Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
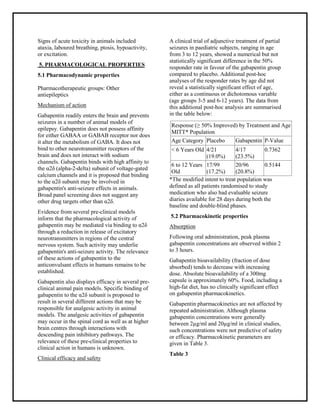
In general, gabapentin is well tolerated over a wide range of doses. However, it is possible to overdose on gabapentin, especially when taken in combination with other substances. A growing body of literature shows that gabapentin overdoses can cause potentially serious physical and psychological effects. Signs and Symptoms of Gabapentin Overdose Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Other medications have been studied more for anxiety, and they’re typically tried first. The recommended gabapentin dosage for anxiety and other conditions can range from 300 mg to 3,600 mg per day. Gabapentin in the management of restless legs syndrome (RLS) has been evaluated in small controlled trials, demonstrating benefits compared with placebo. Gabapentin enacarbil is FDA-approved for the treatment of RLS Garcia-Borreguero 2002, Saletu 2010. The . Social anxiety disorder, adjunct to antidepressants or monotherapy (alternative agent)c Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. Gabapentin capsules are usually taken orally three times a day (morning, afternoon, and evening) with plenty of water, with or without food. Gabapentin is available in 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg capsules, and in 600 mg and 800 mg tablets. The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. Changes to your dose. To prevent side effects, your doctor will prescribe a low dose to start with and then increase it over a few days. Once you find a dose that suits you, it will usually stay the same. How to take it Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral capsule. Effective Dose: Reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days; the effective dose in patients 5 years of age and older is 25 to 35 mg/kg/day in divided doses (3 times a day). The effective dose in pediatric patients ages 3 and 4 years is 40 mg/kg/day and given in divided doses (3 times a day). Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight. Initial dose: 300 mg on day one, 300 mg twice daily on day two, and 300 mg three times daily on day three. Maintenance dose: 900-1800 mg per day, divided into three doses. Treatment is typically long-term. Initial dose: 300 mg once daily, with gradual increases as needed. Maintenance dose: 900-3600 mg per day, divided into three doses. The effective dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The effective dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. How is gabapentin supplied (dosage forms)? Gabapentin is available as Gralise, Neurontin, and generic gabapentin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. Initial: 300 mg orally every 8 hours. Day 1: 300 mg orally once per day. Day 2: 300 mg orally every 12 hours. Day 3: 300 mg orally every 8 hours. Maintenance: Subsequently titrate as needed up to 600 mg orally every 8 hours; doses greater than 1800 mg/day have demonstrated no additional benefit. Gralise. Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization; Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin enacarbil) Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: The starting dose is 10 to 15 milligrams (mg) per kilogram (kg) of body weight per day and divided in 3 doses. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed and tolerated. Children younger than 3 years of age—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor. Analysis of responder rate using combined data from all three studies and all doses (N=162, gabapentin; N=89, placebo) also showed a significant advantage for gabapentin over placebo in reducing the frequency of secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures. In two of the three controlled studies, more than one dose of gabapentin was used. What dosage strengths and forms does gabapentin come in? Gabapentin is available as: Gabapentin tablets. It’s available as 300- and 600-milligram tablets (Gralise) and 600- and 800-milligram tablets (Neurontin or generic gabapentin). Gabapentin oral solution.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |