Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
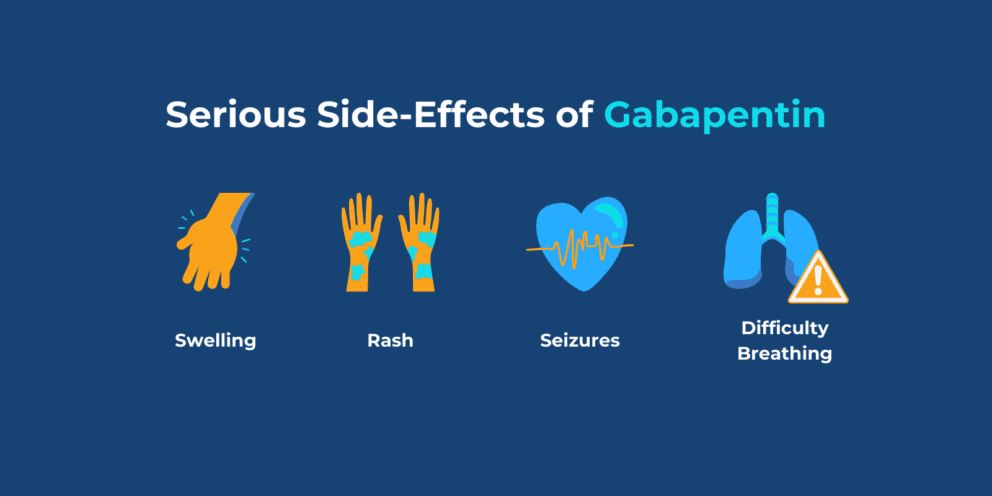
pain is often worse at night and may be paroxysmal or continuous. Characteristic signs and symptoms are: • Hyperalgesia – increased sensitivity to a normal pain stimulus, e.g., temperature • Allodynia – pain created by a stimulus that does not ordinarily produce pain, e.g., application of a cotton swab, wearing of clothes second line treatments for peripheral neuropathic pain. The NHS Tayside guidance and algorithm for the treatment of neuropathic pain reflects the SMC advice and should be followed for the treatment of neuropathic pain within NHS Tayside. NICE clinical guidelines such as the guideline for the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain, do Gabapentin is used to help reduce pain. It is especially good for nerve pain, such as burning, shooting, stabbing, pins and needles, crawling, electric shock like pain. How does it work? Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. If the messages are reduced, then the pain will be reduced . can help to control your pain when you are changing treatments. If at any stage your pain has got worse despite treatment, your doctor may refer you to a specialist pain clinic or another specialist clinic. While you are waiting for your appointment, you may be offered an alternative painkiller called tramadol for a short time. Read about how gabapentin treats epilepsy and nerve pain and how to take it. NHS medicines information on gabapentin – what it's used for, side effects, dosage, and who can take it. the side effects. You have had your pain for quite some time, and it is unfair to expect the pain to disappear straight away with the treatment. A period of four weeks of treatment will allow you to judge whether the medicine has helped your pain. If it has helped your pain to some extent, and the side effects have not been too NHS medicines information on dosage for gabapentin, how to take it and what to do if you miss a dose or take too much. Gabapentin is used to help reduce pain. It is especially good for nerve pain, such as burning, shooting, stabbing, pins and needles, crawling, electric shock like pain; Gabapentin belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants and can also be used to treat epilepsy 714FM.3 MANAGEMENT OF NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN ADULTS Public Health England guidance PHE-NHS England Pregabalin and Gabapentin Advice 5Dec 2014 Gabapentin is used to treat some types of persistent pain. It is especially good for nerve pain, such as burning, shooting or stabbing pain. Gabapentin belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants which are also used to treat epilepsy. Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. With nerve pain, it's thought to block pain by affecting the pain messages travelling through the brain and down the spine. Gabapentin is available on prescription. It comes as tablets, capsules and a liquid that you swallow. Gabapentin. Please read the leaflet included in your prescription. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic / anti-convulsant drug that can be used in to treat pain caused by damage to the nerves (neuropathic). How to take Gabapentin Gabapentin needs to be gradually increased over a period of time until a maximum daily dose of 600mgs Like gabapentin, it's taken for epilepsy and nerve pain. It can also be taken for anxiety. But there are differences between pregabalin and gabapentin. Pregabalin can be taken less often and in different doses to gabapentin. If you need to change to pregabalin, your doctor will explain how to swap safely from gabapentin. Gabapentin is a drug used to treat nerve pain. This type of pain is often not relieved by normal painkillers. It can be used in combination with other painkillers to improve your pain relief. How does gabapentin work? Gabapentin works by changing the way in which nerves send messages to your brain. of gabapentin falls from 60% to 33% as the total daily dosage increase from 900mg to 3600 mg. For safety reasons the Nottinghamshire APC guideline recommends that the maximum daily dose of gabapentin should NOT exceed 1800mg. Gabapentin in renal impairment (ref: Neurontin SPC): Creatinine Clearance (ml/min) Dose ≥80 300mg TDS to 600mg TDS A 42-year-old woman takes 200mg of pregabalin twice a day for neuropathic pain. Due to lack of efficacy, you wish to switch to gabapentin. Use the step-wise approach, to calculate an appropriate dose of gabapentin: 200mg x 2 times a day = 400mg pregabalin daily; 400mg x 6 = 2400mg gabapentin daily Gabapentin provides significant help with pain symptoms for some people, although it does not work for everyone. It usually reduces pain rather than relieving it completely. The best dose varies between people, but in general we are aiming for a balance between helping with your pain and minimising side-effects. Gabapentin is a medicine which helps improve your pain control. It is different from other pain relievers. It is especially good for nerve pain e.g. shooting pains or burning pains. How should I take Gabapentin? Please take Gabapentin as per the chart on the reverse of this leaflet. The chart will help you begin taking the medicine. Current NHS England guidance (March 2015) is that Pregabalin should only be prescribed for the treatment of neuropathic pain under the brand name Lyrica® (unless there are clinical contra- indications or other special clinical needs e.g. patient allergic to an excipient, branded product Analgesic Tapering Guidelines for adult patients with persistent pain patients taking strong opioids and/or gabapentinoids. Prescribing of gabapentinoids for neuropathic pain should be reviewed in line with the criteria set out in NICE4 and should be gradually discontinued if ineffective.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |