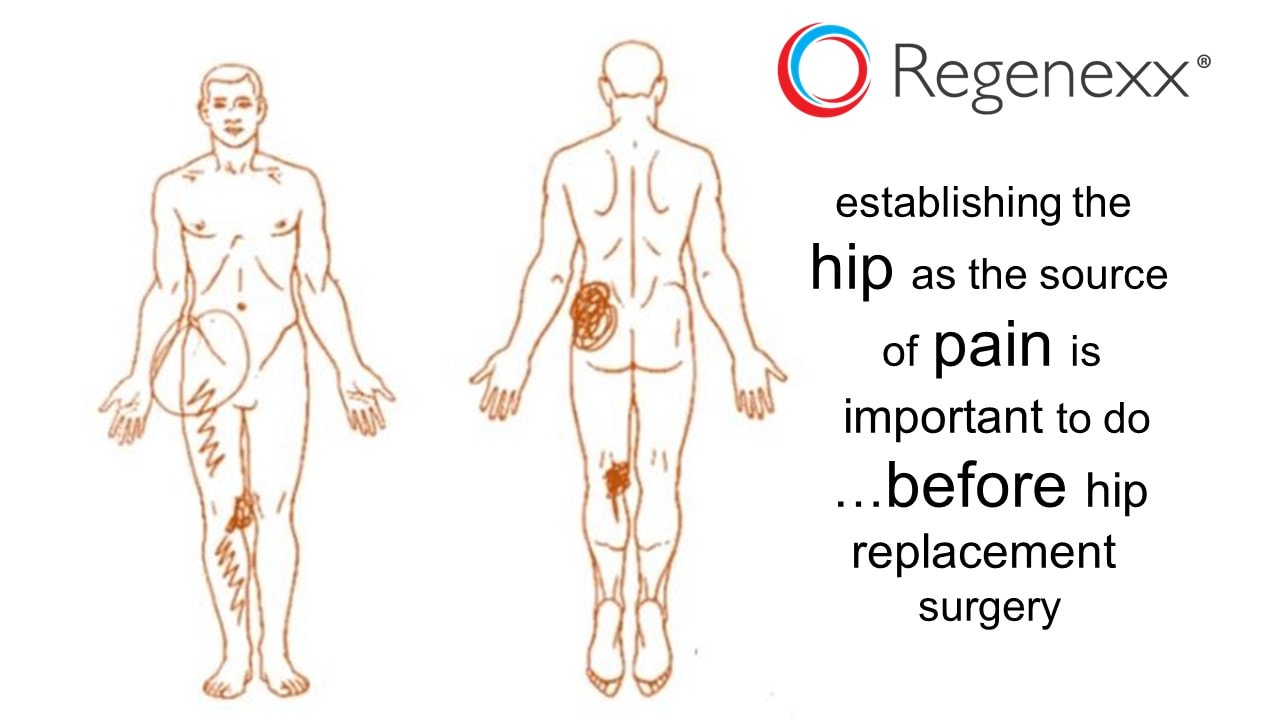 |
 |  |
 |  |
/hip-replacement--illustration-1155266197-3a4fe05bca314a5fbeeb7336a0d55067.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 | 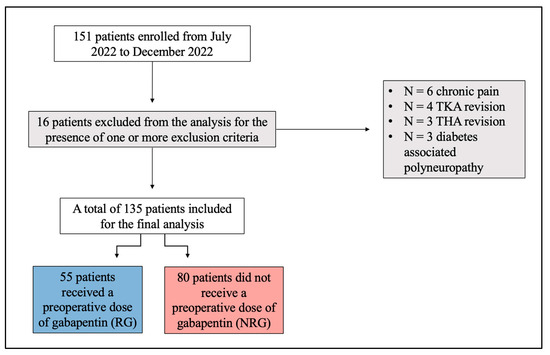 |
By taking Gabapentin as prescribed, hip replacement patients can effectively manage their pain levels and enhance their overall comfort during the recovery process. This medication specifically targets nerve-related pain, making it an ideal choice for hip replacement patients who often experience nerve irritation and inflammation as part of Hwang SH, Park IJ, Cho YJ, et al. The efficacy of gabapentin/pregabalin in improving pain after tonsillectomy: a meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2016; 126:357–366. [Google Scholar] 11. Peng PW, Wijeysundera DN, Li CC. Use of gabapentin for perioperative pain control—a meta-analysis. Pain Res Manag 2007; 12:85–92. Background: Postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA) influence patients' rehabilitation and life quality. Although gabapentin has been widely used for analgesia, its efficacy is still controversial in TKA and THA. Some people may get nerve block injections for pain control after hip replacement surgery. This numbs the area around your new hip to lower the hurt a lot in the first few days post-surgery. It’s one way to handle pain without using lots of pills. Gabapentin resulted in less total patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) morphine use over 48 hours postoperatively (P <0.05), better active knee flexion on postoperative days (PODs) 2 and 3 (P <0.05 for both), and less pruritus (P <0.05) than placebo.¹⁰. Gabapentin as a third-generation antiepileptic drug that selectively affects the nociceptive process has been used for pain relief after THA. This meta-analysis was conducted to examine the Pain management after total hip arthroplasty (THA) varies and has been widely studied in recent years. Gabapentin as a third-generation antiepileptic drug that selectively affects the nociceptive process has been used for pain relief after THA. Postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA) influence patients’ rehabilitation and life quality. Although gabapentin has been widely used for analgesia, its efficacy is still controversial in TKA and THA. Background Postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA) influence patients’ rehabilitation and life quality. Although gabapentin has been widely used for analgesia, its efficacy is still controversial in TKA and THA. This meta-analysis was performed to assess the efficacy and safety of gabapentin following TKA and THA. Method Electronic databases Another type of medicine used as part of a multimodal pain regimen after hip replacement are medicines that target nerve pain – namely gabapentin (Neurontin) or pregabalin (Lyrica). Using these medications decreases the amount of opioids required after hip replacement . Keywords: total hip replacement, total hip arthroplasty, pain management, preemptive analgesia, peri articular injection, type of anesthesia, acetaminophen Introduction and background Osteoarthritis (OA) represents a major burden as it exerts a drastic impact on patients’ quality of life. Another type of medicine used as part of a multimodal pain regimen after joint replacement are medicines that target nerve pain – namely gabapentin (Neurontin) or pregabalin (Lyrica). Using these medications decreases the amount of opioids required after joint replacement. Some patients report that these medicines cause drowsiness, but they Background: Pain management after total hip arthroplasty (THA) varies and has been widely studied in recent years. Gabapentin as a third-generation antiepileptic drug that selectively affects the nociceptive process has been used for pain relief after THA. This meta-analysis was conducted to examine the efficacy of gabapentin in THA. Gabapentin is classified as an anticonvulsant medication and is commonly used to treat epileptic seizures. However, it has also been found to be effective in treating various types of neuropathic pain, including hip pain. The use of gabapentin for managing hip pain is supported by scientific evidence. After discharge, gabapentin does not reduce postoperative pain or opioid consumption, but pregabalin reduces both postoperative pain and opioid consumption. Conclusion: Moderate evidence supports the use of pregabalin in TJA to reduce postoperative pain and opioid consumption. demonstrated a favorable reduction in pain scores evaluated pregabalin for treatment of pain after total hip arthroplasty (THA) while the other study evaluated total knee arthroplasty (TKA) patients. Perioperative gabapentin may reduce the incidence and intensity of postoperative pain up to 6 months after otolaryngology, orthopedic, mastectomy, and abdominal/pelvic operations. 12-15 Professional guidelines advocate for perioperative administration of gabapentin as a component of multimodal analgesia, 16 but its efficacy in the context of Gabapentin and the related, more potent compound pregabalin have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of neuropathic pain as well as postoperative pain following spinal surgery and hysterectomy. Gabapentin is routinely used in preoperative multimodal anesthesia to reduce pain following total joint arthroplasty (TJA) surgery. Evolving evidence has shown it is ineffective in reducing postoperative pain and should be used cautiously in this patient population due to its adverse effects. Background Multimodal analgesia regimens are recommended for the postoperative period after hip and knee replacement surgeries. However, there are no data on practice patterns for analgesic use in the immediate postoperative period after hip and knee replacements in Australia. Objectives To describe analgesic prescribing patterns in the inpatient postoperative phase for patients undergoing hip
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/hip-prosthesis--surgery-586033988-5bec4193c9e77c0051f4746b.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
/hip-replacement--illustration-1155266197-3a4fe05bca314a5fbeeb7336a0d55067.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |